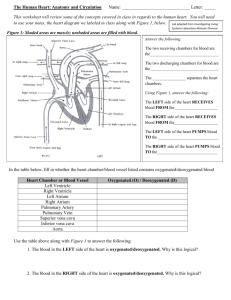
Circulatory System Review Sheet 7A
advertisement

Circulatory System Review Sheet 7A 1. What is the function of the circulatory system? • Transport of materials throughout the body. 2. What is the liquid part of the blood? What is it’s function? • Plasma transports materials in the blood such as nutrients, hormones, enzymes… 3. Fill in the chart below to describe the types of blood cells and the function of each. Cell Type Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets Description Function Disc shaped, most numerous No nucleus, live for 120 days Carried oxygen and Contain hemoglobin (protein) carbon dioxide Largest blood cell Fewer than RBC’s Cell fragments Protects the body against disease Clotting (produces fibrin to stop bleeding) 4. Identify each of the blood vessels below and tell the function of each: . A . Arteries • Carries blood away from the heart Veins • Carries blood to the heart C B Capillaries • Allows materials to be exchanged between the blood and cells • Connects arteries and veins 5. a. The largest artery is called the aorta. b. Function: Carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body 6. a. The largest vein is called the vena cava. b. Function: Carries deoxygenated blood from the cells of your body back to the heart 7. Trace the path of a drop of blood, starting from the left atrium until it returns to the left atrium again. Name all the major structures through which it passes. • Left Atrium, Left Ventricle, Aorta, BODY, Upper & Lower Vena Cava, Right Atrium, Right Ventricle, Pulmonary Arteries, LUNGS, Pulmonary Veins, Left Atrium 8. Label the picture of the heart below: D aorta E Pulmonary artery C Upper vena cava F Left atrium G Pulmonary veins Right atrium B H valve I Left ventricle lower vena cava A J Right ventricle 9. Tell which of the structures above carry oxygenated blood and which carry deoxygenated blood. • Oxygenated: pulmonary veins, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta • Deoxygenated:, upper and lower vena cava. right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary arteries 10. Explain the differences between pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins. • Pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs from the right side of the heart. • Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the left side of the heart. 11. For each blood type indicate the type of antigen carried by the red blood cells and antibodies found in the plasma. A: A antigens, anti-B antibodies B: B antigens, anti-A antibodies AB: both A and B antigens, no antibodies O: no antigens, both anti-A and anti-B antibodies 12. A person has blood type B+. a. Who can this person donate blood to? • B+, AB+ b. Who can this person receive blood from? • B+, B-, O+, Oc. Can this person donate to someone who is B-? Why or why not? • No, because the person with B- blood does not have the Rh factor so if they enter the body, the blood will clump. Respiratory System 1. The main job of the circulatory system is the get oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide out of the body. 2. The walls of the trachea are made up of rings of cartilage. 3. The large, flat muscle that produces the movement of inhalation and exhalation is the diaphragm. 4. In the chest, the trachea divides into 2 bronchi. 5. The main passageway that leads to the lungs from the throat is the trachea. 6. The first tubes to branch off the trachea are called bronchi. 7. During swallowing, the air passage of the pharynx is covered by the epiglottis. 8. What is the correct sequence for the path of oxygen through the respiratory system starting with the trachea? • Trachea, bronchi, bronchial tubes, bronchioles, alveoli 9. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the external environment and blood occurs in the alveoli. 10. Which structure contributes to pressure changes in the chest cavity? • Diaphragm 11. a. What gas is represented by A? • oxygen b. What gas is represented by B? • Carbon dioxide c. What is structure C? • capillary d. What process occurs here? • Gas exchange by diffusion 12. What structure is affected by emphysema? • Alveoli 13. What happens in the body during inhalation? • Diaphragm contracts or moves down • Pressure decreases • Rib cage expands 14. What happens in the body during exhalation? • Diaphragm relaxes or moves up • Pressure increases • Rib cage relaxes 15. Label the diagram below. A. Nose/nostrils B. Nasal cavity C. Pharynx D. Epiglottis E. Larynx F. Trachea G. Bronchi H. Bronchial tubes I. Bronchioles J. Diaphragm Excretory System 1. What is the principle nitrogenous in humans? • urea 2. Nitrogenous wastes may be produced as a result of the breakdown of proteins 3. Compared to blood entering the kidney, blood leaving the kidney normally contains a lower concentration of wastes/urea. 4. Which organ produces urea? • Liver 5. This organ excretes salt from its surface: skin 6. The functional units of this organ are known as alveoli: lungs 7. The functional units of this organ are known as nephrons: kidneys 8. In humans, the nitrogenous wastes are removed from the blood in structures called kidneys/nephrons. 9. Which excretory organ maintains normal body temperature? • skin 10. As urine is excreted, muscle contractions in the bladder will cause the urine to pass into the urethra. 11. Use the diagram to answer the following questions. a. Which structure produces urine? • A: urine b. Name structure B. • Ureters c. Name structure C. • Urinary Bladder d. Name structure D. • Urethra 12. Use the diagram to answer the following questions. a. What does structure A Excrete? (2 substances) • Carbon dioxide and water vapor b. Which structure regulates the amount of water in the blood? • kidneys c. How does structure B play a role in excretion? • It produces urea (deamination) and detoxifies the blood. d. What does structure D produce? • urine