
Strategic Marketing
1. Imperatives for Market-Driven Strategy
2. Markets and Competitive Space
3. Strategic Market Segmentation
4. Strategic Customer Relationship Management
5. Capabilities for Learning about Customers and Markets
6. Market Targeting and Strategic Positioning
7. Strategic Relationships
8. Innovation and New Product Strategy
9. Strategic Brand Management
10. Value Chain Strategy
11. Pricing Strategy
12. Promotion, Advertising and Sales Promotion
Strategies
13. Sales Force, Internet, and Direct Marketing Strategies
14. Designing Market-Driven Organizations
15. Marketing Strategy Implementation And Control
Chapter 10
Value Chain
Strategy
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2009 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Value Chain Strategy
*
*
*
*
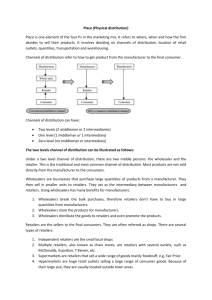
Strategic role of value chain
Channel strategy
Managing the channel
International channels
10-3
Dell’s dilemma
* Business built around powerful direct
business model
* Direct model poor fit with customer
preferences in new target markets and weak
on service
* Dell is braodening business model
* Targeting computer re-sellers
* Global retail strategy (including Wal-Mart, Dellbranded stores, kiosks in malls)
* Redesigning value chain is critical strategic
move
10-4
Strategic role of value chain (1)
Distribution functions
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Buying and selling
Assembly
Transportation
Financing
Processing and storage
Advertising and sales promotion
Pricing
Reduction of risk
Personal selling
Communications
Servicing and repairs
10-5
Value chain structures - consumer products
Consumer Products
Producers
Supply Chains
Sales
Agents
Direct
Channel
Retailers
Wholesalers
Wholesalers
Retailers
Retailers
Consumers
10-6
Value chain structures - organizational products
Organizational Products
Producers
Supply Chains
Sales
Agents
Direct
Channel
Distributors
Distributors
Sales
Agents
Distributors
Re-sellers
Organizational Customers
10-7
Strategic role of value chain (2)
* Channels for services
* Direct distribution by manufacturers
*
*
*
*
Buyer considerations
Competitive considerations
Product characteristics
Financial and control considerations
10-8
Factors Favoring Distribution by Manufacturer
Profit margins
adequate to support
distribution
organization
Complete line
of products
Opportunity for
competitive
advantage
Distribution
by the
manufacturer
Purchases are
large and
infrequent
Small number of
geographically
concentrated
buyers
Rapidly changing
market environment
Early stages of
product life cycle
Complex product
application
Supporting
services are
required
Extensive
purchasing
process
10-9
Branded manufacturers enter retail
* Nespresso (Nestle) “coffee boutiques” to
establish lifestyle brand
* Heineken branded beer bars in airports and
retail
* Strategic logic is to avoid control of thirdparty retailers over brand
* Move from selling “A product in a box” to
offering a superior service experience for
the brand
10-10
Channel strategy (1)
* Types of channel
* Conventional channel
* Vertical marketing systems
* Ownership VMS
* Contractual VMS
* Administered VMS
* Relationship VMS
* Horizontal marketing systems
* Digital channels
* Product digitization
* Channel digitization
10-11
Channel strategy selection
1. Type of distribution channel
Conventional
Horizontal
marketing system
Vertical marketing system
Ownership
Contractual
Administered/
Relationship
2. Intensity of distribution
Intensive
Selective
Exclusive
3. Channel configuration
10-12
Channel strategy (2)
* Distribution intensity
* Intensive
* Exclusive
* Selective
* Channel configuration
* End-user considerations
* Product characteristics
* Manufacturer's capabilities and resources
* Required functions
* Availability and skills of intermediaries
10-13
Channel strategy (3)
* Channel maps
* Selecting the channel strategy
*
*
*
*
*
Market access
Value-added competencies
Financial considerations
Flexibility and control considerations
Channel strategy evaluation
10-14
Illustrative channel map for heating units
Production =
100,000 units
Consumption =
100,000 units
Direct sales = 10,000 units
84,000 units
Independent
Distributors
Construction
SubContractors
42,000 units
42,000 units
Production
Of Central
Heating
Boilers
Small
Hardware
Retailers
5,000 units
Direct sales = 1,000 units
Large
Hardware
Retailers
40,000
units
75,000 units
Commercial
Construction
Companies
(85,000 units)
7,000
units
2,000
units
5,000 units
Domestic
Customers
(15,000 units)
10-15
Channel strategy (4)
* Changing channel strategy
* Channel strategy modification
* Channel migration
* Channel audit
10-16
Illustrative Channel Strategy Evaluation
Evaluation
Criteria
Manufacturer’s
Representatives
Company
Salesforce
Market access
Rapid
1 to 3 year
development
Value-added competencies
Medium
Sales forecast (2 years)
$20 million
$30 million
Forecast accuracy
High
Medium to low
Estimated costs
$2 million*
$3.6 million**
Selling Expense (cost/sales)
10%
12%
Flexibility
Good
Limited
Control
Limited
Good
*
High
Includes 8% commission plus management time for recruiting and training
representatives.
** Includes $150,000 for 10 salespeople, plus management time.
10-17
Managing the Channel (1)
* Channel leadership
* Management structure and systems
* Physical distribution management
* Supply chain strategy
* The impact of supply chain management
on marketing
* E-procurement
10-18
Efficient Consumer Response
Traditional channel problems
* Forward buying and diverting
* Excessive inventories
* Damages and unsaleable goods
* Complex deals and deductions
* Too many promotions and coupons
* Too many new products
Efficient Consumer Response
* Category management
* “Value” pricing replaces promotions
* Continuous replenishment and cross-docking
* Electronic data interchange
* New performance measures
* New organizational processes and structures
* Internet-based network for supplier-buyer trading
10-19
Lean Supply Chain Elements
1. Definition of Value
2. Identification of Value Streams and
Removal of Muda (Waste)
3. Organizing Around Flow, Instead
of “Batch and Queue”
4. Responding to Pull Through
the Supply Chain
5. The Pursuit of Perfection
10-20
Marketing/supply chain relationship
* Focus on real drivers of customer
value not just technical
* Do not create inflexibility and inability
to respond to change
* Protect brands and competitive
strength over short-term cost savings
* Do not confuse supply chain strategy
with competitive advantage
10-21
Managing the channel (2)
* Channel relationships
* Degree of collaboration
* Commitment and trust among channel members
* Power and dependence
* Channel globalization
* Multichanneling
* Conflict resolution
* Channel performance
* Legal and ethical considerations
10-22
Channel metrics
Performance
Objective
Possible Measures
Applicable Product and
Channel Level
PRODUCT AVAILABILITY
Coverage of relevant
retailers
Percent of effective
distribution
Consumer products at
retail level
In-store positioning
Percent of shelf
facings or display
space gained
by product,
weighted by store
importance
Consumer products at
retail level
Coverage of
geographic markets
Frequency of sales
calls by customer
type; average
delivery time
Industrial products;
consumer goods at
wholesale level
10-23
Channel metrics
Performance
Objective
Possible Measures
Applicable Product and
Channel Level
PROMOTIONAL EFFORT
Effective point-ofpurchase (POP)
promotion
Percent of stores
Consumer products
using special
at retail level
displays and POP
materials, weighted
by importance of store
Effective personal
selling support
Percent of
Industrial products;
salespeople’s time
consumer durables at all
devoted to product;
channel levels; consumer
number of salespeople convenience goods at
receiving training on wholesale level
product’s characteristics
and applications
10-24
Channel metrics
Performance
Objective
Possible Measures
Applicable Product and
Channel Level
CUSTOMER SERVICE
Installation,
training and
repair
Number of service
technicians receiving
technical training;
monitoring of
customer complaints
Industrial products,
particularly those involving
high technology; consumer
durables at retail level
MARKET INFORM,ATION
Monitoring sales
trends, inventory
levels, competitors’
actions
Quality and
timeliness of
information
obtained
All levels of
distribution
COST-EFFECTIVENESS
Cost of channel
Functions relative
To sales volume
Middleman margins
and marketing costs
as percent of sales
All levels of
distrbution
10-25
Value chain ethics
* Retailers’ Global Social Compliance
Program
* Growing “green consumer” pressure
* B2B suppliers increasingly mandated
to meet customer’s values in
employment practices, environmental
standards, ethical behavior
10-26
International channels
* Examining international distribution
patterns
* Factors affecting global channel
selection
* Global issues regarding multichannel
strategies
10-27
International Channel of Distribution Alternatives
Home country
Foreign country
The foreign marketer or
producer sells to or through
Domestic
producer or
marketer sells
to or through
Open
distribution
via domestic
wholesale
middlemen
Exporter
Importer
Foreign
agent or
merchant
wholesalers
Foreign
retailer
Foreign
consumer
Export management company
or company
sales force
Source: Philip R. Cateora, International Marketing, 7th ed., Homewood, Ill.: Richard D. Irwin, Inc., 1990, 572.
10-28








![[DATE] Mary Ziegler Director Division of Regulations, Legislation](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007212021_1-b96b03cd98cadfc74a22865c0247494d-300x300.png)

