Document
advertisement

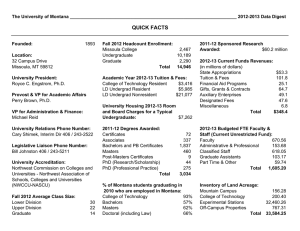
Social Networks in Healthcare Health Quality Learning Group Monthly Call – March 16th 10 – 11 am The Network Lens Org. Chart Understanding • • • • Network Visualization This is the same IT department seen in two ways – Firstly through a traditional organizational chart that illustrates reporting lines. Then a network map created by studying work and communication flows Blue nodes connecting directly to one another both with internal team members and external team members Green (supervisor role) communicating with each (not always) What else does this tell us? Valdis Krebs orgnet.com Influence of Social Networks Some ways that social networks effect us • Gain Weight or Lose Weight • Quit or continue smoking • Suicide • Happiness •A person is 15% more likely to be happy if directly connected to a happy person (1 degree) • At 2 degrees 10% more likely to be happy • At 3 degrees 6% more likely to be happy • Each unhappy friend deceases the likelihood of happiness 7% Source: Christakis and Fowler The Obesity “Epidemic” • 66% of Americans are overweight or obese • From 1990 to 2000, the percentage of obese people in the USA increased from 21% to 33% Green Node: nonobese Yellow Node= obese (size of circle is proportional to BMI) 1975 Source: Christakis and Fowler 1990 Mapping Networks Obvious clusters, not well integrated Core not dense enough St. Patrick Hospital in Missoula Montana – Initial Map before MRSA Initiative Core not diverse – too small Mapping Networks Core is much denser Core is more diverse – more department and roles represented St. Patrick Hospital in Missoula Montana – Second Round Map Still room for improvement Working with Maps 1. Comparing clusters / lack of connections to infection / colonization rates? Can we learn something? 2. Who’s on the map and who is missing? Any surprises? Focus your efforts to get more people involved and connected. 3. Identify people with common interests and create the necessary opportunities for them to work together – close the triangles Working with Maps 4. Print maps – large and small – display on units – people are instantly engaged when they see their names on a map 5. Use maps in presentations to senior leadership – how has the network changed – where can it be better – who can help? Social Network Mapping and Positive Deviance • We are using Positive Deviance (PD) with the hope that it will start to change how people interact and work • Social network mapping helps measure social interaction – it takes a snapshot in time • By mapping at the start and end of the project, we hope to see a change in the social network maps that will indicate a change in culture and behaviour, or at the very least – a change in how people are relating and working together • The first map may also be useful on its own by pinpointing ‘champions’ or ‘nodes’ that we may be currently unaware of – these individuals may be important people to engage in PD!