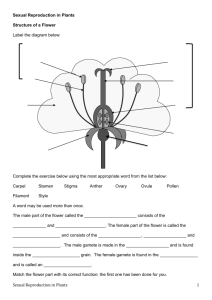
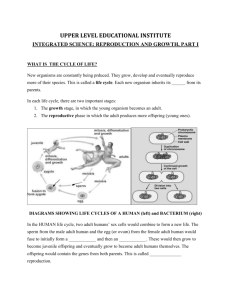
FlowerPlants
advertisement
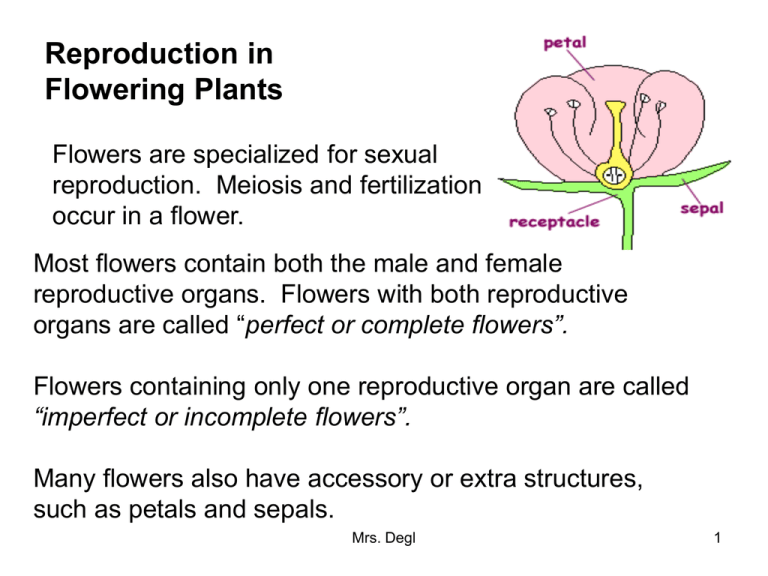
Reproduction in Flowering Plants Flowers are specialized for sexual reproduction. Meiosis and fertilization occur in a flower. Most flowers contain both the male and female reproductive organs. Flowers with both reproductive organs are called “perfect or complete flowers”. Flowers containing only one reproductive organ are called “imperfect or incomplete flowers”. Many flowers also have accessory or extra structures, such as petals and sepals. Mrs. Degl 1 Reproductive parts of a flower: The stamen is the male reproductive organ of a flower. It is composed of an anther and a filament. As a result of meiosis, the diploid (2n) cells of the anther produce pollen grains which contain monoploid (n) nuclei. The pistil is the female reproductive organ of a flower. It is composed of the stigma, style, and the ovary. During meiosis, the ovary produces ovules, which contain the monoploid egg nucleus (n). Mrs. Degl 2 Mrs. Degl 3 Pollination Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma. Pollination may be accomplished by wind, insects, and birds. In some cases, the colored petals of a flower act as a visual attraction for insects. Nectar can also act as an attractant. Self-Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or from the anther to the stigma of another flower that is part of the same plant. Cross pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther on one flower to a stigma of a flower on a different plant. Cross pollination is an adaptation which causes variation among flowers. Mrs. Degl 4 Pollen •In flowering plants, the problem of reproduction in a dry, external environment is partially solved by the presence of the thick wall of the pollen grain. •The pollen grain wall prevents dehydration of the contents while it is transferred to the stigma (female organ). •After pollination, the pollen grain germinates (is activated) on the stigma and forms a pollen tube, which extends to the ovule. •Sperm nuclei is formed at this time, in the pollen tube, from the monoploid (n) nucleus in the pollen grain. •The pollen tube is an adaptation for internal fertilization. Mrs. Degl 5 Flower Fertilization and Embryo Development. •The union or fusion of the male and female nuclei in the ovule results in a zygote. •The zygote continues to develop into an embryo. •The ripened ovule, with the embryo, develops into the seed. •The seed consists of a seed coat, which develops from the outer coverings of the ovule and embryo. •The ripened ovary develops into the fruit. •The plant embryo consists of three parts: hypocotyl, epicotyl, and cotyledon. (1 cotyledon = monocot) (2 cotyledons = dicot) (cotyledon) Mrs. Degl 6 Germination and Growth Fruits are specialized structures that which aid in seed dispersal. Seeds develop inside the fruit. If the temperature and moisture and oxygen levels are sufficient, the dispersed seeds will germinate (activate and grow). Growth in most plants occurs in the meristems. The organs of a plant are developed in the meristems. Apical Meristems are found in the tips of roots and stems and cause the plant to grow in length. Lateral Meristems (Cambium) are between the xylem and phloem and cause the plant to grow in diameter (get wider). Mrs. Degl 7