Lecture 19 - drcink.net

Lecture 22
Female Reproductive System
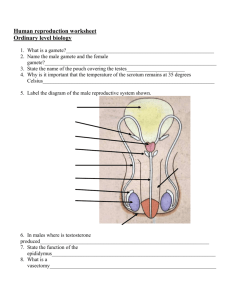
Ovaries o These gonads produce __________ cells and sex hormones o Almond-shaped and measuring about 3 cm long, 1.5 cm wide and 1 cm thick o Medulla is a zone of fibrous connective tissue containing arteries and veins o Cortex is the site of the ovarian __________________
Each follicle consists of one developing ovum surrounded by numerous small follicular cells o Ovaries are held in place by tissue ligaments
The ovaries are attached to the uterus by the ovarian
________________
At the opposite ends, the ovaries are attached to the pelvic wall by suspensory ligaments
The anterior margin of the ovary is anchored by a peritoneal fold called the ___________________
This extends to a sheet of peritoneum called the broad ligament which runs along the side of the uterus
Oogenesis and ova o The production of female gametes is called oogenesis o It employs meiosis to produce haploid gametes o It differs from spermatogenesis in that
it is not a ____________________ process.
it occurs in a rhythm called the ovarian cycle
it produces only one functional gamete
The other daughter cells are called polar bodies which die o In the (female) fetus, germ cells differentiate into oogonia which multiply until the fifth month of gestation
They produce 6 to 7 million and then go into a state of
_________________ development until shortly before birth
Some of them then transform into primary oocytes and go as far as early meiosis I
Most primary oocytes degenerate before a girl is born
2 million remain at birth
By the onset of puberty, only 400,000 remain o This is the female’s ________________ supply of germ cells o During a woman’s reproductive years, about 20 to 25 oocytes and follicles begin to develop each month. o Normally, just one of these reaches maturity and ovulates, and the rest degenerate o The stages of oogenesis are accompanied by changes in the follicle
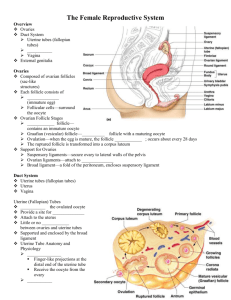
The primary oocyte is initially enclosed in a primordial follicle
A ________________ layer of squamous follicular cells surrounding the oocyte
About 3 days before the menstrual period begins, pituitary secretion of FSH stimulates primordial follicles to develop into primary follicles
The follicular cells thicken into a cuboidal epithelium, multiply, and become stratified
One of the primary follicles forms a fluid-filled cavity called an
_________________
The follicle is then called a secondary follicle
The secondary follicle enlarges to as much as 2.5 cm in diameter and bulges like a balloon
This is called a mature follicle (or a graafian follicle)
The release of the oocyte from the follicle is called ovulation
It typically occurs at about day 14 of the ovulation cycle
When the oocyte is expelled, the follicle collapses and becomes a structure called a corpus _________________
The corpus luteum secretes a large amount of progesterone, which stimulates the uterus to prepare for possible pregnancy
Uterine tubes o The ovulated oocyte travels through this tube to reach the uterus o Also called the oviduct or ____________________ tube o At the distal end of the tube it has feathery projections called fimbriae that direct the egg into the tube o The wall of the tube has smooth muscle that produces contractions to direct the egg towards the uterus o The mucosa has ciliated cells that direct the egg towards the uterus
Uterus o This is a thick ____________________ chamber that opens into the roof of the vagina o It usually tilts forward over the urinary bladder o Its functions:
Harbor the fetus
Provide it with a source of nutrition
Expel the fetus at the end of gestation o It’s somewhat pear-shaped
It has a broad superior curvature (the dome-shaped part) called the
_________________
It had a midportion called the body
It has a narrow inferior portion called the cervix
The opening through the cervix to the vagina is the cervical canal o The uterine wall
The myometrium is composed mainly of bundles of smooth muscle
The ____________________ is the inner lining
The stramum functionalis is shed each menstrual period
The stratum basalis stays behind an degenerates a new funtionalis in the next cycle
Ligaments
The broad ligament, cardinal ligament, uterosacral ligaments, and round ligament all hold the uterus in place
Menstrual Cycle
___________________ phase – time of building the endometrial tissue from .5 mm thick to about 2 to 3 mm thick through mitosis
Secretory phase – time of further thickening, but as a result of accumulation of fluid rather than mitosis
Premenstrual phase – period of endometrial degeneration occurring in the last 2 days of the menstrual cycle o Tissue and blood fall away from the uterine wall, forming menstrual fluid
_________________ phase – begins when enough menstrual fluid has accumulated in the uterus that it begins to be discharged vaginally
Vagina o This is a tube that allows for
Discharge of menstrual fluid
Receipt of the penis and semen
The birth of a baby o It is thin-walled but very distensible o At the lower end is the _________________ , which stretches across the opening of the vagina
The hymen may be ruptured by sexual intercourse, but is commonly ruptured before then in other ways o The lower end has vaginal rugae which stimulate the penis and help induce ejaculation
External Genitalia o Collectively known as vulva o The mons pubis is the _________________ mound of adipose tissue overlying the symphysis pubis o The labia majora are a pair of thick folds of skin and adipose tissue
Inferior to the mons pubis
Between the thighs o The labia minora are thin folds of tissue medial to labia majora o The vestibule is the area enclosed by the labia minora o The clitoris is found at the anterior junction of the labia minora
Its function is entirely __________________
It’s the primary center of erotic stimulation o The vestibular bulbs are pairs of subcutaneous erectile tissues
They are just deep to the labia majora
They become congested with blood and cause the vagina to tighten somewhat around the penis o The vestibular __________________ are found next to the vagina
They keep the vulva moist and provide lubrication during sexual intercourse
Breasts and Mammary Glands o The breast is a mound of tissue overlying the pectoralis major o The mammary gland develops within the breast during pregnancy
It remains active in the lactating breast
At atrophies when a woman ceases to nurse o The breast has two principle regions
The body – the conical to pendulous part
At its apex is the nipple
The ______________________ tail – the portion that extends toward the armpit o The areola is a circular colored zone that surrounds the nipple
Dermal capillaries and nerves come closer to the surface here than in the surrounding skin
It makes the area more sensitive and reddish in color
In pregnancy, the areola and nipple may darken, to make them more visible to the nursing infant
Sensory nerve fibers are important in triggering a milk ejection reflex when an infant nurses o Internally, the non-lactating breast is mostly adipose and collagenous tissue o Suspensory ligaments attach the breast to the dermis overlying the skin and to the fascia of the pectoralis major o When the mammary gland develops during pregnancy, it exhibits 15 to 20 lobes arranged radially around the ________________
Each lobe is drained by a lactiferous duct
Lactiferous ducts dilate to form a lactiferous sinus which opens into the nipple