Chapter 2_Revolution,etc notes&Econ
advertisement

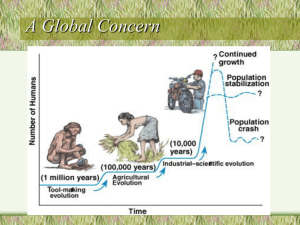
Easter Island & Cultural Revolutions & Economics Unit 1 (Chapter 1 and 2) Summary of Easter Island Polynesians arrived around 1200 AD. There was abundant forest and wide variety of trees. Population grew and trees were cut for agriculture and structural materials and to move the huge stone heads By 1600, all the trees were gone no roots, the land failed to hold water, and the soil washed into the sea. The work became harder and the rewards fewer The gap between the haves (religious ruling class) and the have nots (secular warriors) widened. Social injustice Revolt of workers Majority of ruling class was killed Anarchy broke out among workers – fought among themselves Starvation and disease became epidemic 10,000-20,000 down to 3,000 Three Major Cultural Revolutions resulting in increased impact of humans on the environment 1) Agricultural Revolution (The Neolithic Revolution) Agriculture in this era was subsistence agriculture, which means people were farming for their own diet (not for sale/profit) and the farmers practiced crop rotation (letting the fields lay in fallow between planting seasons). Without agriculture, the emergence of many of the traits popularly referred to as “civilization" would not have been possible (e.g. cities, advanced technology, social hierarchies, organized warfare.) 2) Industrial-Medical Revolution Began in England in the mid-1700's with the development of the steam engine Began in the US in the 1800's It involved a shift from… - 3 main component of the I.R. o – o o – The new “urbanites” came looking for jobs in factories and a better way of life. This created enormous new markets for agricultural products Big determinant in which areas of the world became commercial agricultural economies. – 3) Information and Globalization Revolution Began in the mid-20th Century - GENERALLY SPEAKING, cultural revolutions are characterized by improved living standards. This provides a good segue into a brief look into ECONOMICS… 1) China: Factory to the World The Chinese economy has grown at _____% per year 2) China: the bottom line But when this growth is at the cost of natural resources and people’s health, it is unsustainable Industrialized countries have environmental laws and regulations to address problems 3) Economics (defined) the social science that deals with a. – b. Economy 4) Economic System - social and legal arrangements people construct to satisfy their needs and wants To improve their well-being a. – b. – 5) How is economic progress measured? Gross national product (GNP): - all goods and services produced (consumed) by a country in a given time frame o The most common indicator of health and wealth Gross domestic product (GDP): GNP minus net income from abroad 6) A Better Indicator Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI) - 7) Benefit-Cost Analysis 8) External costs