Is there a potential for P recycling in the mineral fertilizer industry?
advertisement

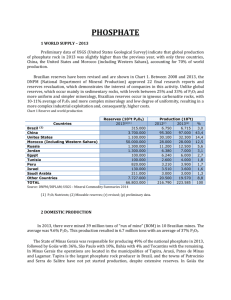
Is there a potential for P recycling in the mineral fertilizer industry? Laetitia Six Co-authors: Antoine Hoxha and Kees Langeveld (ICL) SPS 2014 Montpellier Production of P fertilizers Mining of phosphate rock Ca5(PO4)2(F,Cl,OH) Transport to Europe The Hague Centre (2012) – based on USGS 2012 P fertilizers such as NPK, TSP/SSP, MAP, DAP, … Consumption in EU28: 2.6 million ton P2O5 /yr Application rate: 23 kg P2O5/ha Production processes Phosphate Rock Wet process + H2SO4 Thermal process: 800-1000 °C H3PO4 P4 + K and N source Acidulation with H3PO4 or H2SO4 TSP/SSP Nitrophosphate route Reaction with HNO3 Mixture H3PO4 and Ca(NO3)2 + K and N source NH3 neutralization MAP, DAP, NPK’s NPK’s Closing the loop… Nutrients are precious and thus losses need to be limited and uptake by plants maximized: • Farming best management practices • R&D for products with higher nutrient use efficiency, lower C footprint, less prone to leaching,… • Right time, right dose, right product, right place • Fertigation and precision farming • P recycling From waste to… … P fertilizer ‘Waste’ streams rich in P are: o Manure o plant residues o animal waste o food waste o waste water Needs: (1) Nutrient accumulation or concentration from P sources into final product when too diluted (2) Nutrient in final fertilizer product should be present in plant-available form (H2PO4- or HPO42-) P-rich waste Problem Solution Manure High water content Dewatering and monoincineration, pyrolysis or gasification Sewage sludge (SS) High water content Organic contaminants Dewatering and monoincineration SSA Meat and bone meal (MBM) Direct use in feed forbidden due to mad cow disease Mono-incineration MBMA Waste water P is too diluted Precipitate to form struvite (MgNH4PO4.6H2O) Main differences between the sources are the solubility of phosphate, the contaminants (mineral and/or organic) they contain and the physical form. 1. Mono-incineration ashes P is not soluble in water or neutral ammonium citrate (NAC) not plant-available form acidulation needed (cfr. phosphate rock). Differences with phosphate rock and acidulation process: •P from ashes is in complexes with Fe, Al or Ca, not always similar to phosphate rock. •Heavy metals and contaminants can react with acid regular acidulation doesn’t yield the physical and chemical results required. •Fine powder no grinding needed, but impact on storage and handling. a) Meat and bone meal ashes (MBMA) MBMA ashes show most similarities with phosphate rock: Form: Ca3(PO4)2 P2O5 content 25-30 % Mix of MBMA with phosphate rock can react with H2SO4 or H3PO4 to give the regular products (SSP or TSP) Acidulation with MBMA alone? More difficult processibility. b) Sewage sludge ashes (SSA) Al, Fe and heavy metal content is much higher compared to phosphate rock, especially when expressed in content per % P2O5 Wt % ppm P2O5 Al2O3 Fe2O3 Cu Mn Pb Zn Cd SSA (average 4 samples) 18 9 7 765 1372 192 1923 <1 Phosphate rock 31 0.1 0.2 14 7 <0.1 260 26 The processing of SSA is a challenge! • During reaction: formation of FePO4, thus less free H3PO4 to react to superphosphate preference for H2SO4 acidulation • Large differences in quality of SSA large spread in resulting products and quality • Acidulation of SSA together with phosphate rock is difficult BUT it is possible to mix acidulated phosphate rock with acidulated SSA in granulator. 2. Struvite Formation: addition of Mg2+ to waste water Mg2+ + NH4+ + PO43- + 6 H2O MgNH4PO4. 6 H2O (15-20 % P2O5) Phosphate in struvite is in plant-available form No need for acidulation, direct input in granulator together with acidulated phosphate rock (max. 20 % of total input). Limiting factor is moisture content. Concerns with struvite: •Presence of pathogens, pharmaceuticals, hormones , etc. encapsuled in crystals. •Odour P recycling? YES but… challenging! Process-related challenges: Fe and Al content, moisture content,… Safety: environmental, animal and human health – Heavy metal content – Organic contaminants (pathogens, farmaceuticals, hormones…) Legislation needs to enable recycling end-of-waste criteria Supply of secondary raw materials – Quantity – Supply – Quality – Price fertilizers are high quality Mineral products, even when they are based on recycled P sources. Cartoon 1 European Sustainable st Phosphorus Conference 2013 Thank you! Laetitia Six www.facebook.com/fertilizerseuropepage www.twitter.com/FertilizersEuro http://www.youtube.com/user/FertilizersEurope Group Fertilizers Europe www.fertilizerseurope.com www.productstewardship.eu www.memberslounge.eu