The Breathing Process An Explanation about the Lung Model
advertisement
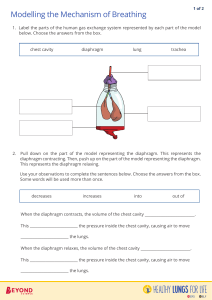
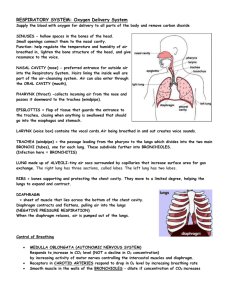
The Breathing Process An Explanation about the Lung Model Breathing In • Breathing in is called INHALING or INSPIRATION. • When you inhale, you fill your lungs with air. Breathing Out • Breathing out is called EXHALING or EXPIRATION. • When you exhale, you push air with more carbon dioxide out of the lungs. Breathing Process • Breathing is an involuntary process because we do not think about it when we do it. • Breathing is important to keep us alive. Breathing Body Parts • The lungs are important and delicate organs. They are protected by a set of bones called rib cage. • The rib cage forms the chest cavity where the lungs are found. • There is a sheet of muscles at the lower part of the chest cavity called the diaphragm. • The diaphragm separates the chest from the abdomen. Pulling it down… • When you pulled down the string tied to the rubber sheet, the space inside the bottle increased. • This action represents the contraction and downward movement of your diaphragm. Pulling it down … • As the diaphragm moves down and the rib muscles contract, the chest wall is lifted upward and outward. • The chest cavity takes up more space and the lungs expand. • When this happens, the air pressure inside the lungs is less than the air pressure outside the body. Pulling it down… • When the air pressure inside is lesser the air outside moves into the nostrils. • This movement of air is called INHILATION. Letting it go…. • When you released your hand from the rubber balloon, the balloons inside returned to their original position. • As the diaphragm relaxes, the rib muscles also relax so the chest cavity becomes smaller. Letting it go …. • The pressure inside the chest cavity becomes greater than the pressure outside. • The difference in pressure pushes the air out of the lungs. • When air is pushed out of the lungs then it is called EXHALATION. Looking Back • The rib cage and the diaphragm are important in the breathing process. • When you inhale, the ribs move upward and outward while the diaphragm moves downward. Breathing In Movements • The volume of the chest cavity becomes larger. • The pressure inside it is lower than the air pressure outside your body. • Air is drawn into the lungs by the atmospheric pressure outside the body. Looking Back • When you exhale, the ribs move downward and inward while the diaphragm moves upward. • These actions make the chest cavity smaller. Breathing Out Movements • The pressure in the chest cavity becomes greater than the air outside the body. • This causes the air to rush out of the lungs and out of the body. THE END