Ch 24 Notes Slideshow–Oil in Southwest Asia
advertisement

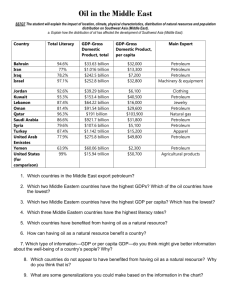
Chapter 24: Oil in Southwest Asia Open your workbook to page 175 and use the following slides to fill in the Geoterms. Geoterms Crude oil: Petroleum after it has come out of the ground and before it has been turn into useful products. Geoterms Nonrenewable resource: a resource that takes so long to make that it can’t be replaced. Geoterms Oil reserves: oil that has been discovered but remains unused in the ground. Geoterms Renewable resource: a resource (like sunlight or wood) that can’t be used up or can be replaced quickly. 24.3 The Geology and Geography of Oil Turn to page 176 in your workbook and use the following slides to answer the questions. How does oil form? Explain the process in at least three steps. The process begins with tiny plants and animals that died in the oceans millions of years ago. Over time, most of them turned to rock. The weight of the water, heat from Earth’s core, and chemical changes turned some of the remains into oil and natural gas. Why is so much oil buried under Southwest Asia? Oil can be found under Southwest Asia because millions of years ago the area was under water. When the Iranian and Arabian tectonic plates hit, they created spaces where oil was formed and trapped. Are oil reserves distributed equally among the countries of Southwest Asia? Explain. Oil is not distributed equally among these countries. The region’s largest country, Saudi Arabia, contains about one quarter of the world’s known oil reserves. Smaller countries like Kuwait also have a lot of oil. Other countries, like Syria and Yemen, have much less oil than others in the region. Use the following chart to complete the map according to the directions on the page. Copy and paste the link to a browser and complete the task on a separate piece of paper. www.youtube.com/watch ?v=0PrSZMOCnWU If oil is mostly made from ancient sea microorganisms and plants, then how is it that oil is found all over the planet? Copy and paste the link to a browser and complete the task on a separate piece of paper. https://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=9Py8Xy9MKo Describe the process of extracting crude oil from the ground, refining it and transporting it to gas stations. 24.4 Oil Wealth and People’s Well Being Turn to page 177 in the workbook and answer the questions using the following slides. How has oil made the people of Southwest Asia better off? Oil money has improved the lives of people in Southwest Asia. life expectancy has increased the number of infants who die in their first year has decreased Why isn’t per capita GDP always an accurate reflection of people’s wealth? Per capita GDP assumes that a country’s wealth is divided equally among its citizens, but that isn’t really true. What are some examples of why some oil countries haven’t been able to end poverty? Yemen: The combination of low oil revenues and a large population has left Yemen poor. Iraq: Former Iraqi president Saddam Hussein used oil money to buy weapons and pay for wars instead of improving life for ordinary Iraqis. Use the following chart to complete the map according to the directions on the page. Copy and paste the link to a browser and complete the task on a separate piece of paper. https://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=lRYhW9wF0 Is&index=5&list=FLlzxc HqTZUYBOmDFcZcV2n Q Iraq used its oil reserves to fight a war in the 1980s. How has Qatar used its fossil fuels for the development of the country now and into the future? 24.5 The Price and Flow of Oil Turn to page 178 in your workbook and fill in the notes using the following slides. What have been the goals of Southwest Asian OPEC members? One goal is to have a steady supply of oil flowing out and money flowing into their countries. Another goal is to keep oil prices steady—not too high or too low. OPEC Members: Use this map to identify the OPEC members on the map on page 178 according to the directions. What two realities have limited OPEC’s power? OPEC can’t control all of the world’s oil sales; it exports less than half of the world’s crude oil. OPEC countries don’t always act as a group. What were the two types of coalition members in the Persian Gulf War? Why were they coalition members? Two types of coalition members were: oil-importing countries who did not want their oil supplies threatened oil-exporting countries who did not want to lose control of their oil reserves. Use the following chart to complete the map according to the directions on the page. Copy and paste the link to a browser and complete the task on a separate piece of paper. https://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=l2TQ8a4LK 3A&list=FLlzxcHqTZUY BOmDFcZcV2nQ Why did the United States fight the first of its wars with Iraq (the Persian Gulf War) in the early 1990s? Quiz Question 1 Crude oil is ________ after it has come out of the ground and before it has been turn into useful products. Answer Petroleum after it has come out of the ground and before it has been turn into useful products. Question 2 A resource that takes so long to make that it can’t be replaced is a _____________________. Answer Nonrenewable resource: a resource that takes so long to make that it can’t be replaced. Question 3 Oil that has been discovered but remains unused in the ground is _____________. Answer Oil reserves: oil that has been discovered but remains unused in the ground. Question 4 What is the first step in the process in how oil formed? a) Humans making it on land b) Dead animals and plants at the bottom of the ocean c) Evolution Answer B. Dead animals and plants at the bottom of the ocean The process begins with tiny plants and animals that died in the oceans 5.________of years ago. Over time, most of them turned to 6._____. The weight of the 7.______, heat from Earth’s core, and 8.________changes turned some of the remains into 9.____ and 10._______ ___. Answers The process begins with tiny plants and animals that died in the oceans millions of years ago. Over time, most of them turned to rock. The weight of the water, heat from Earth’s core, and chemical changes turned some of the remains into oil and natural gas. Oil can be found under Southwest 11.____ because millions of years ago the area was under 12._____. When the Iranian and Arabian tectonic 13.______ hit, they created spaces where oil was 14._______ and 15.________. Answers Oil can be found under Southwest Asia because millions of years ago the area was under water. When the Iranian and Arabian tectonic plates hit, they created spaces where oil was formed and trapped.