State Level Best Practices - Department Of Industrial Policy
advertisement
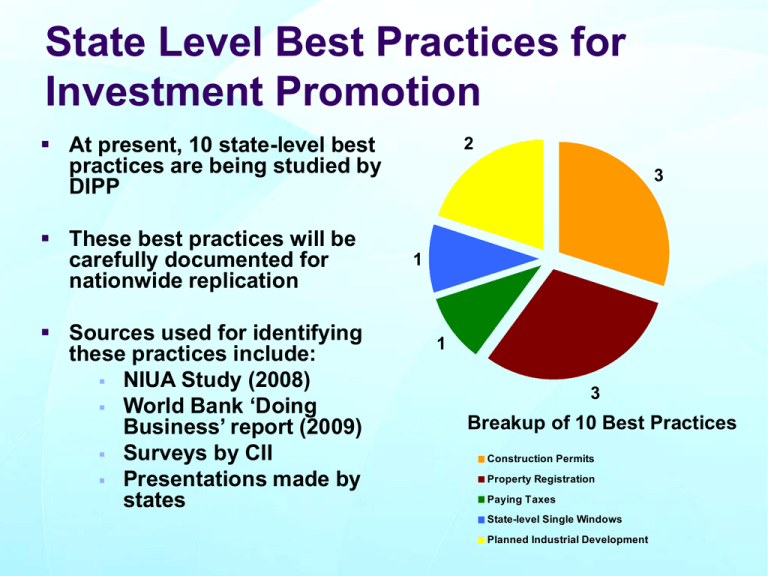
State Level Best Practices for Investment Promotion At present, 10 state-level best practices are being studied by DIPP These best practices will be carefully documented for nationwide replication Sources used for identifying these practices include: NIUA Study (2008) World Bank ‘Doing Business’ report (2009) Surveys by CII Presentations made by states 2 3 1 1 3 Breakup of 10 Best Practices Construction Permits Property Registration Paying Taxes State-level Single Windows Planned Industrial Development Identified Best Practices Land Acquisition Package, Haryana Standardization of Property Documents, Rajasthan SIR Ordinance, Gujarat Water & Sewerage connection and Occupancy Permit, Greater Noida E Stamping, New Delhi Single Window System for Industries, Orissa GIS System, Bhubaneshwar Development Authority Registering, filing & payment of state V.A.T and CARD, Andhra Pradesh List of Best Practices Procedure Best Practices Key Feature ‘GIS System’ of BDA (Orissa) Comprehensive development plan for the town was integrated with Remote Sensing maps to prepare upto-date land use map 2. Water & Sewerage Connection Greater NOIDA (UP) Provision of water connection with all civil works is done before giving possession to allottee 3. Occupancy Permit ‘Architect on Record’ of Greater NOIDA (UP) Approvals given on certification by Registered Architects 4. Registration, Filling and Payment of State V.A.T Andhra Pradesh Simplicity in Registration, electronic filing of return & payment of taxes 5. Encumbrance & Title Verification CARD of Andhra Pradesh Search of Title, Property Registration & Valuation are done electronically 1. Issue of Construction Permits by Area Development Authority. List of Best Practices Procedure 6. E-Stamping 7. Standardization of Property Documents 8. Land Acquisition Package 9. Single Window System for Industries 10. SIR Ordinance Best Practice Key Feature Delhi Secured electronic payment of stamp duty Rajasthan Ease of preparing property documents due to standardization of property documents Haryana The land owners will be paid annuity for 33 years over & above the usual land compensation Orissa Submission of composite application and single nodal point of contact Gujarat To facilitate development of economic hubs as per global standards Best Practices Relating to Construction Permits Geographic Information System (GIS) - BDA • GIS was developed by BDA for capturing, managing & analyzing geographical information such as types of land, census tracts, sites, roads, buildings etc. • Comprehensive development plan for the town was integrated with Remote Sensing maps to prepare up-to-date land use map • Digitalization of BDA Development plans using GIS system first implemented in 1999 and subsequently updated constantly Geographic Information System (GIS) - BDA Key Benefits to Public • It is fastest to obtain land use permission (1 day) in Bhubaneshwar In India on an average it takes 16 days to obtain land use permission In Bhubaneshwar, it used to take 50 days to obtain land use permission Key Benefits to Government • Helps State Revenue Authority to know the up to date status of land utilization • Effective development control and reduction in unauthorized constructions GIS System - Bhubaneshwar Development Authority Legal & Administrative Changes The Orissa Development Authorities Act, 1982 was revised to give legal status to the GIS system Land use information cell was established to provide information related to land use and building byelaws to the public Proper training was provided to staff to use new computerized system Technology Maps were digitalized using ARCINFO and ARC VIEW software Financial Implications Project was funded by BDA internal funds Recovery of cost planned through user fees (i.e. 100 Rs/ User) Water & Sewerage Connection GNIDA Key Features • Provision of water & sewerage connection with all civil works are done before giving possession to allottee. • Design / Specification / Modules for water & sewer connections institutionalised according to land-use and plot sizes • • GNIDA using this practice since 1998-99 Layout for sectors along with detailing of Water & Sewer connections to individual plots are pre planned Key Benefits to Public • It is fastest to obtain water and sewerage connections (7days) in Greater NOIDA In India on an average it takes 16 days to obtain permanent water & sewerage connection Key Benefits to Government • Pre-possession of connections avoids repetitive road cutting at later stages Architect on Record – Greater NOIDA (GNIDA) Key Features GNIDA empowers the architects registered with the Council of Architecture (COA) for sanction/ approval of Building Plans/ Occupancy Certificate on individual residential plots allotted by the authority GNIDA using this practice since 2003 Acknowledgement of application along with checklist to the authority deemed as of Occupancy / Completion Certificate Key Benefits to Government Key Benefits to Public • Immediate grant of occupancy permit approval facilitated by third party certification receipt • • No separate staff to be engaged for granting occupancy permit Also no payment are required to be paid to architect by GNIDA Best Practices Relating to Paying Taxes Registration, Filing & Payment of State VAT in AP Key Features • • • • Registration certificates are issued through VATis, an online software application e-Registration application software has been developed and will be launched shortly. This will help dealers to apply for V.A.T registration online ( Internet) Dealers can file the return through internet and e-seva centers Dealers can view the details of returns and the payments filed by them through the internet using ‘Dealer ledger’ application facility Key Benefits to Dealers • • • Registration certificate is issued within 24 hours in case of non risk dealers Dealers are not required to pay fee and security deposit at the time of registration Simplicity due to electronic payment and filing Key Benefits to Government • • There was a 20.21% growth in tax revenues after implementation of this system. Cost of tax collection came down significantly Registration, Filing & Payment of State VAT in AP Legislative and Administrative changes • • The Andhra Pradesh Value Added Tax (V.A.T) Act, 2005 came into force on 1 April 2005 The V.A.T Act in Andhra Pradesh is administered by the Commercial taxes department (department to collect VAT and other taxes) • Training was provided to tax officials prior to implementation of V.A.T Technology • Custom build software was developed to handle registration, filing & to accept payment of V.A.T Best Practices Relating to Property Registration Computer Aided Registration of Deeds (CARD) - AP Key Features CARD is a simplified and decentralized digital property registration system through 200 Sub- Registrars’ offices (SRO) of Andhra Pradesh This system simplifies and expedites the registration process, provides certificates for non encumbrance and assists in market valuation of properties In 1997 CARD system was introduced in two SRO In 1998 CARD system was extended to about 432 SRO CARD was adjudged one of the ten finalists in the International Innovation awards 2000 Computer Aided Registration of Deeds (CARD) - AP Key Benefits to Public • Approximately 1 day is required to register property under CARD system Earlier it used to take approx 17 days to register property Key Benefits to Government 19.75 • 9.76 • 3.32 % Growth (in net revenue) 1997-98 1998-99 1999-00 AP Land Registration Revenue, 1997-2000 Land revenue growth of 19.75% was recorded in the year preceding when CARD system was introduced Within Six months of the launch of the CARD project, about 80% of all land registration transactions were carried out electronically Computer Aided Registration of Deeds (CARD) - AP Legal & Administrative Changes The Registration Act, 1908 (Central Act), in its application to the state of AP, was amended to facilitate for the following: • The process of registration of any category of documents may be completed and copying done with the help of electronic devices like computers, scanners and CDs and copies preserved and retrieved when required. • Copies of documents registered and stored electronically, retrieved, printed and certified by the sub-registrar shall be received as evidence • The software to be used for registration shall be prescribed by the Inspector General. SROs were divided into 3 categories based on the number of documents registered and the revenue derived from each office. One to three weeks training was organized for different categories of officers ( cost 9% of total project cost ) Technology A 386 server operating with 14 terminals was set up at a cost of about $31,000 (Rs 13.3 lakh) Financial Implications Initially USD US$3 million (Rs.13 crore) were spent. E Stamping - Delhi Key Features E Stamping is computer based stamping of documents where record keeping agency maintains the database electronically instead of physical stamping of documents which could be forged or duplicated Have special Security features such as optical watermark, 2D Barcode and microprint (superfine printing of important details invisible to naked eyes) Delhi government introduced E-stamping since 1st Apr 2008 Prevented circulation of Fake Stamp papers in market E Stamping - Delhi Key Benefits to Public No fear of fake paper or forgery. The certificate generated is tamper proof Certificate generated has a Unique Identification Number Key Benefits to Government Curbs the revenue loss in future due to fake or forged stamp papers Saving on the cost of printing and handling of Stamp papers The new system generate the audit trail, MIS reports, verify certificate Standardization of Property Documents -Rajasthan Key Features • Bureau of Investment Promotion of Rajasthan introduced 34 types of standardized property registration documents • • This practice was implemented under Sarathi project which was initiated in 2003 Time for entire process of registration was brought down from 72 hours to 25 minutes Key Benefits to Public Ease of preparing property documents due to standardization of property documents Enables self preparation of property registration documents Best Practices for State Level Single Windows Single Window Clearance Orissa Key Features 18 out of 20 major approvals / clearances are provided through single nodal point by using a Combined Application form (CAF) Provision for deemed approval by department/ authority, in case the approval is not granted within the time limit specified by GoO under Orissa Industrial (Facilitation) Rules Single Window Clearance Orissa Key Benefits to Government Key Benefits to Private Firms • • Time Bound Clearances – Faster clearances Concerned authority process the application and communicate its decision to the nodal agency within the time limit specified (not to exceed 30 days from set time limit) • Higher industrial growth will contribute to overall economic growth High rate of Orissa’s Economic growth through industrialization The economic growth rate is up from 4 % in the 1990s to about 8.5 % over the past five years Single Window Clearance Orissa Legal & Administrative Changes Orissa Industries Facilitation Act (OIFA) 2004 was introduced to facilitate single window industrial clearance Industrial promotion and Investment corporation of Orissa Ltd. (IPICOL) was designated as state level nodal agency and high level clearance authority DIC was designated as District level Nodal Agency OIFA envisages a three-tier approval mechanism for according expeditious projects based on the level of investment. clearance to industrial • District Level Single Window Clearance Authority (for investments up to Rs. 50 crore) • State Level Single Window Clearance Authority (for investments more than Rs.50 crore but less than Rs. 1,000 crore) • High Level Clearance Authority (for investments more than Rs. 1,000 crore) Financial Implications Govt. of Orissa charge process fee within Rs.l.00 lakh to Rs.2 .00 lakh depending on the value of the application Single Window Clearance Orissa Need for Single Window Clearance in Orissa Approximately 20 approvals are needed to set up an Industry in Orissa. To transform the state from a ‘lagging state’ to a rapidly developing industrial State. Clearance Authoritie s Secretarial Services Investor s Consultation & Escort Services Project Annual Clearance Inspection s Project Appraisal Reports Nodal Agency Project Annual Clearance Inspection s Post Implementation Facilitation Concerned Department s Source: CII telephonic discussions with Team Orissa and State Presentations Best practices for Planned Industrial Development Rehabilitation & Resettlement of Land Owners - Haryana Rationale for This Policy • To facilitate private sector developers to acquire land for industrial/ commercial purpose Key Features Under this the developers are liable to pay Rs.30,000/- per acre per annum with annual increase of Rs.1,000/- per acre for a period of 33 years for the land acquired for setting up of SEZ, technology city and park In case of acquisition by the State Government, the payment shall be Rs 15,000 /acre per annum with an annual increase of Rs 500 / acre The allotment of Plots will be made to each co-sharer depending upon his share in the land acquired for HUDA and HSIIDC as per scale mentioned in the entitlement This policy is applicable to all those lands where award of compensation was announced on or after 5th March, 2005 Rehabilitation & Resettlement of Land Owners - Haryana Key Benefits to Private Developers State Government assists in the acquisition of land for all the joint venture projects for development of SEZs The State Government also assists in acquiring left out pockets to ensure contiguity of SEZs. Key Benefits to Land Owners Other source of long term sustainable income in form of fixed annuity Provision of yearly increment In addition to the residential plots, commercial sites, measuring 2.75 X 2.75 mtrs. will be allotted in HUDA sectors • Such allotment shall be made to each co-sharer provided his share exceeds 2.5 acres, otherwise all the co-sharers will be allotted a single site Rehabilitation & Resettlement of Land Owners - Haryana Key Benefits to Government Facilitates land acquisition by private sector - will boost industrial infrastructure development in Haryana As a result of Policy for Rehabilitation & Resettlement of land owners, many private sector players have shown interest in the state for developing Industrial Model Townships, Industrial Parks and Technology Cities through private initiatives as well as in public private partnership SIR Act 2009 - Gujarat Why SIR Act ? Around 38 % of the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) fall in Gujarat As part of DMIC, six mega industrial nodes (four industrial areas and two investment regions) have been proposed to be set up in Gujarat On 6th January, 2009, the Gujarat Government promulgated a legal framework – The Gujarat Special Investment Regional Ordinance, 2009 SIR Act 2009 - Gujarat Key Features The Ordinance enables to establish, develop, operate and regulate the Special Investment Regions in Gujarat The state government is empowered to declare Investment Region or Industrial Area and designate them as Special Investment Region (SIR) by notification An Investment Region will be developed in an area of more than 100 sq. kms and an Industrial area will be developed in an area of more than 50 sq. kms The Ordinance provides for effective internal dispute settlement mechanism by setting up a three tier system. SIR Act 2009 - Gujarat Key Benefits to industry/ projects The ordinance provides for a single window clearance system • The Apex Authority- the GIDB will be the point of contact for establishing an economic activity, infrastructure or amenity in the SIR Key Benefits to Government It Will help government to set up world class hubs of economic activity on the lines of fast growing countries of the world Legal & Administrative Changes The proposed structure under SIR Ordinance will comprise of an Apex Authority (GIDB), a Regional Development Authority (RDA) for each region, a Project Development Agency and project specific SPVs. The Apex Authority and RDA will make provisions for development, operation, regulation, management, planning and to grant permission and approval for any economic activity or amenity to be established in the SIR











