Muscular System NL Ch 10-2
advertisement

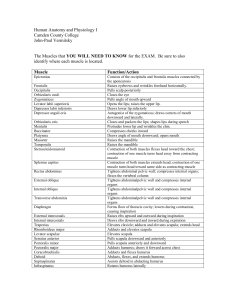
Chapter 10 Muscular System Interactions of Muscles Muscles can be classified into 4 functional groups! – Synergist- they help prime movers by adding extra force, reducing unneccessary movements. – Fixators- Holds parts of the body in proper position for the action of other muscles, primarily postural muscles. Interactions of Muscles Muscles can be classified into 4 functional groups! – Prime Mover- A muscle that provides the major force for producing a specific movement. – Antagonists- muscles that oppose, or reverse, a particular movement. Muscles Work!! Muscles never push they just pull!! Muscles are usually in pairs because whatever one muscles or muscle group can do, there is another muscle or group of muscles that “undoes” the action. Naming of the Skeletal Muscles! Skeletal muscles are named according to a number of criteria, each of which describes the muscle in some way. Paying attention to these cues can simplify the task of learning muscle names and actions. Naming of the Skeletal Muscles! 1. Location of the Muscle (temporalis) 2. Shape of the Muscle (Deltoid) 3. Relative size of the Muscle (Maximus, minimus) 4. Direction of the Muscle Fibers (rectus –straight: oblique, transverse mean to run at right angles.) Naming of the Skeletal Muscles! 5. Number of Origins (triceps and biceps) 6. Location of the attachments (Sternocleidomastoid) 7. Action (adductor longus) Muscles of Facial Expression Head/Neck Orbicularis Oculi The WINKER A ringlike band of muscle, called a sphincter muscle, that surrounds the eye. It lies in the subcutaneous tissue of the eyelid Closes eye in blinking It also aids in the compressing the tear glands Orbicularis Oris The “Pucker Up” Muscle Sphincter muscle that surrounds the lips. Closes and puckers the lips. Often called the “kissing muscle” Zygomaticus Extends from the zygomatic arch downward to the corner of the mouth Raises corner of mouth when smiling and laughing Platysma The Frowner Thin sheet like superficial neck muscle. Plays a role in facial expression. Tenses skin of neck. (e.g. during shaving) Epicranius The epicranius covers the upper part of the cranium and consists of two muscular parts. – Frontalis and Occipitalis Frontalis Lies over the frontal bone Wrinkles forehead Occipitalis Moves scalp Sternocleidomastoid Praying Muscle Long muscle in the side of the neck that extends upward from the thorax to the base of the skull behind the ear Pulls head to one side Masseter “The Chewer” A thick flattened muscle that can be felt just in front of the ear when the teeth are clenched Elevates mandible Closes mouth Buccinator Blower or Whistler!! Thin, horizontal cheek muscles; Draws corner of mouth laterally, compresses cheek , well developed in nursing infants. Muscles that Move the Pectoral Girdle Chest/Back Muscles Trapezius o A large triangular muscle in the upper back that extends horizontally from the base of the skull and the cervical thoracic vertebrae to the shoulder o Rotates scapula. Rhomboideus The Rhomboids are very thin muscles which have tremendous responsibility. Connects the upper thoracic vertebrae to the scapula. Raises the scapula and adducts. Serratus Anterior A broad curved muscle located on the side of the chest Arises from narrow strips on the upper ribs and extends along the medial wall of the axilla to the ventral surface of the scapula Pulls scapula anteriorly and downward Used to thrust the shoulder forward when pushing something. Muscles that move the Arm Chest/Arm Pectoralis Major A thick fan shaped muscle located in the upper chest. Extends from the center of the thorax through the armpit to the humerus Adducts and medially rotates humerus; draws scapula anteriorly and inferiorly. Pulls the arm forward and across the chest. Pectoralis Minor A thin, flat muscle that lies beneath the larger pectoralis major Stabilizes scapula by drawing it inferiorly and anteriorly against thoracic wall Teres Major Medially rotates and adducts arm. Stabilizes shoulder joint Connects the scapula to the humerus Teres Minor Small muscle connecting the scapula to the humerus. Rotates arm laterally Infraspinatus Occupies the depression below the spine of the scapula on its posterior surface. Attach the scapula to the humerus; helps to hold humeral head in glenoid cavity of scapula. Laterally rotate arm Latissimus Dorsi It is a wide, triangular muscle that curves upward from the lower back, around the sides, and to the armpit. Extends, adducts, and rotates arm, pulls shoulder down or back Deltoid Muscle Abducts, extends, and flexes the arm It is a thick, triangular muscle that covers the shoulder joint. Muscles that Move the Forearm Biceps Brachii It is a fleshy muscle that forms a long, rounded mass on the anterior side of the arm Connects the scapula to the radius and ulna Flexes forearm at elbow Rotates hand laterally Brachialis A large muscle beneath the biceps brachii Connects the shaft of the humerus to the ulna Flexes forearm at elbow Brachioradialis Connects the humerus to the radius. Flexes forearm at elbow Triceps Brachii Has three heads and is the only muscle on the back of the arm Connects the humerus and scapula to the ulna It is the primary extensor of the elbow. Flexes forearm at elbow Extensor Digitorum Runs medially along the back of the forearm. Connects the humerus to the posterior surface of the phalanges and then extends the fingers. Extends hand at wrist joint Muscles of the Abdominal Wall External Oblique A broad, thin sheet of muscle whose fibers slant downward from the lower ribs to the pelvic girdle. Tenses abdominal wall Compresses contents Internal Oblique A broad, thin sheet of muscle located beneath the external oblique Runs up and forward from the pelvic girdle to the lower ribs. Tenses abdominal wall Compresses contents Rectus Abdominis Long, straplike muscle that connects the pubic bones to the ribs and sternum. Tenses abdominal wall Compresses contents Flexes vertebral column Muscles that make up the Leg Biceps femoris Has 2 heads, one attaches to the ischium and the other attached to the femur. Passes along the back of the thigh on the lateral side and connects to the proximal ends of the fiubla and tibia. Flexes and rotates leg laterally and extends thigh. 1 of the hamstring muscles Semitendinosus (the 2nd muscle of the hamstring) Semitendinosus- long bandlike muscle on the back of the thigh. Connecting the ischium to the proximal end of the tibia. Flexes and rotates the leg medially and extends the thigh Semimembranosus (the 3rd muscle of the hamstring) Semimembranosus the most medially located muscle in the back of the thigh; it connects the ischium to the tibia. Flexes and rotates the leg medially and extends the thigh Sartorius An elongated, straplike muscle that passes obliquely across the front of the thigh and then descends over the medial side of the knee. Connects the ilium to the tibia and flexes the leg and the thigh. Flexes leg and thigh Abducts and rotates thigh laterally Quadriceps Femoris This is a large fleshy muscle group Occupies the front and sides of the thigh and is the primary extensor of the knee Includes….Rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius (I am not holding you accountable for the last one) These parts connect the ilium and femur to a common patella tendon, which passes over the front of the knee and attaches to the patella. Rectus Femoris Extends leg at knee Vastus Lateralis Extends leg at knee Vastus Medialis Extends leg at knee Muscles that move the Thigh Gluteus Maximus The largest muscle in the body and covers a large part of each buttock Connects the ilium, sacrum, and coccyx to the femur by fascia of the thigh and extends the thigh. Extends thigh at hip, helps to straighten the lower limb, also used to raise the body from a sitting position Gluteus Medius Partly covered by the gluteus maxium. Its fibers extend from the ilium to the femur Abducts and rotates thigh medially Adductor Longus A long triangular muscle that runs from the pubic bone to the femur Adducts, flexes, and rotates thigh laterally Adductor Magnus The largest adductor of the thigh. A triangular muscle that connects the ischium to the femur. Adducts, extends, and rotates thigh laterally. Gracilis A long straplike muscle that passes from the pubic bone to the tibia. Adducts thigh Flexes leg at knee Muscles that move the Foot Tibialis Anterior An elongated, spindleshaped muscle located on the front of the leg Arises from the tibia, passes medially over the distal end of the tibia, and attaches to bones of the foot Dorsiflexion and inversion of foot Extensor Digitorum Longus This is situated along the lateral side of the leg just behind the tibialis anterior. Dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot Extension of toes Gastrocnemius On the back of the leg forms part of the calf. Plantar flexion of foot and flexion of leg at knee Soleus A thick, flat muscle located beneath the gastrocnemius and together these two muscles form the calf of the leg Arises from the tibia and fibula and extends to the heel Plantar flexion of foot Fibularis Longus It is a long, straplike muscle located on the lateral side of the leg. It connects the tibia and the fibula to the foot. Plantar flexion and eversion of foot Supports arch