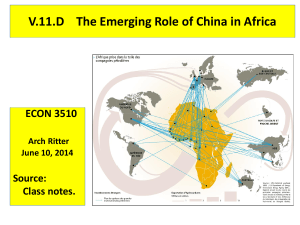
Changing china, changing Africa: future contours
advertisement

CHANGING CHINA, CHANGING AFRICA: FUTURE CONTOURS OF AN EMERGING RELATIONSHIP Peter Draper South African Institute of International Affairs (presenter) Martyn Davies and Hannah Edinger Frontier Advisory OVERVIEW • Background • China in Africa: Current Frame • China’s Economic Rebalancing – Implications for Africa • Broader Considerations Background • Moving beyond the current frame • Key driver: Chinese economic rebalancing China in Africa: Current Frame • Politics/security • FOCAC • Conflict zones and human rights • Non-interference • Economics • State capitalism (SOEs; policy banks; ODA) • Resources • Trade structure NB: ‘Deindustrialization’ concerns • SEZs and their development impacts China in Africa: Current Frame • Social • Corporate social responsibility • Labour practices • Environmental impacts • Culture • Formal engagements (eg Confucius institutes) • Informal/community (eg Chinese traders) China’s Economic Rebalancing – Implications for Africa • Chinese drivers • Increased domestic cost structure • Concerns over resource-intensive manufacturing • Major problems in the financial sector • Emphasis on new sectors (services) • Domestic competition China’s Economic Rebalancing – Implications for Africa • Implications for Africa • Increased outward FDI from China • Changing composition of OFDI towards middle-sized private firms • Role of SOEs will probably decline, relatively • Therefore less emphasis on resource acquisition, relatively • And relatively declining emphasis on role of policy banks/finance China’s Economic Rebalancing – Implications for Africa • Is Africa the ‘final frontier’ for export-oriented manufacturing FDI? • Will take time, perhaps a long time • Enduring Chinese advantages • Broader Asian advantages • African challenges • But consider the ‘flying geese’ paradigm • In relation to some emerging African advantages, particularly demographic 9 African Population growth dynamics Mostly a west and east African phenomenon Rapid growth and urbanization, mostly from low bases, holds out the ‘middle class’ proposition China’s Economic Rebalancing – Implications for Africa • The most likely to benefit are those that: • Grasp the governance reform nettle • Are favoured by geography and resource endowments • Welcome FDI by MNCs • Chinese SEZs could be a key policy tool to faciitate this process Broader Considerations • Smarter Chinese diplomacy towards Africa will be required to service diversified footprints • Commercial (project oriented): • targeting new sectors • working more with the Chinese private sector • Economic (rules of the game): • Greater emphasis on good governance in order to secure Chinese commercial interests • Promoting trade liberalization • Securing investments through BITs Broader Considerations • Politics, society and culture • Policy of non-interference could become increasingly strained • Increasing contact with emerging African middle classes will require greater attention to human rights agendas, corporate social responsibility, labour rights, and the environment