Chapter 7
Training
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
Learning Objectives
1. Discuss how training, informal and continuous
learning, and knowledge management can
contribute to companies’ business strategy.
2. Explain the manager’s role in identifying training
needs and supporting training.
3. Conduct a needs assessment.
4. Evaluate employees‘ readiness for training.
5. Discuss strengths and weaknesses of presentations,
hands-on and group training methods.
7-2
Learning Objectives
6. Explain potential e-learning training advantages.
7. Design a training session to maximize learning.
8. Choose an appropriate evaluation design based on
training objectives and analysis of constraints.
9. Design a cross-cultural preparation program.
10. Develop a program for effectively managing
diversity.
7-3
Training can...
Increase employees’ knowledge of foreign competitors
and cultures.
Help ensure that employees have skills to work with
new technology.
Help employees understand how to work effectively in
teams to contribute to product and service quality.
Improve employee performance which leads to
improved business results.
7-4
Training can...
Ensure that the company’s culture emphasizes
innovation, creativity and learning.
Ensure employment security by providing new
ways for employees to contribute when their jobs
change or interests change or skills become
obsolete
Prepare employees to work more effectively with
each other.
7-5
Continuous & High-Leverage Training
• Training facilitates employees’ learning job-related
knowledge, skills and behavior.
• Continuous learning requires employees to understand the
entire work process, acquire and apply new skills and share
what they have learned.
• High-leverage training is:
linked to strategic business goals and objectives,
supported by top management,
relies on an instructional design model, and is
benchmarked to programs in other organizations.
7-6
Features of Continuous Learning
7-7
2 Types of Knowledge
• personal knowledge based on individual
experience difficult to codify.
• well documented, easily articulated and
transferred person to person.
7-8
Key Features of Continuous Training
Continuous
Learning
7-9
ADDIE Model
Design
Analysis
Evaluate
Develop
Implement
7-10
Training Process
Needs assessment
Ensure readiness
Create learning environment
Ensure transfer
Select methods
Feedback
Evaluate programs
7-11
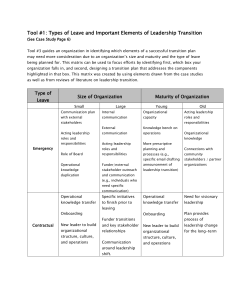
Needs Assessment Process
What is the content?
Who needs training?
In what do they
need training?
7-12
3 Factors to Choose Training
SupportManager and Peers
7-13
5 Factors That Influence
Employee Performance and Learning
Feedback
Consequences
Input
Output
7-14
Task Analysis
7-15
Factors That Influence Motivation to Learn
Self-
Basic Skills
Efficacy
7-16
Ensure Employee Motivation for Learning
Motivation to learn – desire to
learn the training program’s content.
Self-efficacy - employees' belief that they can
successfully learn the training program’s content.
7-17
Ensuring Employee Readiness for Learning
To increase employees' self-efficacy level:
1. Let employees know that training’s purpose is to improve
performance.
2. Provide information about the training program and
purpose prior to actual training.
3. Show employees their peers’ training success.
4. Provide employees feedback that learning is under their
control and they have the ability and responsibility to
overcome learning difficulties experienced in the program.
7-18
Basic Skills
7-19
7 Conditions for Learning
Know
why
they
should
learn
Observe
Training
content
Practice
Feedback
experience,
and
interact
Good
program
coordination
and
administrati
on
Commit
training
content
to
memory
7-20
Work Environment Characteristics
Influencing Transfer of Training
(EPSS)
7-21
How Managers Can Support Training
Table 7.5
Understand the content.
Know how training relates.
Evaluate employees on how they apply training.
Support employees’ use of training on the job.
Ensure they have equipment and technology to apply training.
Prior to training, discuss how to use content.
Explain why they have been asked to attend.
Give feedback and recognize those who use content.
Be a trainer.
Give release time.
7-22
Manager’s Support - Action Plans
7-23
Selecting Training Methods
Presentation Methods
Instructor-led classroom instruction
Distance learning, teleconferencing & webcasting
Audiovisual techniques
Mobile technology
Hands-on Methods
On-the-job training, apprenticeships and internships
Self-directed learning
Simulations, avatars
Business games and case studies
Behavior modeling
E-learning
Social media
Blended learning
Learning management system (LMS)
Group or Team Building
Experiential programs
Cross, coordination and team training
Action and adventure learning
7-24
Evaluating Training Programs
7-25
Evaluation Designs
Pre-test/Post-test
with comparison
group
Post-test only with
comparison group
Pre-test/Post-test
7-26
Determining Return on Investment (ROI)
7-27
Cross-Cultural Preparation
Expatriate - is an employee sent by a company to manage
operations in a different country.
Expatriates need to be:
1. Competent in their area of expertise.
2. Able to communicate verbally and nonverbally in host
country.
3. Flexible, tolerant of ambiguity and sensitive to cultural
differences.
4. Motivated to succeed, able to enjoy the challenge of
working in other countries, and willing to learn about the
host country’s culture, language and customs.
5. Supported by their families.
7-28
3 Phases of Cross-Cultural Preparation
Inclusion
7-29
Managing Diversity and Inclusion
Diversity - any dimension that differentiates a person from
another.
Managing Diversity - process of creating an environment that
allows all employees to contribute to organizational goals and
experience personal growth.
Types of Diversity Training - attitude awareness and change
programs and behavior-based programs
Goals of Diversity Training and Inclusion:
1. Eliminate values, stereotypes, and managerial practices that inhibit
2. Allow employees to contribute to organizational goals
7-30
Managing Diversity Programs
7-31
Onboarding and Socialization
Onboarding or socialization – process of helping new
hires adjust to social and performance aspects of their
new jobs.
4 Steps of Onboarding:
7-32
Characteristics of
Effective Onboarding Programs
Employees are encouraged to ask questions
Program includes information on both technical and social aspects
Manager has some onboarding responsibility
Embarrassing new employees is avoided
Learn about the company culture, history, language, products, services,
and customers
Follow-up of employee progress
Involves participation, active involvement, and formal and informal
interaction
Relocation assistance is provided
7-33
Summary
Technological innovations, new product markets, and a
diverse workforce have increased the need for companies to
reexamine how their training practices contribute to learning.
Training can contribute to effectiveness through establishing a
link with the company’s strategic direction and demonstrating
through cost–benefit analysis how training contributes to
profitability.
The key to successful training is choosing the most effective
training method.
Managing diversity and cross-cultural preparation are two
training issues relevant to capitalize on a diverse workforce
and global markets.
7-34