Slide 1 - School
advertisement

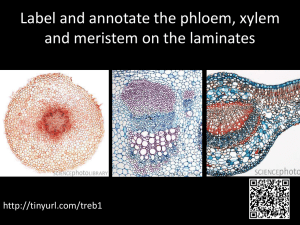
Why is the heart called a double pump? The left sideThe right side- Superior Vena cava aorta Pulmonary artery Pulmonary vein LA RA RV Why are there valves in the heart and veins? Pulmonary vein How does blood get moved between atrium and ventricles? LV Vena cava Evaluate the use of saline/plasma as a blood substitute. Readily available. __tissue match needed (no ____). Ideal for emergency paramedics to retain blood _____ and blood pressure of casualty. Reduced _______ and carbon dioxide carrying capacity, though a little will ______ in plasma. Evaluate the use of PFCs as a blood substitute Very ____ – can fit through a bruised tissue / vessel. Doesn’t carry as much oxygen. No _______ passed on. Longer shelf life of _ y____. Body breaks PFCs down quickly 4-12 hours. Weaker _____ system as a result. PFCs do not easily d_______. Evaluate the use of haemoglobin as a blood substitute Carries far ____ oxygen. __ tissue match needed (no _____) and therefore a longer shelf life. Body breaks down haemoglobin quickly so constant supply needed. Plant transport Xylem transport water _______. Phloem transport sugars in ___ directions. In the roots, xylem tubes are just found as a m____. In the stem and leaves the xylem and phloem are found as vascular b______. What is the importance of elastic fibres in arteries? What is the importance of muscle fibres in arteries? Evaluate the use of stents to treat coronary artery blockages. ______supressant drugs needed. Doesn’t make recipient change diet. Drug coated stents very e________ but do not r______ unlike artificial stents. Evaluate the using of artificial heart valves. Very expensive. N_____need to be replaced. Will not r____. Immunosupressant drugs not needed. Evaluate the using of biological heart valves. Readily available. Need _________every 15 years. Immunosupressant drugs needed. Evaluate the use of artificial hearts. L______ than normal heart / un__________. No need to match t_____ type. Immunosupressant drugs not needed. Blood Plasma-liquid carries blood cells and other substances e.g. glucose and CO2. Red blood cells contain ___________this binds to oxygen creating oxyhaemoglobin, the oxygen can then be released to cells. This unbinding happens faster in tissues where there is high levels as the haemogblobin naturally becomes less oxygen s______. White blood cells make a________, a__________ Platelets help ________ at a wound Why is the heart called a double pump? The left side- pumps blood to body The right side- pumps blood to lungs Superior Vena cava aorta Pulmonary artery Pulmonary vein LA RA RV Pulmonary vein LV Why are there valves in the heart and veins? To prevent the backflow of blood How does blood get moved between atrium and ventricles? They contract squeezing the blood through a valve. Vena cava Evaluate the use of saline/plasma as a blood substitute. Readily available. No tissue match needed (no cells). Ideal for emergency paramedics to retain blood volume and blood pressure of casualty. Reduced oxygen and carbon dioxide carrying capacity, though a little will dissolve in plasma. Evaluate the use of PFCs as a blood substitute Very small – can fit through a bruised tissue / vessel. Doesn’t carry as much oxygen. No diseases passed on. Longer shelf life of 2 years. Body breaks PFCs down quickly412 hours. Weaker immune system as a result. PFCs do not easily dissolve. Evaluate the use of haemoglobin as a blood substitute Carries far more oxygen. No tissue match needed (no cells) and therefore a longer shelf life. Body breaks down haemoglobin quickly so constant supply needed. Plant transport Xylem transport water upwards. Phloem transport sugars in all directions. In the roots, xylem tubes are just found as a mass. In the stem and leaves the xylem and phloem are found as vascular bundles. Artery Toward heart No valves Vein Away from heart Has valves Capillary Join artery to vein No valves What is the importance of elastic fibres in arteries? Stretch to let the blood pass through What is the importance of muscle fibres in arteries? Withstand the high pressure of the blood flow Evaluate the use of stents to treat coronary artery blockages. Immunosupressant drugs needed. Doesn’t make recipient change diet. Drug coated stents very expensive but do not reclose unlike artificial stents. Evaluate the using of artificial heart valves. Very expensive. Never need to be replaced. Will not rust. Immunosupressant drugs not needed. Evaluate the using of biological heart valves. Readily available. Need replacing every 15 years. Immunosupressant drugs needed. Evaluate the use of artificial hearts. Larger than normal heart / uncomfortable. No need to match tissue type. Immunosupressant drugs not needed. Blood Plasma-liquid carries blood cells and other substances e.g. glucose and CO2. Red blood cells contain haemoglobin this binds to oxygen creating oxyhaemoglobin, the oxygen can then be released to cells. This unbinding happens faster in tissues where there is high levels as the haemogblobin naturally becomes less oxygen saturated. White blood cells make antibodies, anti-toxins Platelets help clotting at a wound