Analysis of Primates
advertisement

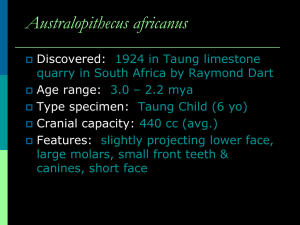
Analysis of Primates Comparisons of Human, Ape, and Australopithecine Characteristics of Primates Hominids Bones of more than 500 early hominids have been found From these bones, we have gained a broad understanding of these related species By 3mya most hominids were bipedal These hominids had a pelvis similar to humans Comparison of Pelvis and Foot Bones Hominid pelvis (like human pelvis) became shorter and bowl-shaped This made the pelvis more stable for upright walking Early hominid leg and foot bones also more similar to human’s Hominid Locomotion Bipedal locomotion is an adaptation for living in open grasslands Bipedal adaptation was selected for because it was easier to see far and move farther Upright posture also gets rid of excess body heat Over many years hominid legs became stronger Over many years hominid feet developed arches for efficient support of their body weight Over many years hominid hands became better at manipulating objects such as food and tools Hominid Head Early hominid heads were very different than ours (evolutionary forces were slower in making changes to heads) Adult brain was 1/3 size of ours The widest part of skull was below the brain case Hominid Skulls Australopithecus boisei Modern Human Early hominids had big teeth, large jaws, large zygomatic arches Early hominids had a sagittal crest (jaw muscle attachment area) (In modern humans, jaw muscles are smaller and attach to skull in temple region) Comparisons of Skulls Modern humans have large cranial capacity, relatively small teeth, less prominent brow ridges, small zygomatic arches, small jaw, no sagittal crest Comparisons of Skulls As a transitional species, (intermediate between modern humans and apes) Australopithecines had less cranial capacity, larger teeth, prominent brow ridges, larger zygomatic arches, larger jaw, sagittal crest Below is an Australopithecine afarensis skull (like Lucy) Comparisons of Skulls Skulls of Apes (see above gorilla skulls) had small cranial capacity, large teeth, prominent brow ridges, large zygomatic arches, large jaw, sagittal crest Comparison of Spinal Cords Ape spinal cord exits the rear of the skull Australopithecus, lower left, spinal cord (like human) exits the bottom of skull Skeletal Comparisons Dental Comparisons Gorilla lower jaw is parallel, and canine teeth are very pointed Australopithecus lower jaw is more angled Modern human lower jaw is even more angled Dental Comparisons Australopithecus afarensis (4.0-2.9 mya) (Lucy) canine teeth were relatively large and pointed, similar to apes Australopithecus africanus (3.3-2.3 mya) canine teeth did not project out—teeth more like humans than afarensis Branches of the Hominid Evolutionary Tree Hominid Species in Order of Appearance in Fossil Record (oldest to newest) Ardipithecus ramidus Australopithecus anamensis Australopithecus afarensis (Lucy) Australopithecus africanus Australopithecus aethiopicus Australopithecus robustus Australopithecus boisei Homo habilis Homo erectus Homo sapien (archaic) Homo sapien neanderthalensis Homo sapien sapien (modern) For tomorrow, below and review Big Neanderthal debate