Wan
advertisement
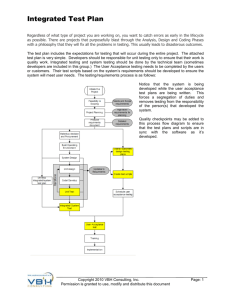
Network design Topic 6 Testing and documentation Agenda • • • • • Testing tasks Prototyping Testing plan Tools Network Design Document Testing • Ensure that the design has met the business and technical goals • Provide assurance and demonstrate to the customer that the solution meets business and technical goals • Identify problems • Acceptance testing – To demonstrate how the solution meets the goals to the customer's satisfaction – To obtain signoff and approval to move to implementation stage Testing tasks • Verify that the design meets business and technical goals • Validate LAN and WAN technology and device selections • Verify the Service Provider plan • Identify bottlenecks or connectivity problems • Test redundancy and effect of link failure • Determine optimisations • Acceptance testing • Identifying risks and planning for the implementation process Industry testing • Vendors, independent test labs and trade journals publish testing information • Generally, most tests are component tests and not whole system tests – Testing results made not be relevant to the design and configuration – How valid are the test results? • For complex networks, design your own tests Prototyping • Prototype is a model of a system which can validate the operation and performance of the system – It is not the complete system – Should include the most important functions and risky functions – Should demonstrate elements of the design to the customer – Use resources effectively: people, equipment, money and time Prototyping • Test network in a lab – Work out the bugs without impacting users – Initial configurations, evaluate products – Model predicted performance and QoS • Integrated into production network but tested off hours • Integrated into a production network and tested in business hours Planning a ‘live’ test • Advise users in advance and ask them to continue with normal work tasks • Advise administrators and managers in advance • Run multiple short tests to minimise user impact • Run tests with small traffic and configuration changes first and move up to larger impact tests Test plan • Test objectives and acceptance criteria • Types of test to run • Network equipment and other resources required • Test scripts • Timeline and milestones for testing the project Objectives and acceptance criteria • • • • Based on the business and technical goals Objectives should be specific and concrete Stated so that a pass or fail can be recorded Test should measure results without industry bias and be based on industry standards where possible • Use baselines as reference point for comparison tests, eg 20% less CRC error rate Types of test to run • Performance tests – – – – – Throughput Delay Delay variation Response time Efficiency • Stress tests – Decreased service when the load increases • Failure analysis – Network availability and accuracy – Causes of outages • Other tests – Manageability, useability, adaptability, security, regression Documenting network equipment • Network topology drawing – Major devices, addresses, names, WAN and LAN links and link capacity • List of devices that will be required – Names, version numbers, availability • Testing tools – – – – Network management and monitoring tools Traffic generation tools Modelling and simulation tools QoS and service-level management tools • Other resources needed – Time in lab – Power, air conditioning, rack space – Staff and users required Test scripts • • • • Test objective Acceptance criteria Topology Testing steps – What tools is used for each step – What measurements will be taken – Initial values and testing parameters – What information will be logged Timeline and milestones • List major tasks and the person assigned to those tasks – Writing test objectives and acceptance criteria – Design the network topology – Determine hardware and software • Order hardware and software • Confirm availability – – – – – Write test scripts Install and configure hardware and software Conduct tests Log results Analyse results • Create test report – Present results to customer Testing tools • Network-management and monitoring tools – Cisco Works – HP OpenView – IOS commands and OS tools • Traffic-generation tools – Protocol analyser – Multiport traffic generators • Modelling and simulation tools • QoS and service-level-management tools – NetPredictor Network design document • • • • Executive summary Project goal Project scope Design requirements – Business goals – Technical goals – User communities and data stores – Network applications • Current state of the network – High level map – Health and performance analysis • Logical design • Physical design • Results of network design testing • Implementation plan – Project schedule – Project budget • Design document appendix Agenda • • • • • Testing tasks Prototyping Testing plan Tools Network design document