Chapter 11: Water and the Major Minerals

Chapter 9
Water and
Minerals
Water
50%-70% of body weight
Muscle contains 73% water
– Fat contains ~20%
Intracellular fluid
– Fluid within the cells
Extracellular fluid
– Fluid outside the cells
Fluid Balance
Water shifts freely in and out of cells
Controlled by electrolyte concentration
– Have electrical charges . . .Na, K, Cl, P, Mg, Ca
Osmosis (where an Ion goes, H2O flows)
Intracellular water volume
– Depends on intracellular potassium and phosphate concentrations
Extracellular water volume
– Depends on extracellular sodium and potassium concentrations
where an Ion goes, H2O flows: fig 9:2
Na Na
Na
Na
Na
Na
H2O
Na
Na
Functions of Water
Body temperature regulation
– Water absorbs excess heat
– Body secretes fluid via perspiration
– Skin is cooled as perspiration evaporates
– Humidity (bad) & fans (good) ~ evaporation
Removal of body waste via urine
– Urea excretion (Nitrogen from Protein breakdown
– Sodium excretion
– Avoid concentrated urine (brownish)
Amniotic fluid, joint lubricants, saliva, bile
Are You Drinking Enough?
Fluid recommendation: 9 cups for women and
13 cups for men as a starting point
Min. 2-4 water bottles/day
Thirst Mechanism
Not reliable
Concerns for infants, older adults, athletes
Athletes
– Weigh before and after training session
– Consume 3 cups for every pound lost
Illness (vomiting, diarrhea, fever)
– Get additional water
Ignoring the Thirst Signal
Shortage of water increases fluid conservation
Antidiuretic hormone (vassopressin)
– Released by the pituitary gland
– Forces kidneys to conserve water (reduce urine flow)
Aldosterone
– Responds to drop in blood pressure
– Signals the kidney to retain sodium (water)
Hydration
Loss of 1%-2% of body weight in fluid
– Thirst signal
Loss of 2% or more of body weight causes muscle weakness (stay hydrated –training)
– Lose significant strength and endurance
Loss of 10%-12%
– Heat intolerance
Loss of 20%
– Coma and death
Too Much Water
Overburden the kidneys
Low blood electrolyte concentrations
Blurred vision
-Confirming your knowledge Q-
What is the Minimal amt. of H2O from fluids that Humans require/day to replace daily loss?
What is the recommended amt. of water from fluids that women and men require/day?
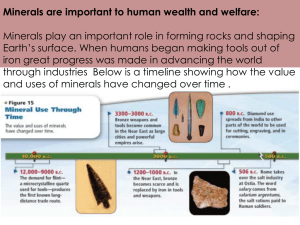
Minerals
Various functions in the body
Major Minerals
– Require >100 mg /day
– Calcium, phosphorus etc.
Trace Minerals
– Require < 100 mg/day
– Iron, zinc, selenium etc.
For 5 pts & Make it a Half day???
What do you say?
Go see “Food Inc.” the movie
Nickelodean theatre (downtown SC)
3, 5, 7 & 9PM showtimes. . .
– Answer 3 short questions (class website)
– Turn in with TICKET STUB Next Wednesday
– See Trailer http://www.newsday.com/entertainment/movies/ny-etfood2612909901jun24,0,6046635.story
5
6
3
4
7
1
2
-Confirming your knowledge-
What are the 7 Major minerals required in the body?
5
6
3
4
7
1
2
-Confirming your knowledge-
What are the 7 Trace minerals required in the body?
Most mineral requirements are obtained without defic. in
N. American diets
Bioavailability of Minerals
Fe
Mg
~Degree of absorption
– Fibrous foods
Cu
Zn
Affected by binders in plants (oxalic acid, phytic acid)
Animal products are better absorbed
Plants depend on mineral content of soil
Refinement lowers mineral content (i.e. milling Grains)
Mineral-mineral competition (e.g. >>Zinc vs <Copper)
– Avoid mega-supplements (2X RDA): unless prescribed
Vitamins-mineral interactions:
– Iron w/ (Vit C), Calcium w/ (Vit. D) most efficient
Mineral Toxicity
Trace minerals are more toxic
– e.g. Fe, stomach irritation
Result of supplementation
– Presence of contaminants (esp. Lead (Pb))
– Look for the United States Pharmacopeia
(USP)-approved brands (most reliable)
Minerals of Concern in the Diet
Sodium (Na) ~ consume too much >2400mg/day
Hypertension (HTN) and CVD
Calcium (Ca) ~ not enough, esp. Women osteoporosis
Iron (Fe) ~ not enough, esp. Women
– Men require 8 mg/day
– Women require 18 mg/ day
Menstral flow
Supplements hard to digest ?
All other Major and Trace minerals (ok) ~ balanced diet
– Avoid supplementing to try and balance or optimize
Leads to mineral competition deficiencies
Sodium
Table salt (NaCl): 40% sodium, 60% chloride
95% of ingested sodium is absorbed
Positive ion in extracellular fluid
Aldosterone regulates sodium balance
Key for retaining body water
Excretion regulated by the kidneys
Muscle contraction
Conduction of nerve impulses
Food Sources of Sodium
Most sodium is added by food manufacturers and restaurants
Milk and dairy products
Processed foods
Sodium content listed on the labels
Sodium Needs
Adequate Intake is 1500 mg for adults
Body only needs 200 mg to function
Daily Value is 2400 mg/day
Upper Level is 2300 mg
Typical intake is 4700 mg/day (US)
Sodium-sensitive individuals should restrict intake (African American)
Calcium
99% is in bones and teeth
Makes up 40% of all the minerals present in the body
Absorption of Calcium
Amount in body is dependent on amount absorbed
Requires slightly acidic environment and vitamin D
Absorbed in upper part of small intestine
Normally absorb 25% of calcium in food
Increase to ~60% during time of need
– (pregnancy, infancy)
Decreased Absorption of
Calcium
Ca
Rapid intestinal motility
High fiber intake
Excess phosphorus
(oxalic acid)
Ca
Vitamin D deficiency
Polyphenols (tannins) in tea
Menopause
Aging
Ca
Ca
(phytic acid)
Blood Calcium is Regulated
Blood level is maintained at the price of bone calcium
Blood level can be maintained despite inadequate calcium intake
Setting stage for future bone fractures
Functions of Calcium
Bone formation and maintenance
Blood clotting
Nerve impulse transmission
Muscle contraction
Cell metabolism
–Activates various enzymes
Building Higher Bone Mass
Adequate diet
Healthy body weight
Normal menses
Weight-bearing physical activity
Moderate intakes of protein, phosphorus, sodium, caffeine
Non-smoker
Lower use of certain medications
Food Sources of Calcium
Bone Strength
Dependent on bone mass and bone mineral density
The more there is, the stronger the bone
Calcium Needs
Daily Value is 1000 mg/day
Adequate Intake is 1000 -1200 mg/day for adults
Adequate Intake is 1300 mg/day for adolescents (9-18 yrs. old)
Average intake: 800 mg/day for women and 1000 mg/day for men
Upper Level is 2500 mg/day
Calcium Supplements
Recommended for people who cannot incorporate Ca into their diets
Not recommended with high-zinc meal
Calcium carbonate (40% calcium)
– For those with ample stomach acid
– Found in antacids (TUMS)
Calcium citrate (21% calcium)
– Enhances absorption due to acidity content
– Recommended for older adults
Break
Osteoporosis - Video
Osteoporosis
Calcium deficiency
“A pediatric disease with geriatric consequences”
Leads to ~1.5 million fractures / year
Slender, inactive women who smoke are most at risk
“Less bones”
Osteoporosis
Bone Structure
Bone Growth and Mass
Rapid and continual throughout adolescence
Peak bone mass
Determined by gender, race, familial pattern, other genetic factors
Bone loss begins ~age 30
Women experience increased bone loss after menopause
DEXA bone scan
Bone Mineral Density
The Trace Minerals
Needed in much smaller amounts
Essential for health
Difficult to study
– Only trace amounts in the body
Animal sources of mineral are generally better absorbed
Most Important: Iron (Fe)
Iron
Found in minute amounts in every cell
18% is absorbed
Heme iron vs. Nonheme iron
– Heme found in animal products better absorbed than nonheme
– Meat protein factor may aid in nonheme absorption
Vitamin C enhances absorption (nonheme iron)
Absorption of Iron
Determined by body’s need
Iron storage in intestinal cells
Absorbed in an acidic environment
Hindered by phytic acid, oxalic acid, high fiber, high calcium, polyphenols
Ca
Ca
(phytic acid)
Ca
Ca
Functions of Iron
Hemoglobin in red blood cells
– Transports oxygen and carbon dioxide
– High turnover, high demand for iron
Myoglobin in muscle cells
Electron transport chain
Enzyme cofactor
Immune function
Drug-detoxification pathway
Iron-Deficient Anemia
Most common form of anemia
Low levels of hemoglobin and hematocrit
Insufficient intake and stores
Reduction in
– Production of red blood cells
– Oxygen-carrying capacity
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Most at risk:
– Infant, toddler, chronic blood loss, vegans, runners, and women of childbearing years
Signs:
– Paleness, brittle nails, fatigue, poor temperature control, poor growth
– Fatigue, decreased Immune sys.
Food Sources of Iron
Iron Needs
RDA is 8 mg/day for adult male
RDA is 18 mg/day for female age 19 to 50
Daily Value is 18 mg
Average intake exceeds RDA for men; low for some women
Upper Level is 45 mg/day
– Take supplements/ cut them down to size
– More easily digested (see product 65mg tab!)
Iron Toxicity
Serious, especially for children
Signs:
– Diarrhea, constipation, nausea, abdominal pain
– Causes death due to respiratory collapse (shock)
Hemochromatosis
– Genetic disease (5-10% N. Americans)
– Iron deposit that can lead to organ damage
– May go undetected until organ damage at 50-60
Mineral Functions
What is safe and effective food product that has nearly all of your vitamins/minerals that is not a supplement?
Get Your Blood work Tested?
Diet Analysis 2 (Due next wed/Friday) includes
– See website
– Ca
– Fe
– Vit E
– Vit C
For next week, organic foods/ food safety
– Please go see Food Inc. –Nickelodian, Downtown
– 5 pts. For class assignment