Urbanization - ISA
advertisement

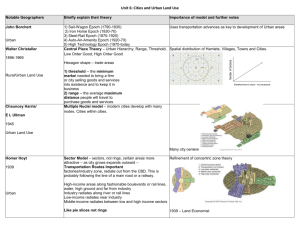
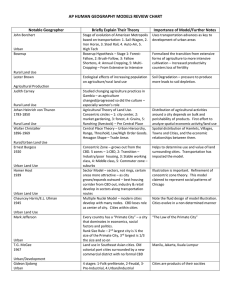
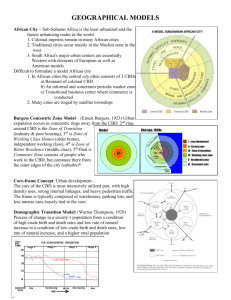
Urban Geography How cities function, their internal systems and structures, and the external influences on them. 2 Ways of studying Urban Geography Systems of cities: how cities influence the landscape around them, how they connect to one another, and how they are distributed nationally and globally Internal cities: internal workings of cities, analysis of patterns of land use, racial and ethnic segregation, architecture, intra-city transportation, cycles of construction and development Uses census data, and narrative accounts Urban Areas What’s an “urban” area? Nucleated-clear core area(s), people that live there have non-agricultural jobs Central City Usually surrounded by Suburbs-nucleated spaces that use much land for residences but are not self-sufficient Modern cities and towns so close together they form an urbanized area that is continuously built up landscapes and buildings=Physical city Metropolitan Area Urban Hierarchy Clustered settlements range in size-arranged by complexity of their centralizing functions Smallest to Largest Hamlet-small cluster of farms, and basic services Village-small cluster of homes, and more specialized services Town-larger than village, has more specialized services (bank, schools, library) has a hinterland (area dependent on the town) City-larger population, functional specialization, larger hinterlands, greater centrality, Central Business Districts (CBD) Megalopolis-multiple cities that have grown together- Social Life of Urban Areas Louis Wirth says 3 characteristics of cities that set it apart from rural areas Large Size- too many acquaintances to keep track of everyone’s personal life Many people but don’t know most very well High Density-people have highly specialized jobs, each person in city serves specific purpose-people compete for space (high cost of living), greater differences in rich and poor Social heterogeneity-lots of diversity, freedom and independence not available in rural ares Origin and Evolution of Cities Ancient and Early River Civilizations: Formative Era Nile, Mesopotamia, Indus River, China As populations grew, the need for decision makers to distribute food came to be (urban elite) Functions of Ancient Cities: Centers of power-government headquarters Religious centers-priests, temples, shrines Economic centers-markets, merchants, traders Educational centers-educators for the urban elite Urbanization around Mediterranean City-states-self-governing communities plus the surrounding countryside Athens, Sparta, Thebes Rome-becomes an urban empire connected by roadways and waterways Urbanization in China Han Dynasty (ruled during Roman Empire) will have largest city in world Chang’an and later Luoyang Located on rivers and near Silk Road trade route Connected by roads, rivers, canals Medieval cities Roman empire falls and cities take a hit in Europe Venice and Genoa (because of sea trade) remained strong Churches were center of Medieval European cities By 1000 AD the largest cities were in Asia Baghdad, Constantinople (Istanbul), Kyoto, Chang’an, Hangchow. Not until 1800 did Europe have the most populated city in the world-London Pre-industrial Cities Pre-industrial cities were the centers for culture (because industry had not moved in yet!) Primate cities-larger than other cities in the area and representing a national culture Kyoto-primate city for old Japan, Paris, London However! One major difference is that religious buildings dominated landscapes of cities in Middle East, Europe, the Americas but not Africa or East Asia Trade routes and networks determined a cities success and growth-called mercantile city where trade was central to design Industrial Cities Because of the Industrial Revolution-the manufacturing city emerged-where factories attracted laborers from all over boosting major population growth in urban areas Transportation to and fro and within develops Problems will grow quickly but so will solutions like government intervention and city planning and zoning World Cities and Megacities Manufacturing cities begin to decline as outsourcing and LDC’s are used for that type of labor World Cities include: Largest regional cities: New York, Tokyo, London Second Tier cities: Chicago, Los Angeles, Brussels, Frankfurt, Paris, Zurich, Sao Paolo, Singapore, Third Tier cities: Bangkok, Bombay, Hong Kong, Manila, Osaka, Seoul, Taipei, Buenos Aires, Caracas, Mexico City, Rio de Janeiro, Johannesburg Tiers of World Cities Based on centrality of these services Business-corporations, banks, insurance companies, stock exchanges, legal and accounting firms, airports, busy harbors, junction of rail and highway networks Consumer-retail business, entertainment and cultural offerings (plays, concerts, restaurants, museums) Public-government headquarters, ambassadors, lobbyists Megacities Term created by UN in the 1970’s 25 total megacities=population over 10 million Some include: Tokyo Mexico City Seoul New York City Sao Paulo Mumbai Delhi Shanghai Los Angeles Osaka Functions of Cities Transportation centers-where major routes converge (roads, railroads, sea traffic, air transport) Special Function Cities-engaged in mining, manufacturing, or recreation Provide goods and services for surrounding area from a central place Economic Base of Cities City workers provide services outside city- “export activities” money flows into city-basic sector of a cities economy. Those who produce goods or services for residents of city-non-basic or service sector Some geographers compare number of workers in service and basic sectors-called base ratio of a city The Changing City Borchert’s 4 Stages in the Evolution of American cities: 1. Sail-Wagon Epoch(1790-1830)-technologies determined job opportunities of people entering city 2. Iron Horse Epoch (1830-1870)-railroad technology changed nature of trade and employment 3. Steel-Rail Epoch (1870-1920)-steel industry transformed urban America and job opportunities of workers 4. Auto-Air-Amenity Epoch (1920-1960)- internal combustion engine came to dominate lifestyles, employment, and economic base of cities Models of Urban Systems 2 theories of settlement geography-patterns of settlement on earth Rank-Size Rule-true for urbanized cities in the US not in LDC’s or in regions with a dominate primate city-nth largest city will be 1/nth the size of the largest city-2nd largest city will be ½ the size of the first ranked city . Models of Urban Systems Central Place Theory-cities are centers for distribution of goods and services for non-urban populations The landscape is divided into noncompeting market areas— complementary regions where each area and its merchants have a monopoly Market areas form a series of hexagons, no area is unserved, no two centers Central place is at the center of each hexagon, supplies all goods and services to that area Market area is determined by the number of goods and services Some hexagons have smaller ones within it, hierarchy of central places Internal Cities Analyze the internal land space of a city, varying uses Use several factors to analyze Accessiblity High cost of accessible space Transportation Societal and cultural needs Models of Urban Land Use Concentric Zone Model-Cites grow outward from a central area (CBD) in a series of concentric rings Sector Model-variant of concentric zone theory, cities develop in sectors not rings from a (CBD) Multiple-Nuclei Model-a city grows from multiple nodes, not just from a (CBD) Patterns of class, age, gender, race, and ethnicity Social area analysis-takes census data and overall picture of how various peoples are distributed within an area (city) Most Urban Land Models support the idea that people prefer to live near others with similar characteristics Social Class, Age and Marital Status, Gender (feminization of poverty), Race and Ethnicity clustered into (ghettos) from historical segregation patterns in US