phrase rules - Madison County Schools
advertisement

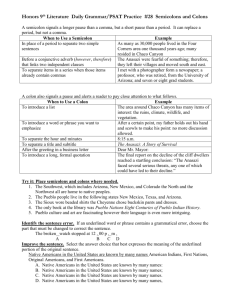
CHAPTER 14 PHRASE RULES 14a. A phrase is a group of related words that is used as a single part of speech and that does not contain both a verb and its subject. 14b. A prepositional phrase includes a preposition, the object of the preposition, and any modifiers of that object. 14c. The noun or pronoun in a prepositional phrase is called the object of the preposition. 14d. A prepositional phrase that modifies a noun or pronoun is called an adjective phrase. 14e. A prepositional phrase that modifies a verb, an adjective, or an adverb is called an adverb phrase. 14f. A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective. **Present participles end in –ing. **Past participles usually end in –d or –ed. Other past participles are formed irregularly. 14g. A participial phrase is used as an adjective and consists of a participle and any complements or modifiers the participle has. 14h. A gerund is a verb form ending in –ing that is used as a noun. 14i. A gerund phrase consists of a gerund and any modifiers or complements the gerund has. The entire phrase is used as a noun. 14j. An infinitive is a verb form that can be used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. Most infinitives begin with to. 14k. An infinitive phrase consists of an infinitive and any modifiers or complements the infinitive has. The entire phrase can be used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. 14l. An appositive is a noun or a pronoun placed beside another noun or pronoun to identify or describe it. 14m. An appositive phrase consists of an appositive and any modifiers it has.