Landforms, Mountains, Folding and Faults quiz 1. What kind of fault
advertisement

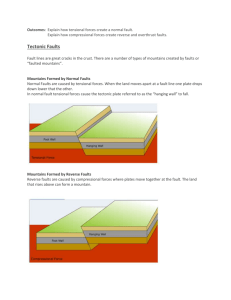
Landforms, Mountains, Folding and Faults quiz 1. What kind of fault forms when the rock above the fault plane (the hanging wall) DROPS relative to the rock below (the footwall)? Reverse Fault Normal Fault Strike-Slip Fault Thrust fault None of the above There are three major ways in which stress affects rigid rock during mountain building: Compression (crustal shortening) ----><---Tension (crustal stretching) <---- ----> Shear (forces parallel but in opposite directions) ----> <---2. What does tensional stress usually cause? Strike-Slip Faults Reverse Faults Normal Faults Thrust Faults Headaches 3. Compressional stress creates: Thrust faults Reverse faults Folded mountains All of the structures above 4. What is the name of the structure that forms when rock layers are uparched? Anticline Basin Graben Horst Syncline 5. What caused the Appalachian Mountains to form? Rifting along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge A continent-continent collision between Africa and North America Extensive hot spring activity Volcanic activity during the Pre-Cambrian Era 6. The mountains of the Great Basin (Basin and Range) of California and Nevada are examples of: Fault block mountains Volcanic mountains Granitic batholiths Folded mountains 7. The Alps, Urals, and Appalachian Mountains are examples of: Fault block mountains Volcanic mountains Domed mountains Complex folded mountains 8. The San Andreas Fault in California is primarily a: Dip-slip fault Reverse fault Strike-slip fault Overthrust fault 9. Non-linear downfolded rock structures like those found in Michigan and Illinois are: Anticlines Basins Grabens Horsts Synclines 10. Folding (of earth's crustal rocks) is usually the result of: Tensional forces Compressional forces Shear forces Faulting 11. Faults in which the movement is mainly horizontal, parallel to the fault, are called: Strike-slip faults Dip-slip faults Normal faults Reverse faults 12. Folded rock structures occur most often in: Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Intrusive igneous rocks Extrusive igneous rocks 13. Most mountain ranges on continents form: At divergent plate boundaries Along transform fault plate boundaries In the interior of continents At convergent plate boundaries