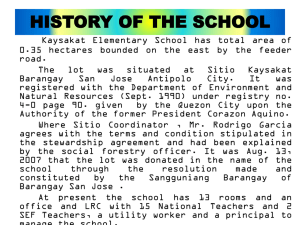
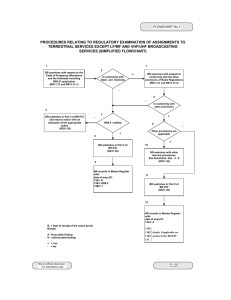
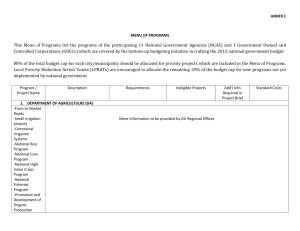
2.3_Project Management Structures

Module II : The NCDDP Context
SESSION 2.3:
KC-NCDDP Structures and
Core Functions of Key Players
Content
1. KC- NCDDP institutional arrangements a. National Program Management
Organization (NPMO) b. Regional Program Management
Organization (RPMO) c. Sub-Regional Program Management
Team (SRPMT) d. LGU participation e. Inter-Agency Committees
Content
2. The Area Coordinating Team (ACT)
composition and functions
core competencies of effective ACTs
competency in mainstreaming gender, IPs, environmental safeguards and peacebuilding
3. Staff Deployment
4. Importance of Teams and Teamwork
Key Message 1
KC-NCDDP is the flagship program of DSWD in response to the GOP
Social Reform Agenda.
Key Message 2
DSWD: lead implementing agency for the KC-NCCDP program
• needs to increase its capacity to deliver the program to a wider, expanded number of target municipalities and barangays; while remaining faithful to the principles of transparency and accountability.
Key Messages 3 and 4
• Competent, dedicated and committed
ACTs determine the effective implementation and facilitation for the achievement of the KC-NCDD Program goals.
• Teamwork between and among the multi-disciplinary members of the ACT and interagency partners is critical to the successful delivery of the program expectations.
• SRPMT strategy aims to manage the large geographic scope of KC-NCDDP and rationalize engagement with provincial government and sector agencies.
• One SRPMT per province is expected to manage 20 municipalities. Provinces with less than 20 participating municipalities will be served by adjacent SRPMT or RPMO.
• RPMO can establish SRPMT for isolated provinces with distinct challenges provided funds are available.
KC-NCDDP Structures
Level
National
Policy-Making and
Coordination with
External Stakeholders
Policy directions of
KC-NCDDP provided by the National Steering
Committee (NSC) supported by National
Technical Working
Group (NTWG)
Program Management and
Internal Coordination
The KC-NCDDP will be managed by DSWD’s National Project
Management Office (NPMO) based at DSWD Central Office and headed by the National
Program Manager who takes care of day-to-day operations. Two reporting to the
Human Development and Poverty Reduction Division (OpD) and b) the
Cabinet cluster Technical Support Services
(HDPRC)
Deputy National Program
Managers: a) the Operations
Division (TSSD) organized for
Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao to supervise sub-projects folded into the KC-CDDP.
KC-NCDDP Structures continuation
Level Policy-Making and
Coordination with External
Stakeholders
Regional Regional Social
Development Committee and Local Poverty Reduction
Action Teams
Regional Interagency
Committee (RIAC)
Chaired by the Reg’l.
Director
Program Management and Internal
Coordination
Regional Program Management Office
(RPMO) based at DSWD Field Offices headed
by the DSWD Regional Director concurrently also KC-NCDDP Regional Program Director.
The RPMO supervises the Area Coordinating
Teams (ACTs). A Regional Program
Coordinator is responsible for operations
mgt including special complementary projects. A Deputy Regional Program
Manager supervises a technical support
team of specialists and technical staff.
Sub-Regional Program Management Team
(SRPPMT) may be organized as extension of
the RPMO to manage the huge scope of the
KC-NCDDP and to rationalize engagement with the provincial governments and local
offices of national sector agencies.
KC-NCDDP Structures continuation
Provincial Provincial Social Development
Committees and Local Poverty
Reduction Action Teams,
Provincial Interagency
Committee (PIAC)
Chaired by the Provincial
Governor
Municipal Expanded Municipal
Development Council in KC-
NCDDP participating barangays
Barangay Barangay Interagency Committee
(BIAC) chaired by the Barangay
Captain through the Barangay
Assembly
Area Coordinating Team
(ACT)
Source: Revised Script KC-NCDDP
PowerPoint Presentation Version
2June 2014
Expected support from LGU’s
1.
Provide technical assistance to barangays;
2.
Provide counterpart funding in all project components;
3.
Provide personnel (full time or part time).
Office space, equipment and other support mechanisms if available;
4.
Participate in capacity-building interventions to institutionalize CDD processes into LGU planning, implementation and evaluation;
5.
Monitor and evaluate the overall performance of the project; and
6.
Convene inter-agency committee meetings in municipal and barangay levels.
HUMAN TOWER
Session2.4. Composition and Core
Functions of the Area Coordinating Team
(ACT)
The ACT is composed of the following:
• Area Coordinator
• Technical Facilitator
(Engineer)
• Mun. Finance
Analyst
• Community
Empowerment
Facilitators
Core Function and Responsibilities of ACT
Area Coordinator – supervises ACT members; establishes and nurtures partnerships /linkages with project stakeholders to include LGU’s, NGO’s/PO’s,
CSO’s and other agencies.
Deputy Area Coordinator/Technical
Facilitator – who is an engineer, assumes supervisory function in the absence of the
AC. Responsible for providing technical assistance together with the municipal engineer to community volunteers.
Core Function and Responsibilities of ACTs
Community Empowerment Facilitator (CEF) implements the Community Empowerment Activity
Cycles (CEAC) at the barangay level. The CEF ensures that:
barangay and community-level development processes and activities are facilitated efficiently, with the direct participation, inclusion, and engagement of all stakeholders
opportunities are provided, processes are designed, and mechanisms are established at the barangay level that would allow all sectors, especially the most marginalized groups, to engage in and benefit from project activities.
Core Function and Responsibilities of ACTs continuation
Municipal Financial Analyst (MFA) – primarily responsible in:
(a) training community volunteers on financial management and fiduciary processes;
(b) assisting and providing technical assistance to community volunteers in setting-up systems and processes for community-based finance management and fiduciary control, and
(c) exercising QA and QC directly, over financial transactions relative to the request for, release, and accounting of community grants.
What we manage?
What the ACT manage?
Key Questions Tools
Time/Schedule • Are we on schedule/on-time?
• Work/Activity Plan
• CEAC accomplishment
• Work & Financial Plan
• Physical Accomplishment
Cost
Performance
• Are we on budget?
• Is the project implementation cost efficient?
• Is the implementation transparent/ free of corruption
• Have we conducted our activities?
• Have we achieved our purpose/outputs
• Have we achieved our goal
• Financial Reports
• Procurement
• LCC and VLCC reports
• Fiduciary reviews
• Accomplishment report
• Quality assurance and quality control checklist
• Minutes of meetings
• Community reporting satisfaction
• Regular assessment/reflection sessions
What we manage?
What the ACT manage?
Key Questions Tools
Time/Schedule • Are we on schedule/on-time?
• Work/Activity Plan
• CEAC accomplishment
• Work & Financial Plan
• Physical Accomplishment
Cost
Performance
• Are we on budget?
• Is the project implementation cost efficient?
• Is the implementation transparent/ free of corruption
• Have we conducted our activities?
• Have we achieved our purpose/outputs
• Have we achieved our goal
• Financial Reports
• Procurement
• LCC and VLCC reports
• Fiduciary reviews
• Accomplishment report
• Quality assurance and quality control checklist
• Minutes of meetings
• Community reporting satisfaction
• Regular assessment/reflection sessions
Essentials for ACT to adhere…
• The ACT members must have a shared goals
• The ACT must be interdependent
• The ACT members must be committed to the idea that working together leads to more effective decisions than working in isolation;
• The ACT must be accountable
Processes
• Strategic meetings
• Tactic session
• Reflection session
• MIAC-MAC meetings
• PIAC meetings
• RPMT meetings