3.6 Place (Distribution) - notes - business-and-management-aiss
advertisement
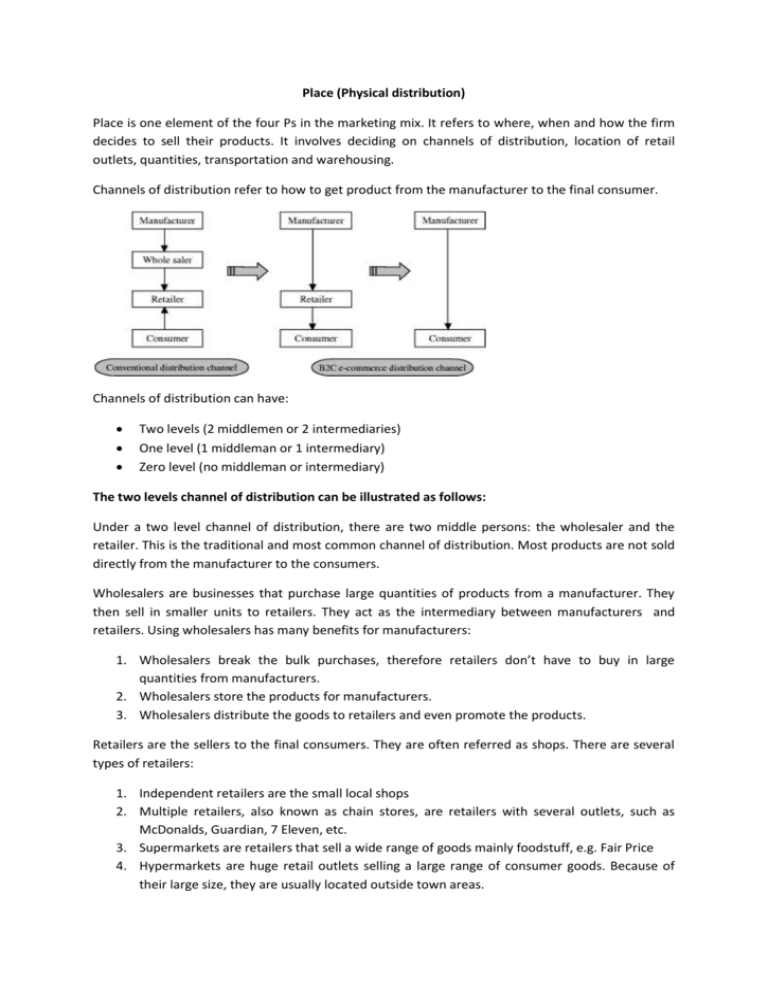
Place (Physical distribution) Place is one element of the four Ps in the marketing mix. It refers to where, when and how the firm decides to sell their products. It involves deciding on channels of distribution, location of retail outlets, quantities, transportation and warehousing. Channels of distribution refer to how to get product from the manufacturer to the final consumer. Channels of distribution can have: Two levels (2 middlemen or 2 intermediaries) One level (1 middleman or 1 intermediary) Zero level (no middleman or intermediary) The two levels channel of distribution can be illustrated as follows: Under a two level channel of distribution, there are two middle persons: the wholesaler and the retailer. This is the traditional and most common channel of distribution. Most products are not sold directly from the manufacturer to the consumers. Wholesalers are businesses that purchase large quantities of products from a manufacturer. They then sell in smaller units to retailers. They act as the intermediary between manufacturers and retailers. Using wholesalers has many benefits for manufacturers: 1. Wholesalers break the bulk purchases, therefore retailers don’t have to buy in large quantities from manufacturers. 2. Wholesalers store the products for manufacturers. 3. Wholesalers distribute the goods to retailers and even promote the products. Retailers are the sellers to the final consumers. They are often referred as shops. There are several types of retailers: 1. Independent retailers are the small local shops 2. Multiple retailers, also known as chain stores, are retailers with several outlets, such as McDonalds, Guardian, 7 Eleven, etc. 3. Supermarkets are retailers that sell a wide range of goods mainly foodstuff, e.g. Fair Price 4. Hypermarkets are huge retail outlets selling a large range of consumer goods. Because of their large size, they are usually located outside town areas. One level chain of distribution (manufacturers to distributors/agents to consumers) Distributors Distributors are independent specialist businesses that trade in the products of only a few manufacturers. E.g. car distributors, mobile phone distributors. Some distributors sell the product of only one manufacturer. E.g. Honda distributor or Dell distributor. Agents Agents are negotiators who act between sellers and buyers. E.g. estate agent, insurance agents. They are experts in their markets and charge a commission for their services. The commission is a percentage of the sales made. Zero Level channel of distribution (Manufacturers to Consumers)- direct marketing Here the producer sells directly to the consumer. Example: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. In the hotel industry, customers can book their own accommodations directly from the hotel In restaurants, services are provided directly to the customers. In E-commerce, goods are distributed directly from the business to the customers. Professionals such as doctors and lawyers sell their services directly to the customers. Telesales or telemarketing involves the use of telephone system to sell the products. Direct mail involves sending promotional materials to make customers to buy their products. Vending machine are specialist machines that stock and sell products such as cigarettes, drinks and snacks Nov 07 S1 3a: Identify the two main channels of distribution used by Gladrags Ltd.











