Sentence Patterns: English Grammar Presentation
advertisement

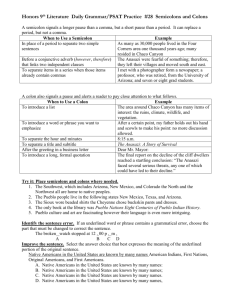
SENTENCE PATTERNS M S . P E N N E L L B H S 2 0 1 3 WHAT ARE SENTENCE PATTERNS? • In the Gwinnett County Public School System, sentence patterns keep track of the sentence parts in any given sentence. The easiest way for a student to remember sentence parts is to look at the second day’s work in his or her Daily Grammar Practice (DGP) exercises. • DGP gives the following sentence parts as examples for students: • Subject, verb (transitive or intransitive), direct object, indirect object, predicate nominative, predicate adjective, appositive or appositive phrase, prepositional phrase (adjective or adverb), gerund phrase, infinitive phrase, participial phrase, object of preposition, object of infinitive, object of gerund, or object of participle. • • • • • • • • • STUDENTS NEED TO MEMORIZE THE DGP ABBREVIATIONS, PARTICULARLY THE ABBREVIATIONS FOR SENTENCE PARTS … Subject S Verb (transitive) VT Verb (intransitive) VI Direct Object DO Indirect Object IO Predicate Nominative PN Predicate Adjective PA Appositive App Appositive Phrase App Ph Prepositional Phrase (adjective) Adj Prep Ph Prepositional Phrase (adverb) Adv Prep Ph Gerund Phrase Ger Ph Infinitive Phrase Inf Ph Participial Phrase Part Ph Object of Preposition OP Object of Infinitive Obj Inf Object of Gerund Obj Ger Object of Participle. Obj Part STUDENTS ALSO NEED TO BE AWARE OF THE FOUR BASIC SENTENCE STRUCTURES PRESENT IN THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE Simple (SS): 1 independent clause and no dependent clause Compound (CD): 2 independent clauses and no dependent clauses Complex (CX): 1 independent clause and 1 or more dependent clauses Compound-Complex (CD-CX): 2 independent clauses and 1 or more dependent clauses Examples: • • • • Simple: I like going to school. Compound: I like going to school, and I like doing my homework. Complex: I like going to school when it is sunny. Compound-complex: I like going to school, and I like doing my homework when it is sunny. LET’S TAKE A LOOK AT IDENTIFYING SOME SENTENCE PARTS … • Sentence 1: • Their team will practice after school. • Sentence Pattern: • Their team will practice after school. • Sentence Type: • Sentence 2: • Each of the girls did her homework. • Sentence Pattern: • Each of the girls did her homework. • Sentence Type: LET’S TAKE A LOOK AT IDENTIFYING SOME SENTENCE PARTS … • Sentence 3: • My friend Alex plays tennis. • Sentence Pattern: • My friend Alex plays tennis. • Sentence Type: • Sentence 4: • Your friend from Switzerland is a good student. • Sentence Pattern: • Your friend from Switzerland is a good student. • Sentence Type: LET’S TAKE A LOOK AT IDENTIFYING SOME SENTENCE PARTS … Sentence 5: Jeb likes cars, but he can’t drive yet. Sentence Pattern: Jeb likes cars, but he can’t drive yet. Sentence Type: Sentence 6: Sara read the novel To Kill a Mockingbird in her English class. Sentence Pattern: Sara read the novel To Kill a Mockingbird in her English class. Sentence Type: LET’S TAKE A LOOK AT IDENTIFYING SOME SENTENCE PARTS … • Sentence 7: Can you come over and watch the movie Casablanca after school? • Sentence Pattern: Can you come over and watch the movie Casablanca after school? • Sentence Type: • Sentence 8: • The Spanish Club traveled to Madrid, Spain, during the summer. • Sentence Pattern: • The Spanish Club traveled to Madrid, Spain, during the summer. • Sentence Type: