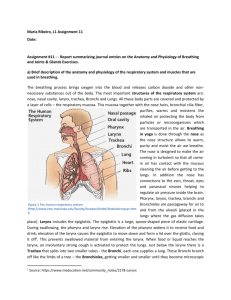
Structure of the Human Respiratory System
advertisement

CHAPTER 1 : RESPIRATION 1.1 : The Human Breathing Mechanism 1.2 : Transport of Oxygen 1.3 : Cell Respiration 1.4 : Importance of a Healthy Respiratory System 1.1 : Human Breathing Mechanism Structure of the Human Respiratory System 1.1 : Human Breathing Mechanism Structure of the Human Respiratory System Bronchioles : Nose : • Fine air tubes; • Always moist with • Ends in cluster of fine hairs to filter the air sacs (alveoli) air Alveoli : Trachea : • Surrounded by • Strong muscular blood capillaries tube; has rings of cartilage Bronchi : • Each bronchus branches into bronchioles 1.1 : Human Breathing Mechanism Structure of the Human Respiratory System Rib muscles : • Called intercostal muscles – contract / relax and caused the ribs move upwards / downwards • Causes thoracic cavity (chest cavity) to expand or contract allowing breathing in & out Ribs : • Works together with breastbone (sternum) to protect the lungs Diaphragms : • Large sheet of muscle that can contract and or relax 1.1 : Human Breathing Mechanism Breathing and Respiration Breathing : • Mechanical process which alternately draws & expels air into & out of the lungs Respiration : • Chemical process that takes place in the cells of the body • Aka internal or cell respiration Normally we breathe from 15 – 20 times per minute Rate of breathing increases during active work / exercise 1.1 : Human Breathing Mechanism The Breathing Mechanism Inhalation : • Breathing in air Exhalation : • Breathing out air Pathway of inhalation : • Nose – trachea – bronchi – bronchioles – alveoli Passing through the nose, the air is : • filtered; • Warmed to body temperature • Moistened by mucus 1.1 : Human Breathing Mechanism The Breathing Mechanism Inhalation : External intercostal muscles contract Ribs are raised & the chest moves forwards Diaphragm muscles contract, is lowered & flattened Thoracic cavity expands Air pressure in the thoracic cavity decreases Air is rushed into the lungs 1.1 : Human Breathing Mechanism The Breathing Mechanism Exhalation : External intercostal muscles relax Ribs are lowered & the chest moves inwards Diaphragm muscles relax & curves upwards Thoracic cavity becomes smaller Air is forced out from the lungs. 1.1 : Human Breathing Mechanism Model to show the Action of the Diaphragm 1.1 : Human Breathing Mechanism Model to show the Action of the Diaphram INHALATION When the sheet of rubber (diaphragm) is pulled down, the volume in the bell jar (thoracic cavity) increases Air pressure in the bell jar (thoracic cavity) decreases Air from outside rushes into the balloons (lungs) via the Y-tube (trachea & bronchi) Balloons expand as filled with fresh air EXHALATION When the sheet of rubber (diaphragm) is pushed upwards, the volume in the bell jar (thoracic cavity) decreases Air pressure in the bell jar (thoracic cavity) & in the balloons (lungs) increases Air is forced out through the Y-tube (bronchi & trachea)