* ***Nuclear *ecuri****afe
advertisement

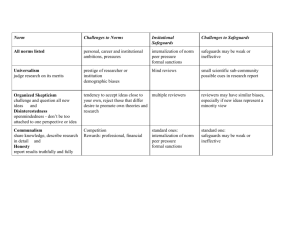
Kenji Murakami Visiting Professor,Tokyo Ci ty University Lessons Learned from Fukushima Accident Accident beyond all expectation Possible to happen could happen in worst way Critical initial response Contain impact and minimize damage Public reaction and social order Fear of radiation and lack of information Adequate accident response and management Coordination, communication and quick response Impact of Fukushima Accident Preparedness for major disaster response Prepare for the unexpected and normal time practice Nuclear disaster caused by nature or mankind Vulnerability of nuclear plant to external event Adequate risk assessment and damage control Robust and flexible assessment of all risks and anticipated damages Consideration of elements of 3S for major disaster Prevention, response, control and management 3S(Security, Safety and Safeguards) Factors Safety Security Safeguards Factors Safety Security Safeguards Human error, Non-state actors: State, Threat Human error, natural cause, Natural cause, terrorists, Diverters Design error Design error Non-state Criminals actors: terrorists, criminals, Threat protestors State (political decision) Timeliness Real time/ Real time/ Month ~ Timeliness Real time/immediate Real immediate immediate time/immediate > Months Role of State Regulate safe Regulate physical Regulate Role of Stateoperation Regulatesprotection safe operation accounting Regulates and physical protection Regulates accounting and control control Role of IAEA Issue safety Issue security Verify compliance Role of IAEAStandards Issue standards to Issue and safety recommendations agreements security Recommendations Verify compliance to monitor and monitor agreements compliance compliance Main Legal Framework of 3S Binding legal framework - NPT, Safeguards Agreement, Additional Protocol - Conventions of PP(2005),Nuclear safety, accident early notification and assistance, safety of SF & waste - UNSC resolutions 1373, 1540 ; UNGC 52, 56 and others Non-binding legal framework - Codes of conduct on safety/security of radioactive sources , research reactor - INFCIRC/225/Rev5 and others There is no common and comprehensive legal instrument for all 3S Concluding Remarks Adherence to Nuclear security, safety and safeguards is a commitment by each State - Each State should implement balanced approach of 3S High standard of nuclear security is essential for peaceful use of nuclear energy - Effective and broader application of security measure by each State is necessary Need for common and universal rules for 3S -Many legal instruments exist but none comprehensive to cover 3S Collective security arrangements and mutual cooperation -Needed to promote transparency and benefits