2. What does knowing a word involve?
advertisement

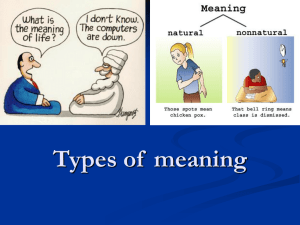
Unit 8 Teaching Vocabulary Teaching objectives : 1. know the meaning of knowing a word 2. grasp ways of presenting vocabulary 3. grasp ways of consolidating vocabulary 4. know how to develop vocabulary learning strategies Contents: 1. Understanding vocabulary and vocabulary learning 2. The meaning of knowing a word 3. Ways of presenting vocabulary 4. Ways of consolidating vocabulary 5. Developing vocabulary learning strategies 1. Understanding vocabulary and vocabulary learning Task 1 Ask students to discuss the following questions: What are the most common ways for Chinese students to learn vocabulary regarding English? What are the most common ways for Chinese teachers to teach English vocabulary, in Primary school, secondary school and university? What are some of the vocabulary learning strategies you have used and found (not) useful or effective? Task 2 People have different understanding of what a vocabulary item is, how an item can be learned and consolidated, which items should be learned, and to what extent the items should be learned and practiced. It is very important for the students themselves to develop vocabulary awareness and vocabulary building strategies. 2. What does knowing a word involve? knowing a word involves knowing its pronunciation, spelling, meaning and usage. According to Hedge (2000), vocabulary learning involves at least two aspects of meaning. The first aspect involves the understanding of its denotative and connotative meaning. The second aspect involves understanding the sense relations among words. 2. What does knowing a word involve? 2.1 Denotative meaning Denotative meaning of a word or a lexical item refers to those words that we use to label things as regards real objects, such as a name or a sign, etc. in the physical world. 2.2 Connotative meaning A connotative meaning of a word refers to ‘the attitudes or emotions’ of a language user in choosing a word and the influence of these on the listener or reader’s interpretation of the word 2. What does knowing a word involve? 2.3 Collocations Collocations refer to words that co-occur with high frequency and have been accepted as ways for the use of words. 2.4 Synonym, antonym and hyponym Synonyms refer to items that mean the same, or nearly the same. Antonyms refer to items that mean the opposites of a word. Hyponyms refer to words which can be grouped together under the same superordinate concepts. 2. What does knowing a word involve? Receptive vocabulary It refers to words that one is able to recognize and comprehend in reading or listening but unable to use automatically in speaking or writing. Productive vocabulary Those words that one is not only able to recognize but also able to use in speech and writing are considered as one’s productive\active vocabulary. 3. Ways of presenting vocabulary a. visual or physical demonstration( pictures, cards, real objects, video clips , mimes and gestures to show the meaning) b. verbal context (e.g. grumble) c. synonyms or antonyms (e.g. sad) d. hyponyms (fruit: apple, pear etc.) e. Translate, definition and exemplify (boxer: someone who fights with his fists for sport) f. word formation ( reader) g. chunks h. the context in real life 4. Ways of consolidating vocabulary Labeling Spotting the differences Describing and drawing Playing a game Using word thermometers Using word series Word bingo Word association Odd man out Synonyms and antonyms Using word category Using word net-work 5. Developing vocabulary learning strategies Review regularly Guessing meaning from context Organize vocabulary effectively The end!


![Transformational Change [Powerpoint Presentation]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005447411_1-da0a83bd34bdb90183940ab700125003-300x300.png)