biology.clc.uc.edu
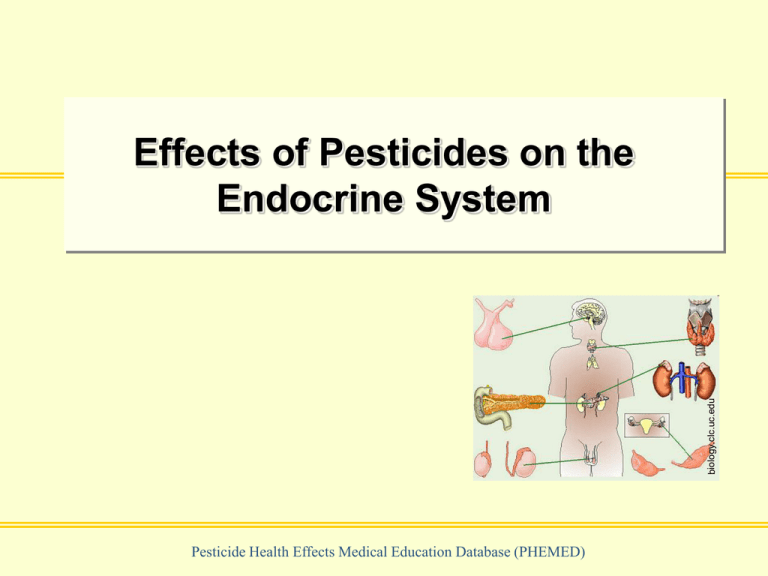
Effects of Pesticides on the
Endocrine System
Pesticide Health Effects Medical Education Database (PHEMED)
Definition
Synthetic chemicals that mimic hormones
Disruption by:
Receptors over-respond to the mimic
Receptors respond at inappropriate times
Block a receptor by competing with other hormones
Stimulate or inhibit the endocrine system causing
over or under production of natural hormones
(thyroid)
Chemicals with established links to
endocrine disruption
DES – diethylstibesterol
Dioxins – CDD’s polychlorinated dioxins
PCB’s – polychlorinated biphenyls
DDT
mimics estrogen
DDE (major byproduct) interferes with
testosterone function
DES
Vaginal CA in offspring of women taking DES as
morning after pill or during pregnancy to avert
SAB’s
DES daughters increased risk for infertility,
miscarriages, ectopic pregnancies.
DES sons: evidence of increased risk:
undescended testicles
smaller penis size
poorer sperm quality
Dioxins
Formed during:
chlorine bleaching process at pulp and paper mills
chlorination of waster and water treatment
contaminant of chlorinated phenols (2,4,5-TCP, PCP)
chlorinated pesticides or herbicides (such as 2,4,5-T,
older 2,4-D, hexachlorophene, Silvex® ) none
currently in use
Agent Orange (combination of 2,4,5-T+ 2,4-D)
Interferes with sex hormones
PCB’s
Persists in the environment + body (lipophylic)
Banned uses that would disperse PCB’s:
Continued use in ‘closed systems’
capacitors and insulating fluids in transformers
vacuum pump fluids and hydraulic fluids
Human exposure
plasticizers in paints and cements
fire retardant fabric treatments
heat stabilizing additives for PVC electrical insulation
Adhesives/ paints and water-proofing
railway ties
appliances, fluorescent light fixtures, electrical equipment > 30 years
old
Contaminated food (contaminated fish, dairy, meat)
Air from hazardous waste sites
Workplaces where closed systems are repaired
Minics estrogen + interferes with thyroid hormones
Pesticides Suspected to be
Endocrine Disruptors
Herbicides:
2,4-D
Alachlor
Amitrole
Atrazine
Metribuzin
Nitrofen*
Trifluralin
http://www.nrdc.org/health/kids/ocar/chap5e.asp
Pesticides Suspected to be
Endocrine Disruptors
Fungicides:
Benomyl
Fenarimol
Mancozeb
Maneb
Vinclozolin
Metiram Zineb
Tributyltin Ziram
Fumigants:
DBCP*
http://www.nrdc.org/health/kids/ocar/chap5e.asp
Pesticides Suspected to be
Endocrine Disruptors
Insecticides:
Aldicarb
Aldrin*
Carbaryl
Chlordane*
Dicofol
Dieldrin*
Endosulfan
Endrin*
Fenvalerate
Heptachlor*
Kepone*
Lindane
Malathion
Methomyl
Methoxychlor
Mirex*
Parathion*
Pentachlorophenol
Permethrin
Toxaphene*
http://www.nrdc.org/health/kids/ocar/chap5e.asp
Health Effects of Endocrine Disruptors (ED’s)
in Humans
No firm causal evidence w/low exposure
Suggestive relationship with :
Reproduction
Endometriosis
Precocious puberty
Nural function
Immune function
Cancers: breast, endometrial, testicular, prostate,
thyroid
Source: WHO/IPCS. Global assessment of the state-of-the-science of
endocrine disruptors. WHO/PCS/EDC/02.2
Reproductive
Decline in human sperm quality
Impaired fertility and increased SAB’s
Relationship to ED’s speculative
Declining sex ratios
Meta analysis studies reached different conclusions
Not necessarily due to endocrine disrupters (ED’s)
Evidence of unidentified external causes but mechanism
unknown
Developmental male reproductive tract
abnormalities
ED exposure evidence unclear
Experimental data with a number of chemicals
demonstrate they can disrupt male reproductive tracts.
Gynecological
Endometriosis
Association with ED reported but studies
equivocal
Precocious Puberty
Concern regarding influence of ED’s on early
onset of puberty
Role of other factors such as nutrition needs
clarification
Neural Function
Prenatal exposure to ED’s (PCB’s) result
in neurodevelopmental, behavioral and
neuro-endocrine function problems.
Human and animal data
Effects more likely a result of altered
thyroid or neuro-transmitters.
In most instances ED mechanism not
demonstrated
Immune Function
Some ED’s alter human and animal
immunity
Unknown if these alterations due to an
endocrine mediated mechanism
Cancers of Hormonally Sensitive Organs
Temporal association between rise in
hormone sensitive organ cancers and
wide spread use of industrial chemicals
Increase incidence not explained by
improved diagnostic techniques.
Hypothesis – is it from ED’s?
Breast Cancer
Studies measuring DDE (DDT metabolite
stored in fat tissue) in adult women do not
support a causative relationship.
New study measuring the more active
p,p´-DDT metabolite in frozen blood from
women at delivery from the 1950’s show a
5 fold relationship. *
*Cohen et al. (2007) DDT and Breast Cancer in Young Women: New Data on the Significance of
Age at Exposure. EHP. 115(10) 1406-1414.
Other Cancers
Endometrial - limited data – no causal
relationship established.
Prostate – some associations positive and
some negative. Mechanism unknown.
Testicular – temporal rise without link to
same time frame as use of ED’s
Thyroid – no direct link to ED exposure
has been demonstrated.
Future
Adverse health outcomes appear biologically
plausible given:
Known effects of endogenous and exogenous
hormones sensitive organs
Demonstrated effects on wildlife and laboratory
animals
They are a high priority research area is
required –
EPA required to screen products for potential
effects on the endocrine system
Other non-ED mechanisms must also be
explored