Adapted Study Guide Sex. Ed. Test The human body begins as one
advertisement

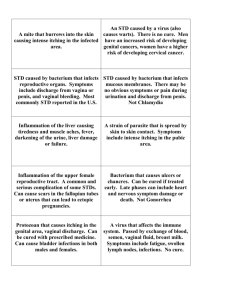
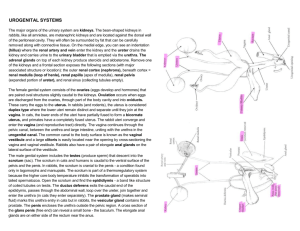
Adapted Study Guide Sex. Ed. Test - - - The human body begins as one microscopic cell The cluster of cells that develop between the third and eighth weeks of pregnancy is an embryo After eight weeks the developing group of cells is called the fetus The thin, fluid filled membrane that surrounds and protects the developing embryo and it also insulates it from changing temperatures is called the amniotic sac The thick, blood-rich tissue that lines the walls of the uterus during pregnancy and nourishes the embryo is called the placenta Materials diffuse from one blood supply to the other through the umbilical cord The zygote attaching to the uterine wall is called implantation The union of the ovum and sperm cells is called fertilization The hormone that causes the testes to produce sperm is testosterone The Cowper’s gland is so important because it secretes a clear liquid to lubricate the urethra and neutralize the acid content before semen is ejaculated 3 suggestions for the care of the male reproductive system are a daily shower, self-examination, and wearing of a supporter The Penis is the MALE external reproductive organ. It is composed of spongy tissue that contains many blood vessels When a female reaches puberty, hormones released by the pituitary gland stimulate the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone The 3 external parts of the vagina are known as the vulva, it includes, Mons pubis, soft tissue that covers that pubic bone; Labia majora, the outer folds of skin that surround the opening of the vagina; Labia minora, the inner folds of skin The ovaries are described as the female sex glands that house the ova and produce female sex hormones The fallopian tubes are described as a passageway where mature ovum are released into The uterus is described as a small, muscular, pear shaped organ The process of menstruation is described as the shedding the lining of the uterus. Usually lasts 3-5 days and the cycle starts all over again. Although there can be great variations the time from one menstrual period to the next is usually 28 days. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD’s) are defined as communicable disease that is spread from person to person through sexual contact 2 reasons people often contract an STD and don’t seek medical help because it is not obvious and they are embarrassed Gonorrhea is defined as a disease caused by bacteria that live in warm, moist areas of the body, primarily the lining of the urethra and the cervix of the female Syphilis is caused by a small bacterium called spirochete and attacks many parts of the body Facts of genital herpes or Herpes 2 are - estimated 40 million Americans have herpes 2 - symptoms include painful itching sores around genitals - sores appear 2 to 20 days after contact - last as long as 3 weeks - the virus will never go away but it will be more contagious at certain times STD Chlamydia Description Most prevalent in the U.S. Common cause of sterility Trichomoniasis Vaginal infection Males rarely infected Symptoms Infection that affects the vagina in females and urethra in males In females a yellowish discharge and no or slight symptoms in males Pubic Lice Tiny insects attach themselves to the skin and hair in the pubic area Intense itching Vaginitis Inflammation of the female genitals Severe itching Genital Warts Pink or Reddish Warts that have cauliflower like tops Appear 1-3 weeks after infection Moniliasis Yeast Infection White Cheesy Discharge A discharge General itching and irritation