Chapter 19 - Gainesville ISD
advertisement

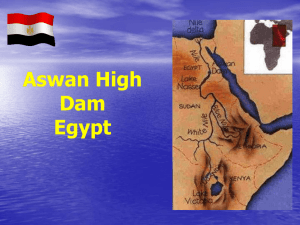
Chapter 19 Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, Central Asia Today Chapter 19:1 Objectives • 1. Discuss how physical geography affects farming and fishing in North Africa, Southwest Asia and Central Asia. • 2. List the region’s important industries. • 3. Explain how improvements in transportation and communications are changing life in the region. Terms to Know • arable • commodity • petrochemical • gross domestic product (GDP) • hajj • embargo Drawing from Experience • Would you say that your lifestyle depends on the use of oil and oil products? • Why or why not? • Most of the world’s oil is found in North Africa, Southwest Asia and Central Asia. • This section focuses on the economic activities, transportation, communications, and interdependence of the region. Introduction • North Africa, Southwest Asia, Central Asia hold great oil reserves. The oil industry is important in the region’s economy. • The regions improved transportation and communications link it with the world. • What industry is important in the region? Meeting Food Needs • The challenge is producing food for a rapidly growing population. • Poor soil and unreliable rain produce small amounts of food. • Rich oil-producing countries can import food while, • other countries like Afghanistan must grow their own. • Sometimes irrigation can be used. • Not much land is suitable for farming but, • a large part of the population is engaged in agriculture. • Citrus fruits, grapes and olives are major crops in the Mediterranean climates. • Grains, cotton and livestock grow on farms in Central Asia. • Fish are an important food source in coastal areas of the region. Industrial Growth • The region has about 70% of the world’s oil supply and 33% of the world’s natural gas reserves. • Petroleum and oil products are the main export commodities, or economic goods in the region. • Other industries use petrochemicals – products made from petroleum or natural gas – to make fertilizers, medicines, plastics, and paints. • Copper and coal are mined in Central Asia. • In North Africa, Morocco is the world’s largest exporter of phosphate used in agricultural fertilizers. Two Major Service Industries • financial • tourism • Banking, real estate, and insurance account for most of Bahrain’s gross domestic produce (GDP). • GDP is the value of goods and services produced in a country in a year. • Tourism is popular in North Africa and Southwest Asia because of their historical importance. • Millions of visitors tour religious sites each year. • Christians and Jews tour Israel, Jordan and other countries in the region. • Muslims make a hajj, or yearly pilgrimage, to Makkah (Mecca). Petra, Jordan – tourist destination Petra Treasury Royal Tombs • AIRLINES connect countries within the region and with the rest of the world. • WATERWAYS and ports on the Black and Mediterranean Seas allow ships to load and unload cargo. • Channels such as the Strait of Hormuz are used by oil tankers to transport oil from the region. Transportation • ROAD systems in Iran, Turkey and Egypt connect major cities with oil fields and seaports. • RAILROADS connect cities with rural areas. • Mass transit systems have been built in urban areas to ease traffic jams. • The Suez Canal, a major human-made waterway lying between the Sinai Peninsula and the rest of Egypt, enables ships to pass from the Mediterranean to the Red Sea. • PIPELINES transport oil and natural gas overland to ports on the Mediterranean and Red Seas and the Persian Gulf. Why is the Suez Canal Important? Suez Canal Red Sea Communications • • • • • a. Television & radio b. satellite technology c. telephone d. computer and internet e. telecommunications cable was laid along the Silk Road. • This cable provides 20 countries with communications services. Interdependence • Interdependence has increased as the more developed countries help the less developed. OPEC • • • • • • • • Eight of the region’s countries: Algeria Libya Iran Iraq Kuwait Saudi Arabia and UAE (United Arab Emirates) • belong to the 11 member OPEC organization, • Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries. • Because other countries depend heavily on the region’s oil, OPEC countries have considerable influence in the world. Embargo • Sometimes OPEC places an embargo, or restriction, on oil shipped to industrialized countries, causing oil prices to rise. • In 1999 OPEC forced oil prices to rise by decreasing oil production. (supply & demand) Key Points • Although North Africa, Southwest Asia and Central Asia have limited arable land, a relatively large percentage of the region’s people work in agriculture. • The oil-producing countries in the region have experienced greater economic growth than other countries in the region. • Expanded and more advanced transportation and communications systems are helping connect the region’s urban and economic centers with one another and with the world. • Interdependence is increasing among the countries of the region, especially in controlling oil production and prices. Chapter 19:2 Objectives • 1. Describe how the peoples in North Africa, Southwest Asia and Central Asia have dealt with scarce water resources. • 2. Discuss the causes and effects of environmental problems in the region. Terms to Know • aquifer • desalination Drawing From Experience • Is freshwater in your area scarce? • Why or why not? • In the last section, you read about economic activity in North Africa, Southwest Asia and Central Asia. • This section focuses on the environmental challenges facing the region. Introduction • Human actions in North Africa, Southwest Asia and Central Asia threaten the environment. • These actions include oil spills, urbanization, and overuse of water supplies. The Need for Water • Freshwater is scarce in the region. • About 97% of the world’s water is saltwater. • 2% of the earth’s freshwater is frozen. • That leaves 1% of the freshwater available for human use. • This region gets its water from rivers, oases and underground aquifers. Desalination • a way to remove salt from seawater and make it fresh • Many countries depend on desalination for their freshwater supply. • It’s very expensive. Libya’s Great Man-Made Lake • While drilling for oil they discovered water! • This underground aquifer was huge. • Libya created a lake with the water that is being pulled out. • Some scientists are afraid these pipelines will drain the aquifer. • Some are afraid that pumping water from the aquifers will draw in saltwater from the sea and ruin the freshwater. Libya’s Great Man-Made Lake Gadhafi (former Libyan ruler) & Obama Question • What are some solutions to the freshwater scarcity in the region? Environmental Concerns • Environmental concerns have grown in the region in recent decades because of new technologies and destructive wars. Aswan High Dam in Egypt • In 1970 the Aswan High Dam was completed. • It controls the Nile River’s flood, irrigates 3 million acres of land and supplies almost 50% of Egypt’s electrical power. • The dam has also created an artificial lake to help the fishing industry. • However, because of the dam the river no longer deposits fertile soil along the riverbanks. • Instead, the dam traps the soil. • To grow crops, farmers must now use expensive fertilizers. • Parasite-related diseases have increased near the dam. Aswan High Dam New dam/old dam Persian Gulf War (1990) • The war had disastrous effects on the environment. • Iraqi troops set fire to oil wells, causing smoke to pollute the area. • The effects of the oil fires threatened millions of birds. • They also dumped millions of gallons of oil into the Persia Gulf. • This killed fish and other marine life. 1990 Bush vs. Hussein – Kuwait oil fires Old Soviet Era Problems • Central Asia • The Soviet regime polluted these countries. • They tested nuclear, chemical and biological weapons in Kazakhstan. • Severe radiation leaks occurred. • Heavy industry in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan polluted the air. • Infant mortality has increased. The Caspian Sea • face severe pollution problems • Pollution and overfishing in the Caspian Sea are killing off sturgeon, an important export in this region. Caspian Sea Sturgeon Caviar The Dead Sea -- Israel • • • • • water level has dropped desalination is one cause used for irrigation lowest spot on earth 1388 feet below sea level. Dead Sea Salt Balls The Aral Sea • severe water level drop • water has been drawn away from the rivers that feed the Aral for irrigation • fishing has been almost destroyed • However, they are working hard to restore the Aral. Sec. 2 Key Points • Countries in the region have modified their environments to meet people’s needs for water for drinking and irrigation. • New technologies and destructive wars have subjected the region’s environment to stress. • People are working to revive areas damaged by past events. Question • What environmental problems does this region face today? End of Slide Show