Population Lab Notes
advertisement

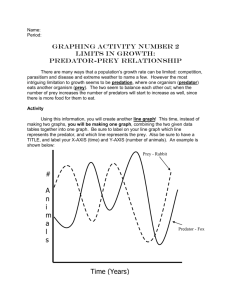
Ecology Predator-Prey Lab Ecology studies organisms and nonliving things and how they interact with each other Ecologists study ecosystems. Ecosystem – all the organisms in a given area, along with nonliving factors with which they interact Biotic factors – living Abiotic factors - nonliving Ecosystem Structure Community Population Species Ecologists specialize and study one of these structures. Population Ecology Individuals in a population – Rely on the same resources – Are influenced by the same environmental factors – Are likely to interact and breed with one another Population ecology is concerned with – Changes in population size – Factors that regulate populations over time Populations are characterized by: Density Dispersion Predator-Prey Lab: Group of (5) Create a habitat for mice and fox. Use beads and plastic container to create the habitat. Will be simulating a predator and prey relationship Read instructions carefully. Post Lab: Using expected data to analyze predator-prey interactions within the community Use the Sample Data Sheet and graph the results on the graph paper provided by your teacher. Graph the initial prey population and the initial predator population neatly and carefully. Answer the questions 1-3 using the Sample Data: 1. Which population (predator/prey) shows the first increase in numbers? Explain your answer. 2. Does a peak in the mice population come at the same time as, after a peak or before a peak in the fox population? What is the explanation for this? 3. What factor seems to determine the size of the mice population in the meadow in any given generation? Fox population? How does this lab relate to the situation in Australia with the Cane Toads? Population Growth Factors that affect population growth are called “population limiting” factors. Population limiting factors can be: Density independent – Density dependent - Population Trends Now complete Lab 4 “How can you show a population trend? Complete Parts B, C and E