5.3 Populations
advertisement

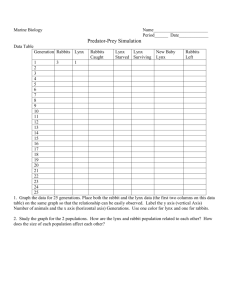
Populations Topic 5.3 Death Immigration Population Emigration Birth Factors that increase population size: •Natality (Birth rate) is recruitment to a population through reproduction •Immigration from external populations e.g. Bird migration Factor reducing population size: •Mortality (death rate) which is the death rate from any source e.g. predation •Emigration, where individuals leave the population for another habitat For a stable population: Immigration + Natality = Emigration + Mortality Decline phase Plateau phase Transitional Phase Exponential Phase Lag phase Population size A Sigmoid (s - shaped) Population Curve Time • • • • • Lag phase: Population growth begins slowly from a few individuals. Exponential Phase: Exponential growth occurs, the conditions are ideal and maximum growth rate is reached. Transitional Phase: Growth rate begins to slow down as factors such as food, water and space become limiting. Plateau phase: Carrying capacity for the population has been reached and the population number becomes stable. The carrying capacity is the population size that can be supported by a particular environment. Decline phase: If there is a sudden change in the environment meaning that the environment can no longer support the population, such as a drought causing food shortage, the population will crash and the whole process begins again. Population size can be affected by the following: • Density dependent factors: These are any factors, dependent on the density of the population in question. Some examples of these are predation, disease and competition. • Density independent factors: These are any factors, not dependent upon the density of the population in question. Some examples of these are climate and catastrophe. Case studies • Rabbits • The Lynx and the Snowshoe Hare. Rabbits in Australia • In 1859, Thomas Austin brought out 24 rabbits, 5 hares and 72 partridges and released them on his property, in Victoria. • In 1887, Rabbits were first sighted in Northern Territory. The gestation period for a rabbit averages 31 days. A rabbit can live as long as 10 years Rabbits can start breeding as early as 3-4 months of age European Rabbits have an average litter size of 7 – 9 but may be as high as 15! 8 Rabbits eat as much grass as 1 sheep! • By 1907 Rabbit numbers had reached plague proportions causing untold environmental damage: So from 1901 -1908 they tried to build a…. It didn’t work….. So in 1950, after research carried out by Frank Fenner, Myxomatosis was deliberately released into the rabbit population, causing it to drop from an estimated 600 million to around 100 million. Genetic resistance in the remaining rabbits allowed the population to recover to 200-300 million by 1991. • To combat this trend, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) scientists developed and accidentally released calicivirus (also known as Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease or RHD) in 1996. The Australian Government refuses to legalise a vaccine to protect pet rabbits against Myxomatosis, for fear the rabbit may escape and transmit resistance to the disease. A legal vaccine exists in Australia for RHD. There is no cure for either Myxomatosis or RHD, and many affected pets are euthanised. Activity: • Draw a population curve for Rabbits in Australia from 150 to present day. • Label relevant parts of the curve and include approximate dates and population sizes. • Discuss with your neighbour whether the methods of control were ethically or environmentally justifiable. Predator Prey Relationships • The lynx and the Snow Hare A lynx -Eats Snowshoe hares A Snowshoe Hare. - Eaten by Lynxs. Activity: • How will increasing numbers of Snowshoe hare affect the numbers of lynx? • How will increasing numbers of Lynx affect the numbers of Snowshoe hare? • How will decreasing numbers of Snowshoe hare affect the numbers of lynx? • Does this explain the population graph? Picture sources: • • • • • • • • • • • Slide 4 http://www.s-cool.co.uk/alevel/biology/ecological-concepts/populations.html Slide 7 http://www.creationsbydawn.net/pi/tutorials/rabbit.jpg Slide 8 http://wwp.greenwichmeantime.com/timezone/australia/_derived/map.htm_txt_australia-map.gif http://library.thinkquest.org/03oct/00128/en/rabbits/history.htm Slide 9 http://highlandviewrabbitry.tripod.com/sitebuildercontent/sitebuilderpictures/breeding.jpg http://www.threelittleladiesrabbitry.com/rabbitfacts.php Slide 10 http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/3/3e/Rabbit-erosion.jpg Slide 11 http://www.onesteelwaratah.com.au/media/81204/rabbit%20fence%20sign.jpg Slide 12 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rabbits_in_Australia#Biological_measures http://images.encarta.msn.com/xrefmedia/sharemed/targets/images/pho/t978/T978475A.jpg Slide 13 http://members.iinet.net.au/~rabbit/rcd2.jpg Slide 16 http://4.bp.blogspot.com/_W9mOaqcNMB4/SVVbtbqziJI/AAAAAAAABgc/WXsJp9Ysgpo/s40 0/lynx+young+walking+on+snow.jpg Slide 17 http://www.ngsprints.co.uk/images/M/100148.jpg Slide 18 https://fp.auburn.edu/sfws/ditchkoff/images/Lecture%20Images/Carnivores/lynxhare_cycle.gif