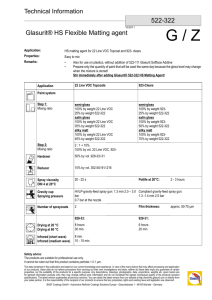
Tools to Achieve Performance Excellence
Translating VOC into
Superior Design
Robert ‘QualityBob’ Mitchell
3M
Quality & Innovation
•
•
•
•
•
•
VOC
QFD
CAGE
Culture
Behavioral Economics
Kano
Translating VOC using the QFD
House of Quality
• Translating Voice of Customer into validated
product/service requirements
• Understanding the competitive environment
• Delivering on the requirements
• Maintaining control
• Knowledge management
QFD Process
Product Planning Matrix
Identifies critical customer requirements and
translates them into technical requirements
Product Qualification Matrix
Translates technical requirements
into product quality characteristics
Process Planning Matrix
Identifies critical materials and
process steps to meet customer
requirements
Process Control Matrix
Identifies control methods
House of Quality Deployment
• First House of Quality
– Customer requirements
– Product performance measures
– Correlation of product requirements
– Competitive analysis information
• Lower Level Houses of Quality
– Product performance requirements
– Product design / features
– Process variables information
– Raw material information
– Control methods
1st House of Quality
Product Planning
Whats
I
m
p
o
r
t
a
n
c
e
Relationships
How Much
Competitive
Analysis
Hows
Correlations
The 1st House of Quality
The 1st House of Quality
10. Correlations of
System Requirements
9. Targets
8. Ideal values
4. Competitive perf.
7. Importance
weights
3. Our performance
6. Relationships
between Needs
& Requirements
2. Importance ratings
1. Customer
Needs (VOC)
5. System
Requirements
Translating Voice of Customer into
Validated Product/Service Requirements
• Gathering customer needs (Voice of
Customer)
• Translating the voices of the customer into
prioritized customer needs
• Validating customer needs with the
customer
• Creating product/service requirements from
the customer needs
Collecting the Voice of the Customer
• Define the objective
• Determine who to contact
• Decide what to ask
Interview Guide
Customer Selection Matrix
Market
Segment
Names for
selected
cells
1.
2.
3.
4.
____________
____________
____________
____________
1.
2.
3.
4.
____________
____________
____________
____________
1.
2.
3.
4.
____________
____________
____________
____________
1.
2.
3.
4.
____________
____________
____________
____________
1.
2.
3.
4.
____________
____________
____________
____________
Our
Customer
Competitor
Customer
Dual
Competitive
Lapsed
Customer Technology Customers
Collecting the Voice of the Customer
• Site Observation
• “Listen” beyond the words
Methods for Gathering Customer Input
Customer Intimacy
Impersonal
Data
Questions or
Statements
Complaints, Customer Svc
Surveys
Written questionnaire
• Paper
• Electronic
Telephone interview
Face-to-face
Diaries (usage)
Quantitative
Discrete or
Continuous
Language data (limited)
Qualitative (limited)
Focus group/Panel
Moderator guided
and recorders
Qualitative
Language data
Open-ended
Focused to cover
specific topics
Qualitative
Language data
Customer-Specific
Requirements;
Specs, P.O.s, etc.
Site observation
Documentation
Field Sales, Tech Svc
Voice of customer (VOC)
Face-to-Face with
Interviewer, Recorder,
and Observer
Become the customer
Integrated Extended on-site visit
Qualitative
Language data
Observations
Direct
Focused to get
specific
Information
High-gain
Open-ended
Limited topics
Additional considerations to prioritize VOC
• Importance to the customer
• Pain for customer
– How well does the competition satisfy the need
now?
– How well do you satisfy that need now?
• How much does the customer value the
satisfaction of this need?
– Purchase driver? (Switching costs)
– Will Customer potentially pay more?
– Does the perceived value offset the switching
cost?
Customer Satisfaction –Three Major Criteria
1. Performance
– Defined by objective criteria
– Focused on functionality
2. Perception
– Subjective
– Focus is on appeal, experience
3. Outcomes
– Results obtained by using the service or product
Creating a Customer-Centered Culture, by Robin L. Lawton (Quality Press, 1993)
Customer Value Prioritization
What
Customers
Value
3
What we
Measure
Performance
1
(Features)
2
Perception
2
(Advantages)
1
Outcomes
3
(Benefits)
Creating a Customer-Centered Culture, by Robin L. Lawton (Quality Press, 1993)
The VOC “CAGE” Model
Key
Regions
Sub-Regions
HOW project teams initially
understand the VOC and
define Success before any
market research
A) All Agree on
WHAT customers tell us
about their needs during
typical VOC research
C) VOC customer
insights
A Bulls-eye; What SELLS.
$$$. A comprehensive and
accurate set of customer
needs that will win in a
competitive marketplace.
(Real-Win-Worth)
E) Excitement
Quality
B) What Customers
got wrong
D) Development
Team got wrong
F) What both got
wrong
G) The “Givens”
Copyright protected; used with permission
(David Verduyn, C2C Solutions Inc. www.c2c-solutions.com)
B
C
B
D
F
A
F
G E
D
Simon Sinek’s “Golden Circles”
“People don’t buy ‘what’ you do (products, services),
people buy ‘why’ you do it (purpose)”
WHAT
HOW
WHY
Apple Computer example:
What (Products/Services): Computers,
iPods, iPads, iPhones, iTunes, etc.
How (Values): Beautiful design,
simple to use, user-friendly
Why (Purpose): Challenge the status quo;
Think differently
MN ASQ section 1203:
What: Classes, Programs, Conferences
How: Professional development
Why: A community of practice that
enhances skills to improve
total customer / patient
experience
CUSTOMER ENGAGEMENT HIERARCHY
Copyright © 2013 Gallup, Inc. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 2013 Gallup, Inc. All rights reserved.
Four Types of Customers
Fully
Engaged
Engaged
Not
Engaged
Strongly
attached and
loyal. Your
most valuable
customers
Beginnings of
emotional
attachment
but not strong
Emotionally
and
attitudinally
neutral
Copyright © 2013 Gallup, Inc. All rights reserved.
Actively
Disengaged
Active
emotional
detachment
and
antagonism
Behavioral
Economics
Why Can’t People See the
Opportunity for Innovation?
Top 5 Innovation Factors
1. Culture (employee attitudes & participation)
2. Senior Leadership Support (risk / long-term results)
3. Capabilities (workforce talent, training, & experience)
4. Strategy (alignment to profitable growth & business goals)
5. Process (effective methods & tools)
Quantitative Study Comprised of 1,486 ASQ Senior and Fellow Responses.
Culture of Innovation
Creating a culture of innovation
• Employee engagement
• Freedom to experiment... and fail
• Teamwork, collaboration
• Customer engagement
• Customers advocate for you
• Participate in product design & test
• Use VOC and QFD to:
• Change the basis of competition
• Create differentiated performance and value
Kano Model
Exciting Quality
(Unarticulated Needs)
Requested Quality
(Stated Needs)
Not
Fulfilled
Fulfilled
Expected Quality
(Basic needs)
Why use QFD?
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Shorter Development Time
Shorter Time to Business Success
Better Process Understanding
Fewer Engineering Changes
Lower Design Cost
Reduced Manufacturing Costs
Satisfaction of Customer Needs
Competitive Advantage
Thank You