AGU2014-ED31E-3455_Fox - Tetherless World Constellation
advertisement
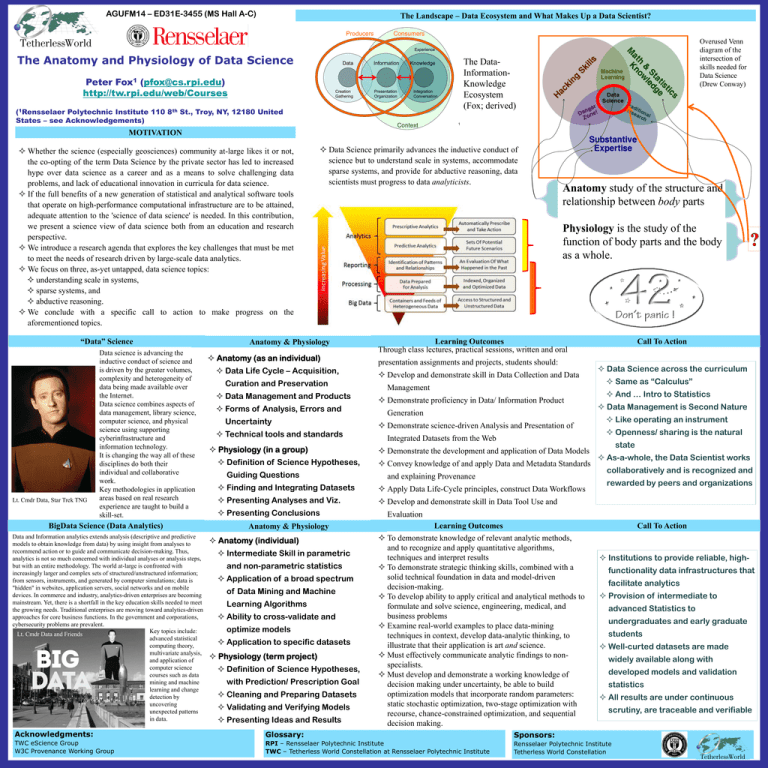
AGUFM14 – ED31E-3455 (MS Hall A-C) The Landscape – Data Ecosystem and What Makes Up a Data Scientist? Producers Consumers Overused Venn diagram of the intersection of skills needed for Data Science (Drew Conway) Experience The Anatomy and Physiology of Data Science Data Peter Fox1 (pfox@cs.rpi.edu) http://tw.rpi.edu/web/Courses Creation Gathering (1Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute 110 8th St., Troy, NY, 12180 United States – see Acknowledgements) “Data” Science Lt. Cmdr Data, Star Trek TNG Data science is advancing the inductive conduct of science and is driven by the greater volumes, complexity and heterogeneity of data being made available over the Internet. Data science combines aspects of data management, library science, computer science, and physical science using supporting cyberinfrastructure and information technology. It is changing the way all of these disciplines do both their individual and collaborative work. Key methodologies in application areas based on real research experience are taught to build a skill-set. BigData Science (Data Analytics) Data and Information analytics extends analysis (descriptive and predictive models to obtain knowledge from data) by using insight from analyses to recommend action or to guide and communicate decision-making. Thus, analytics is not so much concerned with individual analyses or analysis steps, but with an entire methodology. The world at-large is confronted with increasingly larger and complex sets of structured/unstructured information; from sensors, instruments, and generated by computer simulations; data is "hidden" in websites, application servers, social networks and on mobile devices. In commerce and industry, analytics-driven enterprises are becoming mainstream. Yet, there is a shortfall in the key education skills needed to meet the growing needs. Traditional enterprises are moving toward analytics-driven approaches for core business functions. In the government and corporations, cybersecurity problems are prevalent. Key topics include: Lt. Cmdr Data and Friends advanced statistical computing theory, multivariate analysis, and application of computer science courses such as data mining and machine learning and change detection by uncovering unexpected patterns in data. Presentation Organization The DataInformationKnowledge Ecosystem (Fox; derived) Knowledge Integration Conversation Context MOTIVATION Whether the science (especially geosciences) community at-large likes it or not, the co-opting of the term Data Science by the private sector has led to increased hype over data science as a career and as a means to solve challenging data problems, and lack of educational innovation in curricula for data science. If the full benefits of a new generation of statistical and analytical software tools that operate on high-performance computational infrastructure are to be attained, adequate attention to the 'science of data science' is needed. In this contribution, we present a science view of data science both from an education and research perspective. We introduce a research agenda that explores the key challenges that must be met to meet the needs of research driven by large-scale data analytics. We focus on three, as-yet untapped, data science topics: understanding scale in systems, sparse systems, and abductive reasoning. We conclude with a specific call to action to make progress on the aforementioned topics. Information 1 Data Science primarily advances the inductive conduct of science but to understand scale in systems, accommodate sparse systems, and provide for abductive reasoning, data scientists must progress to data analyticists. Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy (as an individual) Data Life Cycle – Acquisition, Curation and Preservation Data Management and Products Forms of Analysis, Errors and Uncertainty Technical tools and standards Physiology (in a group) Definition of Science Hypotheses, Guiding Questions Anatomy study of the structure and relationship between body parts Physiology is the study of the function of body parts and the body as a whole. Learning Outcomes Through class lectures, practical sessions, written and oral presentation assignments and projects, students should: Develop and demonstrate skill in Data Collection and Data Management Demonstrate proficiency in Data/ Information Product Generation Demonstrate science-driven Analysis and Presentation of Integrated Datasets from the Web Demonstrate the development and application of Data Models Convey knowledge of and apply Data and Metadata Standards and explaining Provenance Finding and Integrating Datasets Apply Data Life-Cycle principles, construct Data Workflows Presenting Analyses and Viz. Develop and demonstrate skill in Data Tool Use and Presenting Conclusions Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy (individual) Intermediate Skill in parametric and non-parametric statistics Application of a broad spectrum of Data Mining and Machine Learning Algorithms Ability to cross-validate and optimize models Application to specific datasets Physiology (term project) Definition of Science Hypotheses, with Prediction/ Prescription Goal Cleaning and Preparing Datasets Validating and Verifying Models Presenting Ideas and Results Call To Action Data Science across the curriculum Same as “Calculus” And … Intro to Statistics Data Management is Second Nature Like operating an instrument Openness/ sharing is the natural state As-a-whole, the Data Scientist works collaboratively and is recognized and rewarded by peers and organizations Evaluation Learning Outcomes To demonstrate knowledge of relevant analytic methods, and to recognize and apply quantitative algorithms, techniques and interpret results To demonstrate strategic thinking skills, combined with a solid technical foundation in data and model-driven decision-making. To develop ability to apply critical and analytical methods to formulate and solve science, engineering, medical, and business problems Examine real-world examples to place data-mining techniques in context, develop data-analytic thinking, to illustrate that their application is art and science. Must effectively communicate analytic findings to nonspecialists. Must develop and demonstrate a working knowledge of decision making under uncertainty, be able to build optimization models that incorporate random parameters: static stochastic optimization, two-stage optimization with recourse, chance-constrained optimization, and sequential decision making. Call To Action Institutions to provide reliable, highfunctionality data infrastructures that facilitate analytics Provision of intermediate to advanced Statistics to undergraduates and early graduate students Well-curted datasets are made widely available along with developed models and validation statistics All results are under continuous scrutiny, are traceable and verifiable Acknowledgments: Glossary: Sponsors: TWC eScience Group W3C Provenance Working Group RPI – Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute TWC – Tetherless World Constellation at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Tetherless World Constellation