INDIAN CONTRACT ACT-1872
advertisement

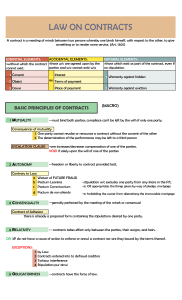
INDIAN CONTRACT ACT-1872 HISTORY OF INDIAN CONTRACT ACT - 1872 Enforced w.e.f. September 1, 1872. Applicable to whole of INDIA except J&K Concerned with rights in PERSONAM As distinguished from rights in REM A CONTRACT is an agreement creating and defining obligations between the parties According to HALSBURY, it is, “an agreement between two or more persons which is intended to be enforceable at law & is constituted by the acceptance by one party of an offer made to him by the other party to do or to abstain from doing some act.” COMPONENTS OF CONTRACT An Agreement It involves proposal or offer by one party and acceptance of the same by the other party. AGREEMENT = OFFER + ACCEPTANCE Enforceable at law An agreement to become a contract must give rise to legal obligations. It must create legal relations and not merely social or domestic relations. Leading Case: BALFOUR V. BALFOUR CONTRACT = AGREEMENT+ENFORCEABILITY AT LAW ELEMENTS OF A VALID CONTRACT Offer and acceptance Intention to create legal relationship Lawful consideration –QUID PRO-QUO Capacity of parties (Sec. 11) Minor Persons of unsound mind Persons disqualified by law to which they are subject Free consent (Sec. 13) Coercion Fraud Mistake Lawful Undue Influence Misrepresentation object if forbidden by law of such nature that if permitted it would defeat the provisions of any law Elements of a valid contract fraudulent involves injury to person or property Court regards it immoral or opposed to public policy Certainity of meaning Possibility of performance Not declared to be void or illegal Legal formalities CLASSIFICATION OF CONTRACTS ENFORCEABILITY FORMATION PERFORMANCE VALID CONTRACTS VOID CONTRACT VOID AGREEMENTS VOIDABLE CONTRACTS UNFORCEABLE CONTRACTS ILLEGAL CONTRACTS EXPRESS CONTRACTS IMPLIED CONTRACTS QUASI CONTRACTS EXECUTORY CONTRACTS EXECUTED CONTRACTS THANK YOU Any Queries!!!!!