Science Chapter 4: Ecosystems Study Guide Vocabulary
advertisement

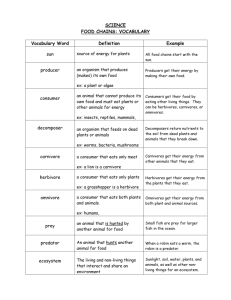
Science Chapter 4: Ecosystems Study Guide Vocabulary environment: all the nonliving things that surround a thing ecosystem: all the living and nonliving things in a certain area population: all the plants or animals of the same kind that live in an ecosystem habitat: the place each population lives community: all the living things in an ecosystem producer: a living thing, such as plants, that produce (make) food that other living things need consumer: an animal or person that must eat plants or animals to get energy decomposer: decomposers help break down dead things and waste; a mushroom is an example of a decomposer herbivore: an animal that only eats plants omnivore: a consumer that eat both plants and animals carnivore: a consumer that only eats meat food chain: the moving of energy through an ecosystem predator: any animal that hunts and eats other animals prey: the animals that a predator hunts food web: a food web is made up of several food chains linked together Facts to Know: Living things grow, reproduce, and interact with the living things around them. Food chains and food webs show how energy moves through an ecosystem. When one part of a food web changes, the change affects the whole food web. Ecosystems are always changing. God made living things able to survive in their environments and to change as things around them change. The number of living things in an ecosystem depends on the resources available. Be able to read a food web (the science book has an example of a food web on page 71). This means you should be able to tell which animals or plants are omnivores, carnivores, or herbivores. You should also be able to identify which animals and plants are eaten by others and identify predators and prey. Short Answer: What is the difference between predator and prey? Give an example of a predator and its prey. o A predator hunts and eats other animals; prey is the animals that are hunted and eaten. An example of a predator is a lion; examples of its prey could be a zebra, buffalo, or antelope. How is a food chain different from a food web? o A food chain shows only one source of food for each animal; a food web is a number of food chains linked together. What is the difference between an environment and an ecosystem? o An environment is all the nonliving things that surround a thing; an ecosystem is all the living and nonliving things in a certain area List at least two examples each of omnivores, herbivores, and carnivores. o Omnivore: bear, humans, fox, skunk, and robin o Herbivore: horse, zebra, koala, elephant, mouse o Carnivore: lion, tiger, eagle, wolf, weasel Study Resources Chapter 4 is pages 60-75 in the science book Activity Manual pages 63-64; 67-70