PPT - CED
advertisement

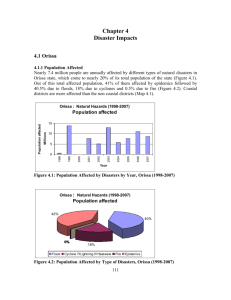
Climate Change, Coastal Vulnerability & Policy Choices G. K. Panda gopalkrishna_panda@yahoo.co.uk Focus on ……… • Foot prints of climate extremes i.e. Floods, Cyclones, Lightning, Heat Waves and Coastal Erosion • Impacts and Vulnerabilities • Practices and policy options Orissa : District Reported by Floods (1970-2007) 30 Number 25 20 15 10 5 0 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 Year Orissa : No. of Floods (1970-2007) 80 Number 60 40 20 0 Jan. Feb. March April May June July Year Aug. Sept. Oct. Nov. Dec. Orissa : Population Affected by Floods (1973-2007 ) Number Millions 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1973-77 1978-82 1983-87 1988-92 1993-97 1998-02 2003-07 Year Orissa : Human Death by Floods (1973-2007 ) 350 300 Number 250 200 150 100 50 0 1973-77 1978-82 1983-87 1988-92 Ye ar 1993-97 1998-02 2003-07 Areas of Possible Submergence ORISSA : TOP 10 DISASTERS BASED ON No. of Deaths (1970 – 2007) Sl.No Year Death Hazard 1 1999 9924 Cyclone 2 1971 5307 Cyclone 3 1998 2042 Heatwaves 4 2007 351 Lightning 5 2005 303 Lightning 6 2004 298 Lightning 7 2006 283 Lightning 8 2001 270 Lightning 9 2003 262 Lightning 10 2005 235 Heat waves Orissa : Total Property Loss by Hazards (1970-2007) 0% 15% 2% 83% Flood Cyclone Lightning Fire Rupeese Millions Orissa : Property Loss by Hazards (1973-2007) 135,000 120,000 105,000 90,000 75,000 60,000 45,000 30,000 15,000 0 1973-77 1978-82 1983-87 1988-92 Year 1993-97 1998-02 2003-07 Orissa : No. of Climatic Hazards (1970-2007) 1970 to 2000 - 37 / Yr 350 Number 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2001- 2008 267/ Yr 1970 -200879 / Yr) Year Seasonal peaks Orissa : No. of Climatic Hazards (1970-2007) 400 shifting from Number 300 200 June- August to April –October. 100 0 Jan. Feb. March April May June July Year Aug. Sept. Oct. Nov. Dec. Climatic Hazards : Population Affected Number Millions Orissa : People Affected by Climatic Hazards (1973-2007) Climatic Hazards of Orissa Population Affected ± 30 SUNDERGARH MAYURBHANJ JHARSUGUDA KEONJHAR BALESWAR SAMBALPURDEOGARH BARAGADA BHADRAK ANGUL DHENKANALJAJPUR SONEPUR BOUDH 20 BALANGIR NUAPADA CUTTACK JAGATSINGHPUR NAYAGARH KHURDA PURI PHULBANI 10 KALAHANDI NABARANGPUR KENDRAPARA GANJAM Legend Population Aff. per year RAYAGADA GAJAPATI 0 - 20000 20001 - 40000 0 KORAPUT 40001 - 60000 1973-1977 1978-1982 1983-1987 1988-1992 1993-1997 1998-2002 2003-2007 Year 60001 - 80000 MALKANAGIRI 80001> Climatic Hazards include: Cyclone & Flood • Annually >1 lakh people are affected from coastal Dist. • Flood & Cyclone accounts for 93 % of population affected. Climatic Hazards : Loss of Life Loss of Life in Nos Orissa: Loss of Life due to Climatic Hazards (1970-2007) Climatic Hazards of Orissa Loss of Human Life SUNDERGARH ± MAYURBHANJ JHARSUGUDA BALESWAR SAMBALPURDEOGARH KEONJHAR BARAGADA 1500 SONEPUR 1000 ANGUL BOUDH BALANGIR NUAPADA CUTTACK PHULBANI KALAHANDI NABARANGPUR GANJAM RAYAGADA 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 GAJAPATI KORAPUT Year KENDRAPARA JAGATSINGHPUR NAYAGARH KHURDAPURI 500 0 BHADRAK DHENKANALJAJPUR Legend No. of human Life Loss per Year 1 - 15 16 - 30 31 - 45 45> Cyclone Flood Lightning Heatwave MALKANAGIRI Climatic Hazards includes: Cyclone, Flood, Lightening & Heat Wave Death due to climatic hazards increasing since 1998 Max. Temp (oC) of coastal stations of Orissa (1965-2010) March April Balasore Chandabali Paradeep Puri Gopalpur May Heat waves : Human Death (1998-2007) Orissa : Heatwaves (1998-2007) Human Death Human Death per year HEATWAVE HAZARD(1998-2004) SUNDERGARH ¯ Human Death In Nos 2100 MAYURBHANJ KEONJHAR JHARSUGUDA BALESWAR SAMBALPUR DEOGARH BARAGADA 1800 BHADRAK ANGUL SONEPUR BOUDH 1500 JAJPUR DHENKANAL BALANGIR NUAPADA JAGATSINGHPUR NAYAGARH 1200 PHULBANI 900 NABARANGPUR KHURDA PURI KALAHANDI RAYAGADA GAJAPATI 600 GANJAM Legend No. of Human Death per year KORAPUT 300 KENDRAPARA CUTTACK 0 50 100 200 300 Kilometers 0 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 MALKANAGIRI Year Annual average human death is 5 times of Flood. Highest human death was in 1998 (2042). Coastal & North Western dists show higher human death Lightning : Human Death (1998-2007) Human Death In Nos Orissa : Lightning (1998-2007) Human Death Human Death per year LIGHTENING HAZARD(1998-2007) SUNDERGARH ¯ 400 MAYURBHANJ JHARSUGUDA SAMBALPUR KEONJHAR BARAGADA SONEPUR ANGUL BOUDH 300 BALESWAR DEOGARH DHENKANAL JAJPUR BHADRAK BALANGIR KENDRAPARA NUAPADA CUTTACK NAYAGARH 200 JAGATSINGHPUR KHURDA PHULBANI KALAHANDI GANJAM PURI NABARANGPUR 100 RAYAGADA Legend GAJAPATI No. of Human Death per year KORAPUT 0 0 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 50 100 200 Kilometers MALKANAGIRI Year Human Causality Increasing. Annual average human death is 205. Highest causality is in 2007 (351). 300 Coastal Erosion in Orissa Photo courtesy: Prof. G.K. Panda Dept. of Geography, Utkal University Bhubaneswar Puri Coastal Erosion in Orissa Gopalpur Podampeta village 10 km NE of Ganjam , Orissa (September 2011 dated Newspaper clipping) Coastal Erosion in Pentha Village & Puri Marine Drive 1929 1994 2008 1 1 2 2 3 3 5 5 4 4 (a) (a) Changing Morphology of the Spits, Bay Mouth Bars & Islands around Hukitola Bay (b) Coastal Erosion in Pentha Village IRS P6, LISS-III Image of Northern Part of Orissa Coastal Zone from Subarnarekha Mouth to Mahanadi Mouth 25 Km. Buffer Zone 10 5 0 10 20 KM Chilika 25 Km. Buffer Zone IRS P6, LISS-III Image of Southern Part of Orissa Coastal Zone from Mahanadi Possible Impacts on………. • Coastal Habitation • Fishing Communities • Low & Marginal Farmers • Daily Wagers & Ag. Laborers • Agriculture & Plantations • Small Traders & Artisans Problems • Cyclone & Storm Surges • Flood & Tidal Inundations • Coastal erosion • Migration of Sand dunes. • Popln. Pres. & LU change • Coastal encroachments • Loss of Mangroves • Loss of Habitat & Bio-Diversity Potential for LHSS • Mangrove based LHSS • Fishing & Aquaculture • Eco-Tourism • Plantations •50 % of the farmers had already applied adaptation strategies to respond to their experience of climate change. i.e changes in crops, crop varieties, planting dates, along with increased irrigation and supplementing livestock. Impediments to adaptation, including poverty, lack of savings and access to credit, insecure property rights and lack of social protection mechanisms to insure against the risks of using new techniques or technologies. Microcredit programs can provide the direct provision of livestock or poultry through asset transfers Mitigation Options • Interventions • Capacity Building & Knowledge Management • Adaptations • Policy and Programs • Research & Development Mitigation Opportunities…….. Interventions 1. Reduction of Climate Change Hazards through Coastal Afforestation with community focus. 2. Providing drinking water to coastal communities to combat enhanced salinity due to sea level rise. 3. Construction of flood shelter, information and assistance centre to cope with enhanced recurrent floods in major floodplains. Capacity Building 1.Capacity building for integrating Climate Change in planning, designing of infrastructure, conflict management and land use zoning & management. 2. Climate change and adaptation information dissemination to vulnerable community to raise awareness. 3. Mainstreaming adaptation into policies and Programs in different sectors, focusing on disaster management, water, agriculture, health and industry Reducing risks to Livelihoods through…… • Developing context specific crop packages and promoting improved agricultural practices • Addressing Fisherman’s issues • Pre- flood paddy cultivation, • Safe storage of seeds and food- grains, • Promoting organic agriculture • Formation and strengthening of Farmer’s Club • Promotion of crop insurance 1. Overall Objective Enhance disaster risk reduction & reduce vulnerability of the poor women, men and children with increased resilience to risks & preparedness and new challenges emanating from climate change. 2. Economic Justice Need to focus on policies & programs to ensure poor people‘s right to resilient and sustainable livelihoods through the reduction of poverty and vulnerability. 3. Essential Services Policies on empowering poor people to realize their rights to accessible and affordable health, education, water and sanitation. Thank You Utkal University, Bhubaneswar, ORISSA