Energy Management System
advertisement

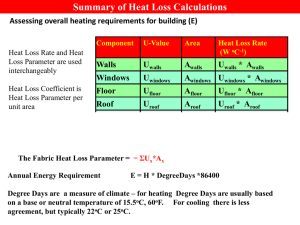
Republic of Serbia Ministry of Energy, Development and Environmentаl Protection LAW ON EFFICIENT USE OF ENERGY Conference on Energy efficiency in Industry Belgrade, 28. may 2013. Energy in Serbia • Energy intensity in Serbia: 2-3 times higher than in the EU • Large dependency on the imported energy: 30% • Large GHG emissions in the energy sector: 76% • The commitment of the Republic of Serbia - Sustainable Development • International obligations - Energy Community: the application of the Directive in the field of energy efficiency - Association to EU: Energy-climate package (20/20/20) - 20% energy savings by 2020. Energy efficiency is an important element of the energy policy of the Republic of Serbia Source: MEDEP-RS Energy Balance in 2011. Primary Energy PE Structure of energy production Primary energy 20011 - Total PE production: 11,163 Mtoe - Total PE consumption: 16,192 Mtoe - Import dependence ~ 30% - Import: NG 24%, Oil 52%, coal 14% 10% Нафта 69% Угаљ 4% Пр.гас 7% Хидро <1%Геотер,ен 9% Биомаса Structure of energy consumption Primary energy 20011 12% 5% <1% <1% Нафта/ Crude oil 6% Нафтни деривати /Oil derivates 7% Гас/ Natural gas Хидропотенцијал/ Hydro 16% Електрична енергија/Electric energy 53% Геотермална енергија/ Geothermal energy Биомаса/ Biomass Угаљ/ Coal Source: MEDEP-RS Energy Balance in 2011. Final Energy FE Share of final energy consumption By sector 1% 13% - Total FE* consumption - 10,042 Mtoe 35% Индустрија/Industry 29% Саобраћај/ Transport Домаћинства/ Households Пољопривреда/ Agriculture Остало/ Other 22% Energy structure in final energy consumption Електрична енергија/Electric energy 26% Биомаса/ Biomass Геотермална енергија/ Geothermal energy Топлотна енергија/Heat energy Гас/ Natural gas * Final energy (or energy used by "end" users) <1% 9% 10% Нафта/ Oil derivates Угаљ/ Coal Source: MEDEP-RS Energy Balance in 2011. 11% 30% 14% Energy Policy and Energy Efficiency • Energy Law: - One of the aims of energy policy, "ensuring the conditions for the improvement of EE in energy activities and energy consumption" • Energy Development Strategy for RS until 2015. year: - The second - directed Priority: rational use of quality fuels and increase EE in production, distribution and end eser`s sector • Strategy Implementation Programme 2006-2012: - Barriers: - unrealistic parity energy prices and their variability - for decades energy was assumed to be a social category Necessary measures: • adoption of legislation on efficient use of energy (EE Law) • establishment of energy management system • funds / institutions for financing EE • subsidies, tax relief for projects in EE • introduction of energy efficiency criteria in public procurement • raising public awareness of the importance of rational use of energy and EE Obligations of RS toward Energy Community (1) Implementation: - Directive 2006/32/EC on Energy Efficiency in Final Energy Consumption and Energy Services - Directive 2010/30/EU on the Labeling of Energy and other Resources for Products that Affect Energy Consumption - Directive 2010/31/EU on the Energy Performance of Buildings Obligations of RS toward Energy Community (2) First National Energy Efficiency Action Plan 2010-2012 - prepared On the basis of the request: • Directive 2006/32/ES European Parliament and of the Council on the energy effecient use of final energy Acording to the recommended model developed by the: •Working Group on Energy Efficiency established in the Energy Community Secretariat - adopted: •29 July 2010. by the Government of the Republic of Serbia -objective: • savings of 1.5% of FE in the period of 2 years, 2010-2012 - (0,1254 Mtoe) (based on FE consumption in 2008) Note: Savings of at least 9% of FE consumption in 9. year of application, 0.7524 Mtoe, (2010 – 2018) Obligations of RS toward Energy Community (3) First National Energy Efficiency Action Plan 2010-2012 - Share of final energy savings by sector till 2012. • Industry (0,057 Mtoe) 44% • Transportation (road and rail) (0,045 Mtoe) 35% • Other (0,026 Mtoe) 21% • Households • Public and commercial activities • Agriculture Second National Energy Efficiency Action Plan • Under preparation • Covers period 2013-2015. Law on Efficient Use of Energy The basic principles: - energy security implementation of EE measures in production, transmission, distribution and energy consumption - competitiveness of products and services reducing the cost of production / service - sustainable use of energy reducing of energy consumption, higher efficiency, eco-design requirements, use of EE technologies, sustainability in terms of environmental impact - energy management system integrated approach to reduce primary energy consumption and environmental impact - cost-effectiveness of energy efficiency measures - minimum energy efficiency requirements for new and reconstructed plants in generation, transmission and distribution of energy Law on Efficient Use of Energy Sectors: - Production, transmission and distribution of energy generation, transmission and distribution of electricity - production and distribution of thermal energy - transportation and distribution of natural gas - - Energy consumption sectors - industry - services sector - public sector - households - transportation - Manufacturers, importers and sellers of products that affect energy consumption - Owners of heating systems and boilers over 20kW - Owners of air conditioning systems over 12kW Law on Efficient Use of Energy Introduced mechanisms: - Energy management system - Energy audits - EE level designation and establishment of minimum requirements for products that significantly affect energy consumption and buildings - eco-design requirements - Minimum EE requirements in generation, transmission and distribution of electricity and thermal energy and natural gas - measurement and consumption based billing - control of boilers, heating and air-conditioning systems - Energy efficiency as a criteria in public procurement - Development of the Energy Efficiency Services Market (ESCO) - Development of Programmes of public transport system enhancement for cities with more than 20,000 inhabitants - Incentives for rational and efficient use of energy - Budgetary Fund for Energy Efficiency Energy Management System Energy Management System introduction is mandatory for: - Companies with the main activities in production sector – industrial plants – if they consume more energy than set as threshold - Companies with the main activities in trade and services sector objects - if they consume more energy than set as threshold bodies - Cities/ Municipalities – number of inhabitants higher then 20 000 - Public buildings and other objects – State Governance Energy consumption Threshold Industry Buildings Number C B A A B C B C C B A Energy Management System will cover about 70% of primary energy consumption A Energy Management System Ministry of Energy, Development and Environmental Protection (MEDEP) Authorized Training Organization Organizing training for: - EM energy managers - Certified energy auditors Dispatching candidates of Energy Manager Periodical Reports Registration AEA Designation Organisation for Training Registration DO, EM • Law and regulations • Policy making • Registration and checking Periodical Reports and making database • Issuing license of Energy Manager and Accredited Energy Auditor • Inspection Info of energy audit Inspection - Random check - Advices - Issuing penalties Inspection of poor energy management Accredited Energy Auditor - external audit Certificate Energy Audit/report Designated Organisation of EMS (industry, buildings, municipalities ...) - appointment of energy managers - collection and analysis of energy consumption data, proposing measures and activities for EE improvement - preparation and submission of plans and programs for efficient use of energy - implementation of the proposed EE measures and activities - preparation and submission of periodic reports Energy manager - implementation of mandatory periodical energy audits Energy Manager EM Energy Manager: person appointed by the DO, which has a license for the performance of EM Duties of EM: - collect and analyze data on energy consumption - prepare plans and programs for EE to MEDEP - propose EE measures - prepare and submit periodical reports to MEDEP Training / Qualification for EM - requirements : - BSc in technical sciences + training for EM + passed exam for EM or - MSc in the field of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering or technology + passed exam for EM License for EM - requirements : - passed exam for EM - 3 years of work experience and - submit application for issuing license to MEDEP Acredited Energy Auditor AEA Acredited Energy Auditor: a person authorized to perform energy audit which has a license Duties of Acredited Energy Auditor: - perform energy audit : - energy balance of the building, production processes and services, - Assess the current level of energy consumption - proposal of EE measures with the evaluation of E, ↓ CO2 and investment cost - prepare and sign a report on conducted energy audit - report to MEDEP on completed energy audit Training / Qualifications - requirements: - passed the exam for EM - minimum of 3 years experience in energy audits / design / technical inspection / field testing - completed training for AEA and - passed the exam for AEA License - Requirements: - Passed the exam for AEA - MSc - master in the field of technical sciences and minimum three years of professional experience and - submit application for issuing license to MEDEP Energy Audit EA Energy audit: a systematic procedure for obtaining necessary data and information on the current status of generation, transmission, distribution and use of energy in building, process, service by which are identified and quantified opportunities for economically viable and efficient use of energy - EA is performed by Acredited Energy Auditor: - Individual - the license - for DO: a legal entity - with at least 2 Acredited Energy Auditor - Who is obliged to perform: - DO - once in 5 years - DO for buildings over 500 m2 - once in 10 years - Buildings / parts of buildings in case of change of use, of owners or if for rent - Those who apply for Budget Fund for EE Products that affect energy consumption Products that affect energy consumption must: - be appropriately labeled with EE designation - have a technical documentation - special requirements when advertising and selling on distance - meet the requirements of Ecodesign EE Designation: - data on the energy consumption - visually indicates the EE class - other important characteristics data Sectors: Generation, transmission and distribution of energy - New and reconstructed plant for generation, transmission and distribution of energy: power, heat and gas - minimum requirements regarding EE - EE study - requirement for construction/energy permit (feasibility study for CHP) -Energy distributors - apply the tariff system: - one of the elements are measured, delivered amount of energy - price of tariff elements - limited by maximum losses - per month, with a bill inform the customer of its energy consumption, the current price of energy, EE measures… - report to Ministry annual statistical data on energy delivered to customers: the dynamics of energy consumption, load profiles ... Heat energy Public and other companies in charge of distribution of heat energy are obliged to: New buildings • Define conditions for the technical documentation preparation which requires installation of the metering equipment of the heating energy supplied for each part of the building representing an independent entity (apartments, commercial units etc.) Existing buildings • Provide offer to install metering equipment on the heating installation in order to measure the delivered heating energy • In the case that other companies installed heating energy metering equipment, to examine the installed equipment and, if the installed equipment provides correct data related to the real heating energy supplied and provides possibility of notifying the time of energy transfer for each part of the building representing an independent entity (apartments, commercial units etc.), to accept the installed equipment. Transportation sector • Cities with more than 20.000 inhabitants are oblige to adopt programs for promotion and improvement of the public transportation systems and report to the Ministry on the realisation • Local self-government units are obliged to provide, where ever it is technically feasible and economically justified, separate lines for the public transportation vehicles • Define and monitor energy consumption in the road transport by Road Safety Agency Control of boilers, heating and ACsystems Control of boilers and heating systems: The owners of the boilers with nominal heating capacity more than 20KW - regular control of combustion process - determination of coeficient of efficiency - undertake measures in order to achieve the nominal values - control of the heating system - when the boiler is an integral part of the heating system - authorized persons Control of the air conditioning system: The owners of the building with AC system nominal cooling capacity more than 12 kW - authorized persons Financing, incentives and other measures Activities financed: - for the implementation of technical measures - to encourage the development of EMS for entities not obliged by Law - to promote and implement energy audits of facilities, production processes and services - to construct a CHP plant, when investor produced thermal energy and power use for its own purposes - to encourage the development of energy services - to encourage use of RES for power and heat production for own use - and others. Budgetary fund Budgetary fund for the improvement of energy efficiency: - managed by Minister - RS Government adoptes annual funding program of activities and measures to improve EE - funds are awarded through open competition and are availableto - legal and - individuals - requirement for investment projects - energy audit or feasibility study on EE - 12 months after the implementation of the project - a review of energy audit Other incentives Tax, customs and other incentives • VAT decreasing for the energy efficient equipment, materials, appliances and technologies • Income tax decreasing for the part of the investment related to the energy efficient equipment, materials, appliances and technologies, as well as energy efficiency projects Public Procurement - take into account the EE of goods and services - endeavor to supply with such products belonging to the highest EE class - The Minister shall prescribe the minimum criteria in terms of EE in the public procurement Energy Services Market Energy Services - service, technology, managing system, appliances or other goods used in any part of the process of energy use, provided in accordance to the contract and which can contribute to the increase of energy efficiency and energy savings ESCOs (Energy Service Companies) - company, or other legal body that undertakes energy services which can contribute to the increasing of the energy efficiency of the objects, technological processes and services, and which accepts financial risk for the undertaken services, since their services are paid, fully or partially, through the savings, arising from the implemented measures Inspection Inspection of the provisions of the Law are related to: - energy management system, - performance of energy audits, - energy efficiency labeling - and complying with the minimum requirements of EE Inspection is performed by: - MEDEP through: - electrical inspector - inspector of boilers - Market inspectors Thank you for your attention! Republic of Serbia Ministry of Energy, Development and Environmental Protection www.merz.gov.rs