Producing Quality Meat Rabbits
advertisement

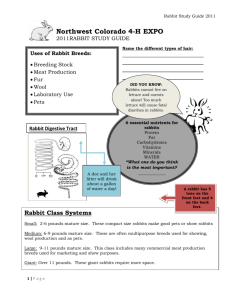
Producing Quality Meat Rabbits Quality Assurance WHAT is Quality Assurance? Quality Standard Assurance: A pledge or a promise To consumers WHO is responsible for Quality Assurance? Everyone involved in food production! Livestock producers Food processors (packing plants, milk plants) Grocery stores & restaurants Consumers Commercial Rabbit Industry 8 to 10 million pounds of rabbit are marketed each year in the US Nutritional Value of Rabbit Meat Rabbit Calories Total Fat (g) Cholesterol (mg) Protein (g) Iron 197 8 82 29 15% 100g Beef 100g 283 19 87 27 12% Parts of a Rabbit Carcass Foreleg Rib Lion Rump Hind leg What are the steps to quality meat rabbits??? 1st – Housing 2nd – Nutrition 3rd – Health/Breeding Programs 4th – Marketing Plan Housing Housing Many types and Varieties Need to provide Ventilation Protection from drafts Housing Provide a dry environment Provide plenty of space General rule of thumb: ¾ square Foot per pound of body weight. Example a 4lb rabbit would need 3 square feet of cage space or a 18”x 24” cage Nutrition – meat type rabbits Major Nutrient Requirements & Simple Feeding Chart Class of Production Pregnant (21d.) or Lactating % Pro % Fat 16-20 3-5.5 Calories (per lb.) % Fiber Daily feeding level 1136 12-14 Free Choice Growing Fryer (1-3 mo.) Replacement (3-5 mo.) 16 2-4 1136 14-16 Free Choice 16 2-4 1136 14-16 6-8 oz. Breeding Bucks 16 2-3 1136 14-20 6-8 oz. 955 14-20 4-6 oz. Dry bucks/does 12-15 2-3.5 Source: National Research Council 1194 Health Common Diseases of Rabbits raised in a meat production system: Digestive Disorders Pasteurellosis Parasites Sore Hocks Digestive Disorders Newly weaned rabbit is most vulnerable Enterotoxaemia is the most common disorder Coccidiosis is a protozoa that causes diarrhea. Pasteurellosis Respiratory Disease (Snuffles) Larger groups of Rabbits Poor Ventilation and high ammonia levels caused by urine. Parasites & Sore Hocks Two main types of Parasites Mites: cause ear and skin mange Protozoa: Coccidiosis Sore Hocks The main disadvantage to wire cages Wear of the fur on the hocks and can create open sores on the hocks Reproduction Traits of concern: Number of kits born Number of kits weaned Litter Weights at weaning Litters per year (usually 5-8) Management Schedule for 6 or 8 litter per Doe per Year Litters per Doe per Year 6 8 Age to Wean Litter 28 days 28 days Time to Rebreed Doe* 28 days 14 days * Age of Litter ** Number of days between litters if no infertile matings Litter Interval** 59 days 45 days Marketing Things to consider with meat rabbits: Slaughtering Facilities Packaging & Labeling Potential Buyers Marketing Selling Rabbit Meat From the Farm- can be slaughtered on farm and labeled as not inspected, no license required. At a Farmers Market- Must be processed by a licensed slaughter facility, mobile retail food license required. Grocery or Restaurant-Must be processed by a licensed slaughter facility, retail food establishment license required. References DATCP- Division of Food Safety: Wisconsin food Regulations Overview for Farmers and Market Gardener Wishing to Direct Market. Backyard Production of Meat Rabbits in Texas. Texas Ag. Extension Publication E-138 Agriculture Alternatives- Rabbit Production. Penn State Cooperative Extension Publication 1994. http://www.elook.org/nutrition/beef/4434.html http://www.elook.org/nutrition/lamb/3909.html http://www.ams.usda.gov/poultry/standards/AMS-RabST-2002.htm