Skeletal, Muscular and Nervous Systems
advertisement

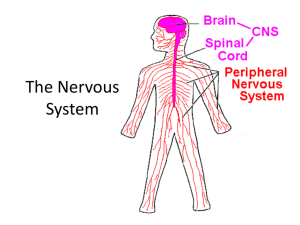
Skeletal, Muscular and Nervous Systems Skeletal System ►The Five main roles of your skeletal system: Provides support Protects internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produces materials needed by the body Skeletal System ►The center of your skeleton is the backbone, or vertebral column. ►It consists of 33 vertebrae. ►It protects the spinal cord. ►The skull protects the brain. ►The ribs protect the heart, lungs and other internal organs. Skeletal System ►Many skeletal bones act as levers for movement. They provide a point of attachment for skeletal muscle. ►Let’s think of some examples. Skeletal System bones store calcium and phosphorous, which are released into the body when needed. ►The breastbone and femur produce red blood cells. ►Your ►Joint: Skeletal System A point where to more bones come together. ►Cartilage: A tough supportive tissue that is softer and more flexible than bone. ►Ossification: cartilage hardens and turns into bone. Remember, babies have approximately 100 more bones than adults. Cells continue to repair themselves after ossification, even when broken. Skeletal System ►Compact bone and spongy bone make bones hard, yet light. ►Bone marrow: fills the spaces in bone. Red marrow: produces blood cells. Yellow marrow: stores fat. Skeletal System ►Bone joints allow for movement, protecting from friction and force. ►Two types of joints, immovable (skull) and movable. ►Types of movable Pivot Gliding Ball and socket Hinge Skeletal System ►Ligament: hold bones together. ►Osteoporosis: bones become weak due to mineral loss. ►Exercise helps increase the strength of bone. ►Fracture: The break of the bone. Several different kinds of fractures. Skeletal System Injuries ►Sprain: An overstretched or torn ligament. R.I.C.E. to treat a sprain. ►Dislocation: Bone ends forced out of their proper location. The bones need to be put back into location and then braced until they heal. ►Torn Cartilage: Cartilage between bones is torn. Typically repaired with surgery. Quite common in the knees. ►Overuse Injuries: Can happen for various reasons, although poor practice in sport and work are often the cause. Skeletal System ►Scoliosis: Curvature of the spine. ►Kyphosis: Curvature of upper spine. ►Lordosis: Curvature of lower spine. Muscular System ►There are three types of muscle tissue in the body ►Smooth Involuntary muscle causing movement in the body. These are found in intestines and blood vessels. Muscular System ►Cardiac This type of muscle only found in the heart and is involuntary ►Skeletal These are voluntary muscles that control motor movement of our body. They are attached to your skeleton. Muscular System ►Muscle Tone: A continuous slight tension in your muscles. Examples? ►Atrophy: The weakening and shrinking of muscle tissue. ►Hypertrophy: The strengthening and enlargement of muscle tissue. Muscular System ►Skeletal muscles work in opposition of each other. For example, the biceps oppose the movement of the triceps. Muscle Injuries ►Strain: a pulled muscle. ►Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendon. ►Muscle Cramps: Strong, uncontrolled muscle contraction. Often caused by dehydration, lack of electrolytes and overuse. ► http://video.about.com/sportsmedicine/Pulle d-Groin-Muscle.htm Muscle Injuries ►How can we prevent injury to the muscle? Nervous System ►The system of the body which receives information internally and externally, process the information, and then develops a response. Nervous System ►Neuron: a cell which is the basic structural unit of the nervous system. ►Three types of neurons Sensory Interneurons Motor Neurons Neurons ►Sensory: These neurons gather information from outside your external and internal environment. ►Interneurons: Receive messages from sensory neurons. These neurons are located in the brain and spinal cord. ►Motor Neurons: Neurons that send commands to muscles and glands to react. The BRAIN The BRAIN ►The Central Nervous System (CNS): Includes the brain and spinal cord, and is the control center of the body. ►Cerebrum: Eighty five percent of the brain’s weight. There are two halves, separated by the corpus collusum. It controls speech, movement, abstract and analytical thought. The BRAIN ►Cerebellum: Coordinates body movements and provides balance. ►Brain Stem: Contains the midbrain, pons and medulla. All of these are responsible for involuntary actions in the body. It contains the midbrain, pons and medulla Spinal Cord ►A thick column of nerve tissue linking the brain to most of the nervous in the peripheral system. ►The vertebrae of the backbone surround and protect the spinal cord. ►It’s like the superhighway of your nervous system. Information is passed throughout your body via the spinal cord. ►An Reflexes automatic response to stimuli. ►What is the stretch reflex? ►How does it apply to exercise? Peripheral Nervous System ►The network of nerves that links the rest of your body to your brain. ►Sensory Division: Nerves from your external and internal environment that carry information to the CNS. ►Motor Division: The nerves that carry a response from the CNS to the rest of your body. Two divisions, somatic and autonomic. Peripheral Nervous System ►Somatic Nervous System: Motor nerves that carry signals for voluntary muscle movements, such as chewing and throwing. ►Autonomic Nervous System: Motor nerves regulate involuntary muscle movements, such as breathing and digestion. Injury and Disease of Nervous Systems ►Concussion: A bruise of the brain caused by a blunt force to the head. ►Coma: A prolonged period of deep unconsciousness, caused by disease, trauma or drugs. ►Paralysis: Loss of the ability to move and feel a part of the body. Injury and Disease of Nervous Systems ►Meningitis: A highly contagious disease that causes inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain an spinal cord. ►Rabies: An infection of the CNS caused by the bite of a rabid animal. THE END