Chapter 1 Powerpoint

Introduction to
Environmental Science
What is environmental science?
• The study of how humans and other species interact with one another and the nonliving environment.
• How the parts of nature and human societies operate and interact - a study of connections and interactions
• A physical and social science that integrates information from a wide range of disciplines:
– biology
– chemistry
– physics
– geology
– geography
– resource technology and engineering
– resource conservation and management
– demography, economics, politics, sociology, psychology and ethics
Current Environmental Problems
1. Population growth
2. Deforestation
3. Global warming
4. Ozone loss
5. Resource depletion:
– mineral
– energy
– soil
– agricultural land
– water
6. Biodiversity
7. Pollution
Sustainability
• Sustainability is the ability to maintain a given state for a specified period of time
• sustainable systems function and survive over a specified time
• environmentally sustainable societies manage their economies, population and resource use within the system's (earth's) ability to absorb insults, replenish resources, and sustain life forms
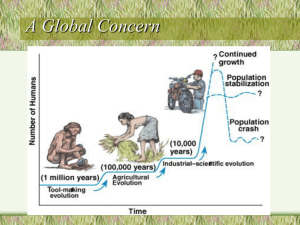
2-5 million years
8000
Hunting and gathering
Black Death –the Plague
?
?
?
1
2000 2100
0
3
2
5
4
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
6000 4000
Time
2000
Agricultural revolution
B.C.
A.D.
Industrial revolution
• Current growth rate: exponential growth at a rate of 1.25%
• Rule of 70:
70/ rate of growth =doubling time
?
Continued growth
Population stabilization
?
(1 million years)
(100,000 years)
Population crash
?
(10,000 years)
Industrial & information revolutions
Agricultural revolution
Tool-making revolution
Time
Who can explain the difference between exponential and linear growth?
Exponential: a quantity increases at a constant rate per unit of time
(such as our current rate of 1.25% per year)
Linear : growth by the same amount over equal time periods
World Population reached
1 billion in 1804
2 billion in 1927 (123 years later)
3 billion in 1960 (33 years later)
4 billion in 1974 (14 years later)
5 billion in 1987 (13 years later)
6 billion in 1999 (12 years later)
World Population May Reach
7 billion in 2013 (14 years later)
8 billion in 2028 (15 years later)
9 billion in 2054 (26 years later)
Tropic of
Cancer
Equator
Tropic of
Capricorn
Antarctic
Circle
Human disturbance
Predominantly natural
Partially disturbed
Human dominated
Economic Growth
Increase capacity to produce goods and services for people's final use
Usually involves increasing flow (throughput) of energy and natural resources
Measured
• GNP: gross national product - market value of all goods and services for either domestic or export produced in that year
• per capita GNP (pcGNP) - divide GNP by total population of the country
Economic Development
• The improvement of living standards by economic growth
Developing / Developed Countries
• Developed countries: defined as highly industrialized with pcGNP > $10,00
– 20% of the world's population
– 85% of wealth and income
– use 88% of natural resources
– generate 75% of the world's waste
• Developing countries: rural, agricultural countries with low pcGNP
– more than 1 billion people try to live on less than
$1 day
– more children increases family's "workforce"
– local populations outstrip available resources
GNP per capita, 1998
Low income
(Under $1,000)
Middle income
($1,000 –$10,000)
High income
(Above $10,000)
12
11
10
9
6
5
8
7
4
3
2
1
1950
World total
Developing countries
2000
Year
2050
Developed countries
2100
• Perpetual resources: on a human time scale, is renewed continuously
* solar energy, winds, tides, flowing water
Renewable resources: On a human time scale, can be replenished fairly rapidly
*fresh air, water, soil, plants & animals
• Nonrenewable resources: on a human time scale, is not replaced; present in a fixed quantity in earth’s crust
*coal, oil, natural gas, metals such as iron & copper, minerals such as phosphates & clay
Environmental Worldview
Planetary management
*humans are the most important species
*resources will not run out b/c we can develop & find new ones
*potential for economic growth is unlimited
*success depends on our management
Stewardship
*we are the most important species, but that carries an ethical responsibility
*resources probably won’t run out, but should be used wisely
*environmentally beneficial forms of development should be encouraged
*our success depends on how well we manage our resources
Environmental wisdom
*nature exists for all species
*earth’s resources are limited, should not be wasted, and are not all ours
*earth-sustaining forms of economic growth should be encouraged
*our success depends on our actins & behaving in a sustainable manner
1. Is current society in developed countries sustainable? Developing countries?
2. Is sustainability a reasonable or desirable goal?
Social Economic
Environmental
Traditional decision making
Social
Sustainable
Solutions
Economic
Environmental
Decision making in a sustainable society