Soft Lithography Research Poster 2
advertisement

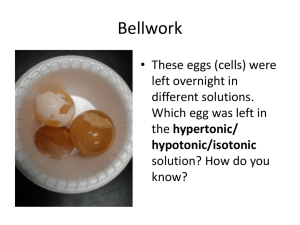
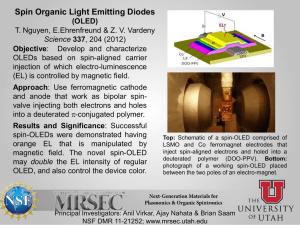
Compact Discs: Music, Data, Lithography? Matthew Javener, Dr. John Kirk Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin-Stout Background Polymer Advantages and Disadvantages • This experiment was designed to determine whether or not simple adhesives could be used in combination with a compact disc as a soft lithography method • Soft lithography is an expensive process which leads to many young students never learning how it is done • The nature of this process makes it unique and useful in many aspects of life such as: Polymer Cost Wood Glue Biotechnology, Electronics, Optics, and Biochemistry White Glue Introduction to Compact Discs • Compact discs have many different uses such as music and data storage • The information stored on the disc is done so in small pits stamped into the polycarbonate layer • Soft lithography is a low cost method for the formation of nanostructures • The process involves stamping nano- or microstructures into a polymer to form a pattern Graphic layer – above data layer Lacquer layer – above data layer Reflective layer – above data layer Polycarbonate layer – data layer is on top $1.67 • Degrades at high magnification with SEM $0.97 • Easily removable • Low Cost • Low viscosity • Degrades at high magnification with SEM • Slow curing (3 hr. approx.) $1.97 • Low Cost • High viscosity • Fast curing (30 min approx.) Successful vs. Unsuccessful Start with master Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA) • Wood glue is a Soft lithography process There are several layers to a compact disc Disadvantages • Fast curing (1 hr. approx.) • Easily removable • Low Cost Introduction to Soft Lithography Tacky Glue Advantages possible polymer to use for lithography • This image shows that the wood glue forms the reverse image of the disc Pour on elastomer Vinyl acetate monomer Polyvinyl acetate polymer • PVA is the polymer that is present in each of the three glues that were used in this experiment Wood glue magnified 3000x • White glue is a Remove polymer possible polymer to use for lithography Allow to polymerize • This image shows that the white glue forms the reverse image of the disc Uses for soft lithography Biotechnology – this process gives people the ability to pattern complex molecules that are associated with biology Electronics – this process allows people to reproduce very small features on electronics quickly and with little cost Data Layer of Compact Disc magnified 3000x Step 1 – Removing Protective Layers • Duct tape was pressed firmly against the top layers and then peeled off Step 2 – Applying Different Polymers • Common adhesives (polymers) were applied to the exposed surface of the disc Elmer’s Glue Wood Glue Tacky Glue • Each polymer was allowed to cure overnight Outer layers removed using duct tape • After the polymers were cured they were removed from the surface • This process was done several times to obtain the clearest surface possible • Care was taken to avoid scratching the features on the polymer • The polymers that were peeled off were coated with gold and examined under the microscope • The polymers had to be examined at slow scan speeds and lower magnification to avoid destruction of the surface • Once images were taken they were compared to determine whether or not the polymer produced a reverse image of the disc • Cross-links form when one polymer chain is connected to another chain Elmer’s glue magnified 2370x • Tacky glue was an unsuccessful polymer to use for lithography • This image shows no sign of the data layer from the disc due to the high viscosity of the polymer Step 3 – Examining Products • The disc was coated with a thin layer of gold and examined under a scanning electron microscope • Although these glues are each made of the same polymer they act differently because of the formation of cross-links Tacky glue magnified 3000x Cross-linking between two polymer chains • Cross-links can form at different rates depending on what other chemicals are present in the glue • The more cross-linking that is present the more dense the material will become Conclusion • Soft lithography can be done using a compact disc and readily available polymers • With a more viscous polymer the chance is greater that the lithography will work • Care should be taken when imaging these types of polymers to avoid damaging the structure • The process done throughout this experiment would be an excellent way to teach young students about lithography Acknowledgments I would like to extend a special thanks to the follow people for their help on this experiment Dr. Ray for his help on experimental design Jack Stransky for his help teaching me how to use the SEM