Pollination
advertisement

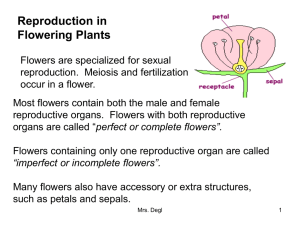
Pollination Pollination Important Terms Pollination – transfer of pollen – Self or cross Fertilization – union of ♂ & ♀ (ovule) nuclei Fruiting – development of fleshy part around zygote Seed dispersal – distribution of mature seeds from parent Flower Anatomy Pollination= Pollen transfer stigma style Connor photo Fertilization = nuclei union petals sepals Flower variation Flowers may have pollen – Ripening w/ ovules or before – On anthers below flowers or outside Flowers may be staminate (pollen only) or pistillate (ovule but no pollen) Plants may be monoecious (2 flower types) – Corn (tassel at top = pollen; silk at ear =stigma) Plants may be dioecious (♀& ♂ plants) – Holly trees may have berries (♀) or pollen flowers (♂) Pollinators Wind Water Animals – – – – – – insects mammals spiders kangaroos humans + others birds monkeys bats mites Human as pollinators Hand applied pollen – dates (since agriculture began) – vanilla Greenhouses (using vibrating toothbrushes) Apply temporary aids – pollen inserts – bouquets No ‘solution-in-a-bottle’ yet Insect Pollination ants aphids beetles butterflies bees + many others flies/midges mosquitoes moths thrips wasps The Big 3 underlined Insect-pollinated Flowers Produce lots of pollen Secrete sweet smelling, sugary nectar Come in colors Grow at conspicuous locations on plant Feature broken patterns Wave in the wind Bee Pollination 4 widely used bees in commercial pollination Bumble Bee Honey Bee Alkali Bee Leafcutting Bee ALSO: BOB (blue orchard bee); hornfaced bee, carpenter bee; pollen bees Managing Colonies for Pollination Queenright Forager bee strong Expanding brood population Limited super space Minimum strength No swarming Dry & in sun Distributed in crop Moved in & out promptly How many? Varies w/ crop Varies w/ beekeeper 75%+ col minimum strength – For example cucumber in eastern US 1 col for every 3-4 acres (small fields near woods) 1-3 col/acre (larger fields in agricultural area) 2 col/acre (high density) 1 bee/100 flowers 1 col/50,000 plants (w/ appropriate ♂/♀ ratio) Pollination Contracts Number & strength of colonies Plan of colony distribution Time of delivery and removal Beekeepers right of entry Degree of protection from pesticides Plan for payment(s) Penalities for poor colonies/service Bonus for excellent service Pollination 4 “major” crops – – – – Alfalfa seed Almond Fruits apples, berries, etc) Vegetables (+ seeds) Over 90 crops Value . $14 billion annually 1/3rd of our diet from bee pollinated crops Increasing, not diminishing, demand Fruit trees Traditional rental income – Pears – Apples – Cherries – others Early bloom in season – set of ‘king’ bloom Bees often insurance for bad weather year Other fruit major nectar source – citrus Pollination Poor Pollination Desired Pollination References: Images: http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3400/3573675917_ace3fc0e28.jpg?v=0 http://www.bio.miami.edu/muchhala/Bat-Flower%20Photos/A_geo_Meriania.jpg http://williamthecoroner.files.wordpress.com/2009/05/bumblebee-onpavement.jpg http://sarahmeyerwalsh.files.wordpress.com/2008/06/honeybee.jpghttp:/ www.everythingabout.net/articles/biology/animals/arthropods/insects/bees/leafcutting_b ee/ http://www.jimirving.com/images/galleries/beeboxes-3.jpg http://www.biology-blog.com/images/blogs/10-2006/Pollinator-2-Raspberry.jpg http://biology.unm.edu/ccouncil/Biology_203/Images/FloweringPlants/Angiolifecycle.jpeg http://www.maine.gov/agriculture/pi/images/bee.jpg http://www.plantstogrow.com/botany/fact_pages/images_2/anther-02crcm.jpg http://www.northernimages.com/photos/242820235_n5tsi-M.jpg http://208.113.167.239/wp-content/uploads/2007/06/bee-cherry-blossoms.jpg http://www.ojibway.ca/p_leucop.jpg http://illinois.sierraclub.org/calumet/Species/GrassPinkOrchid.jpg www.gettyimages.com