Temperature and Rates
advertisement

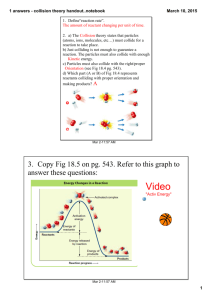
The heat is on Monday, 13 April 2015 C2.19 Speeding up reactionsTemperature LO: Explain reaction rates in terms of particles and how temperature affects this Starter: Imagine you have a jelly baby Your task is to dissolve this in water faster than anyone else in the room. How will you do this? Write your method down in your book Please put your bags & coats away Objectives • Define activation energy. • Describe the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. • Explain the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. A brief background • Reactions take place when particles collide with a certain amount of energy. • The minimum amount of energy needed for the particles to react is called the activation energy and is different for each reaction. Activation – the minimum amount • In your energy own words write a definition of activation energy – 3have minutes of energy particles must to react Objectives • Define activation energy. • Describe the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. • Explain the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. Collision theory • The energy of collisions and the frequency (how often) affect the rate of reaction • We are going to investigate how temperature affects this. 2Mg + 2HCl 2MgCl + H2 • Investigating how temperature affects reaction rate between magnesium ribbon and hydrochloric acid. Answer these questions in your book: 1. What is the dependent varible? 2. What is the independent varible? 3. Which varibles must be kept constant? Wear your goggles Method Room temp. Hcl Cold Hcl 1. Collect equipment listed on sheet 2. Measure out 10 cm3 of cold hydrochloric acid 3 cm Magnesium ribbon 3. Take temperature and record it in the table below 4. Add a strip of magnesium and start timer 5. Stop clock when all magnesium has reacted 6. Record results in table 7. Repeat steps 2-6 for room temperature acid and warm acid 8. Tidy away 9. Stick your sheet in your book Hot Hcl Method 1. Measure out 10cm3 of chilled HCl into a boiling tube 2. Take the temperature and record it 3. Add 3cm length of Mg ribbon and start stop watch, 4. Record how long it takes for the Mg to be used up and record it in the table 5. Repeat using room temperature and then warm acid Copy and complete Our fastest reaction was __________ Our slowest reaction was __________ Our investigation showed that as temperature increased the rate of reaction __________________ Objectives • Define activation energy. • Describe the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. • Explain the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. Explaining the effect of temperature • So how can we explain this in terms of particles? Particle temperature animation • What happens when the temperature is increased? WHAT WILL THIS DO TO COLLISIONS? 2 minutes in pairs to explain FULLY SUMMING UP • Increasing the temperature increases how often particles collide (frequency of collision) AND how much energy they collide with This means there are far more successful collisions every second = faster rate of reaction Objectives • Define activation energy. • Describe the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. • Explain the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. PROVE IT COMPLETE THE WORKSHEET YOU HAVE 5 MINUTES 1. What happens if particles collide with less energy than the activation energy? E 2.Describe what happens to the rate of reaction when the temperature is decreased. C 3. Use the graph to answer these questions; a) Explain in terms of particle why the rate of reaction doubles between 60C and 80C. b) Estimate the rate of reaction at 30C. A* C2.19 1. Nothing / no reaction 2. The colder the slower/ it gets slower / slows down 3. a) The particles move faster at 80 (deg) that they do at 60 (deg), there are more frequent collisions at the higher temperature, the collisions are more energetic, and so more likely to be successful. b) About 36 s Objectives • Define activation energy. • Describe the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. • Explain the effect of changing temperature on the rate of reaction. PROVE IT COMPLETE THE WORKSHEET YOU HAVE 5 MINUTES