BUILDING TOMORROW ™
Innovation in Banking
Tony Clegg & Tom Macdonald
24th February 2012
rbs.com/gts
Cards in Public Sector
Tony Clegg - Business Development Manager
RBS00000
1
GPC III
RBS only dual scheme issuer in GPCIII i.e. MasterCard and Visa
MasterCard OneCard preferred solution with Integrated MI package
Comprehensive reporting system – Smart Data Online
Solutions encompass both Travel & Entertainment and Purchasing style spend
Tiered rebate structure available, based on annual spend and settlement period
RBS00000
2
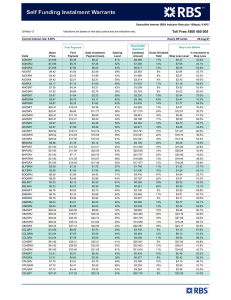
Rebate matrix
Size of customer
% Rebate
(annual value of transactions)
Standard terms - 14 days
Up to £499,999 per annum
0.00% Up to £499,999 per annum
Size of customer
(annual value of transactions)
For delayed settlement - 28
days
0.000% Up to £499,999 per annum
£500,000 to
0.10% £500,000 to
0.175% £500,000 to
£999,999
Size of customer
% Rebate
(annual value of transactions)
For early settlement - 7 days
£999,999
£999,999
% Rebate
0.000%
0.000%
£1,000,000 to £2,999,999
0.15% £1,000,000 to £2,999,999
0.225% £1,000,000 to £2,999,999
0.000%
£3,000,000 to £4,999,999
0.20% £3,000,000 to £4,999,999
0.275% £3,000,000 to £4,999,999
0.050%
£5,000,000 to £9,999,999
0.35% £5,000,000 to £9,999,999
0.425% £5,000,000 to £9,999,999
0.150%
£10,000,000 to £29,999,999
0.40% £10,000,000 to £29,999,999
0.475% £10,000,000 to £29,999,999
0.200%
£30,000,000 to £49,999,999
0.45% £30,000,000 to £49,999,999
0.525% £30,000,000 to £49,999,999
0.225%
£50,000,000 to £74,999,999
0.50% £50,000,000 to £74,999,999
0.575% £50,000,000 to £74,999,999
0.275%
£75,000,000 to £99,999,999
0.60% £75,000,000 to £99,999,999
0.675% £75,000,000 to £99,999,999
0.325%
In excess of £100,000,000
0.65% In excess of £100,000,000
0.725% In excess of £100,000,000
0.375%
RBS00000
3
Comprehensive Controls
Individual transaction limit
Cardholder monthly limit
Corporate monthly limit
Merchant Category Group Blocking (inc option to prohibit cash withdrawals)
Preferred Vendor
‘Approved’ Supplier lists
‘Hosted’/Virtual cards
Smart Data On-Line (SDOL)
Corporate Liability Waiver/ Lost or Stolen Card Liability
£50k per c/holder
£1.5 Million per programme
RBS00000
4
Declining Balance Cards - Uses and Benefits
Declining balance cards are an ideal solution for any programme where there is a
need for a set budget or a fixed spending amount.
Examples of Declining Balance usage would be…
- Incentives
and Per Diem
Meetings & Events
Projects
Travel and Expense
-
Consulting Projects
-
Board Meeting Arrangements
- Recruiting and Relocation
- Disaster Recovery Projects
- Conferences & Conventions
- Rewards and Recognition
- Educational Grants
- Parties
- Temporary Workers Expenses
- Government Grants
- Sales / Team Meetings
- Training Budgets
- Pilot / Test Programmes
- Trade Shows & Events
- Allowances
- Short-Term Projects
- Product Launches
RBS00000
5
Virtual Cards
A rapidly growing area for cards use
No Cards issued
Virtual cards can be set up in any name as not constrained by Chip & Pin regs
Usually set up in name of Department or key supplier
If with key supplier, card number is lodged with supplier
Purchases made and charged to card
Data supplied is usually level 3 compliant removing requirement for VAT receipts
Card details held securely
Coding can be added as part of transactions to assist cost allocation
RBS00000
6
Reporting options
Functionality Includes :
Integrated MI systems or 3rd Party solutions available
Large variety of reporting options, allowing you to compile, track and manage
transactions.
VAT reports accredited by Customs and Excise as evidence for VAT reclaim.
Manipulate raw data to produce your own bespoke reports.
Web based services that enable you to access management information reports,
helps analyse your cardholder’s spending, ensure internal policies are being
adhered to.
Create your hierarchy for reporting purposes.
Cardholder logon
Assignment of GL Codes
Download data to your General Ledger/Account software systems
RBS00000
7
Summary benefits
RBS Commercial Cards through GPC, can offer increased value to both internal and end
user customers through ;
Reducing the need for cash - Global Acceptance
Cash flow management – Free up cash flow of upto 45 days from date of purchases
Process efficiency – Reduce cost of invoice processing by approximately £33 (manual
versus electronic)
Cost control - Card transaction limits and monthly card limits – Tight Control on Spending
On line Management Information – 24/7 visibility of Purchases
RBS00000
8
Innovation in Banking
Tom Macdonald - Cash Management
RBS00000
9
Banking Innovation
Backdrop
Banking landscape more regulated to ensure greater future stability
Liquidity and cash flow management increasingly important
European initiatives driving efficient business interaction across the single market
Technology continues to transform how we pay and interact
Growing expectations for mobility, speed and interoperability
Online is moving to Mobile as smart phone and tablet use increases
Consumers are changing faster than businesses but what does this mean in the way they
pay businesses?
RBS00000
10
Regulation – Stability and Compliance
The New Landscape
Europe Basel III
1) International Agreement on the amount of capital held
by banks
– Goes live from 2013
Prudential Regulatory Authority
US Dodd Frank Act
1) Promotes the stability of the US financial system
– Improves accountability and transparency
– Protects American taxpayer by ending bailouts
– Protects consumers from abusive financial services
practices
3) FCA supervises the individual organisations
1) New entity that will sit alongside the Financial Conduct
Authority
2) PRA works with Bank of England to ensure market
stability
Payment Services Oversight
1) Banking Act 2009 gives the BoE responsibility in the UK
for ensuring that critical payment schemes operate
prudently
– More banks will join schemes in their own right
UK independent Commission on Banking
1) Ring fences UK retail operations
2) Improves loss absorbency, e.g. equity/leverage
3) Sets higher UK capital requirements for systemically
important FIs
– Bacs payments will move to a £20m value cap from
May 2012
2) UK Payments Council tasked to oversee and drive
these changes
RBS00000
11
UK Payments Council
Key Objectives
Innovation – research, enhance, facilitate
Inclusion – improve access & inclusion
Integrity – robust and secure systems
RBS00000
12
Payments Council – National Payments Plan
Activity
Innovation
Mobile Payments Service development of a ‘proxy’ database to
route payments to a bank account
using a linked mobile phone number
Multiple Authorisation for all business
online channels to support small
business demand for online banking
services
Investigating solutions to ensure
electronic payments are made to the
right payee
Inclusion
Integrity
Linked closely to innovation
•
Working closely with the Charities &
Voluntary sectors to ensure that
payment services meet the needs
Frameworks/concepts easy to
recycle
Payment system resilience e.g. Bacs
transaction value cap of £20m from end
May 2012
•
Develop minimum standards for customer
authentication on internet and telephone
banking
•
New best practice guidance on Payment
Referencing for Billers and Payers in late
2010
Recent research on how older people
interact with the service sector for
payments
RBS00000
13
UK Payments Trends 2010 - 2020
Winners and Losers
100%
40%
41%
24%
22%
17%
All Payments
(Non Cash)
Debit Cards Credit Cards Direct Debits Auto Credits Standing Orders
ATM
3%
CHAPS
Cash
Cheques
9%
35%
100%
Source: Payments Council UK Payment Markets 2011
RBS00000
14
Wider Innovation
Business Efficiency
Worldwide Government initiatives driving business and citizen e-enablement and
activity
Across Europe, mandatory B2Gov e-invoicing is spreading - Denmark, Finland,
Italy, Spain and Sweden have done and other countries are expected to follow
e-invoicing generally is experiencing 30-40% annual market growth
In turn it supports better cash flow management and accounts payable/ receivable
process efficiency,
The SEPA project aims by end 2014 to deliver across participant countries
mandated use of SEPA credits and direct debits
For consumers UK drive to get more people on line and extend broadband reach/
speed
So what might the future look like?
RBS00000
15
Fast growing expectations – consumers and businesses
Customers today demand payment methods that :
Conform to the highest standards
Don’t have onerous identification methods
Are completed within hours
Use devices that exist for other reasons
Are 100% accurate and reliable
Are widely accepted by businesses
Are globally usable
Are value for money
Use data to enhance the bank’s offer, but not
intrude
Do you agree?
16
RBS00000
16
And what might this mean?
Mobile, globally
accepted and secure
Cash is dead
Possible Consumer
Scenario
x
Efficient*
Replaced by mobile phones
and contactless cards
Or by biometric identification
and verification which brings
up a list of cards/accounts to
choose from stored on ‘the
cloud’
Networked*
Paper is dead: all
payments are initiated
electronically
Possible Corporate
Scenario
Networked*
Flexible*
Insightful*
Most are straight-through,
enabled by....
Efficient*
Freeing people to
provide insights and
build relationships
With transparent pricing
17
17
RBS00000
*Source: characteristics of a Bank of the Future
And data is used to improve
tailoring and support
Insightful*
And approval
on the go
...E-invoicing
Flexible*
Innovation Activity
PayAway-IP Direct Mobile App
Intelligent Deposit Safes
• Mobile app for iPhone & iPad
• Service piloted in live customer premises
• View BACS reports and file submissions
‘on the move’
• Proposition under assessment for potential
full delivery
• Secure solution for cash takings
• Mobile app for iPhone and iPad - File
authorisation
• Technology counts cash reducing errors
and saving time
PayAway-IP Direct – new features
• Combats fraud from employees and
counterfeit notes
• Evaluating enhancements based on customer feedback:
• Sage integration (50 and 200)
• Direct Debit Manager
Mini Cash in Transit Pick Up
• Regional customer pilot conducted of Bank Branch alternative
• Proposition under assessment for potential full delivery
• Bank provides small CIT vans collect notes/coin from customer
premises (£3k - £10k)
• Bureau module
Mobile Channel
• Assessing Mobile Channel opportunities
• Potential prototypes being worked on:
• SME E-invoicing prototype on handheld
and iPAD
• Order coin to be delivered with collections
• Business cheques also collected
• Quick apps - “bookshelf” and “expenses”
• Mobile app for iPhone and Blackberry
users linked to Bankline
• Mobile wallets/Payment options
RBS00000
18
Summary
Definition of ‘Innovation’
The act of starting something for the first time
Introducing something new
A new method of doing something
“If at first the idea is not absurd, then there will be no hope for it.” (A. Einstein).
RBS00000
19
No representation, warranty, or assurance of any kind, express or implied, is made as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this document and RBS accepts no obligation to any
recipient to update or correct any information contained herein. The information in this document is published for information purposes only. Views expressed herein are not intended to be and should not
be viewed as advice or as a recommendation. You should take independent advice on issues that are of concern to you. This document does not purport to be all inclusive or constitute any form of
recommendation and is not to be taken as a substitute for the recipient exercising his own judgement and seeking his own advice. This document is for your private information only and does not
constitute an analysis of all potentially material issues nor does it constitute an offer to buy or sell any investment. Prior to entering into any transaction, you should consider the relevance of the
information contained herein to your decision given your own investment objectives, experience, financial and operational resources and any other relevant circumstances. Neither RBS nor other persons
shall be liable for any direct, indirect, special, incidental, consequential, punitive or exemplary damages, including lost profits arising in any way from the information contained in this communication.
The products and services described in this document may be provided by The Royal Bank of Scotland plc, The Royal Bank of Scotland N.V. or both.
The Royal Bank of Scotland plc. Registered in Scotland No. 90312. Registered Office: 36 St Andrew Square, Edinburgh EH2 2YB. The Royal Bank of Scotland plc is authorised and regulated in the
United Kingdom by the Financial Services Authority. The Royal Bank of Scotland N.V. is authorised by De Nederlandsche Bank and regulated by the Autoriteit Financiele Markten (AFM) for the conduct
of business in the Netherlands.
The Royal Bank of Scotland plc is in certain jurisdictions an authorised agent of The Royal Bank of Scotland N.V. and The Royal Bank of Scotland N.V. is in certain jurisdictions an authorised agent of
The Royal Bank of Scotland plc.
Copyright 2012 RBS. All rights reserved. This communication is for the use of intended recipients only and the contents may not be reproduced, redistributed, or copied in whole or in part for any purpose
without RBS’s prior express consent.
RBS00000
20