3.5.2: Photosynthesis
advertisement
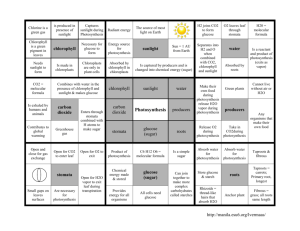
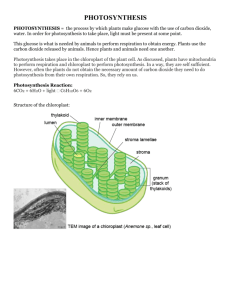
S.HS.3.5.2 The student understands the Sun is the primary source of energy for life through the process of photosynthesis What is Photosynthesis? The process of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions. -For living organisms it is the most important chemical reaction on our planet What is the equation for the chemical reaction for photosynthesis? chlorophyll enzymes The equation described: Chlorophyll enzymes 6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Low energy Low energy High energy Low energy Six molecules of carbon dioxide react with six molecules of water to form 1 molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen. Energy moves through the food chain from life form to life form. The first step is photosynthesis in which the sun's radiant energy, that pours onto the earth everyday, is turned into carbohydrate(C6H12O6) molecules. These carbohydrates are used by nearly all living things as fuel for energy, and as building blocks to biosynthesize larger molecules such as polysaccharides, protein, nucleic acids and lipids. DESCRIBE PHOTOSYNTHESIS It is the process of changing light energy to chemical energy stored as sugar It occurs in plants and algae Plants need light energy, CO2, and H2O It takes place in the thylakoids of chloroplasts, Chlorophyll the green pigment in plants is used to absorb wavelengths of light 2 stages: light dependent and Calvin Cycle or light independent WHAT HAPPENS DURING PHOTOSYNTHESIS? Plants capture light energy and use that energy to make glucose Sunlight provides the energy needed by chlorophyll to change molecules of carbon dioxide and water into glucose Oxygen is also released in this reaction CONTINUED…… Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through pores called stomata CO2 combines with the stored energy in the chloroplasts through chemical reactions to make glucose The sugar is moved through cells in the leaf to the roots, stems and fruits of the plants Some of the sugar is used right away by the plant for energy; some is stored as starch; and some is built into plant tissue WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT TO US? We cannot make our own food (glucose, energy), we must get our food from plants. Plants are the first step in the food chain. PATH OF ENERGY The flow of energy through life is a one-way process. Energy is not recycled. It is eventually lost as heat to space. Energy passes through the food chain. The lower on the food chain/trophic level, the more energy is available. As energy moves up the food chain there is less and less of it to go around. That's the main reason there aren't as many big fierce predators (lions and tigers and bears-Oh my!) compared to the herbivores (mice, rabbits and deer). Not enough energy for them! TROPHIC LEVELS! The plants only get a small amount of the solar energy that hits the earth. And.... The herbivores only get a little bit of the energy that hits the plants. And.... The carnivores and decomposers only get a little bit of the energy that was eaten by the herbivores. Only 10% energy is gained each trophic level Why is this important to us? Do you breathe? The oxygen released during photosynthesis is necessary for most living things. WHY OXYGEN IS IMPORTANT? Oxygen is not just used by our bodies for respiration. It's not just in the air. It's the most abundant element on earth. And about 65 percent of the mass of your body is oxygen. QUESTIONS 1. What is the term for the transfer of energy and matter within a food web? 2. The first stage of photosynthesis in a chloroplast is? 3. Which molecule in plant cells first captures the radiant energy from sunlight? ANSWERS 1. A food web showing the tropic levels and where energy is transferred 2. Light Dependent Reaction 3. Chlorophyll pigment QUESTIONS 4. Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into? 5. A student is collecting gas given off from a plant in bright sunlight at a temperature of 27 °C. The gas being collected is? 6. If carbon dioxide is removed from a plant’s environment, what would you expect to happen? ANSWERS 4. Oxygen and Sugars 5. Oxygen 6. No sugars would be produced Prepared are two beakers with identical sprigs of water plants as shown. One was placed in the shade and the other by a lamp. Then the distance of the beakers from the lamp was changed. Bubbles were counted given off by each plant. Read the graph. 7. QUESTIONS 7. If the student later tested the bubbles collected in the test tube, what would she find they are made of? How do you know? 8. At what distance from the light source was the greatest number of bubbles produced per minute? 9. What do the student’s data show? ANSWERS 7. Oxygen because release oxygen gas during the first stage of photosynthesis 8. 5 cm-closest to the light source 9. The closer to the light source the more oxygen bubbles produced.