Stage_Gate_Processes - Gatton College of Business and Economics
advertisement
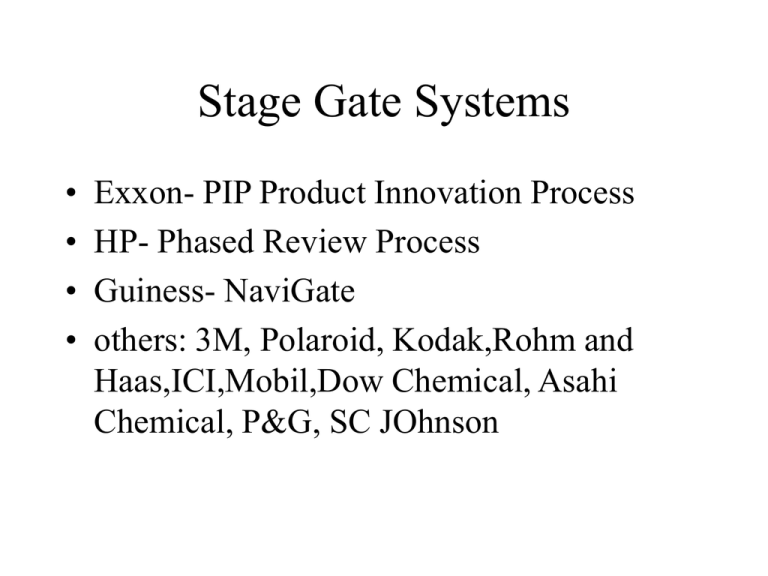
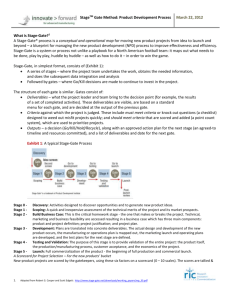
Stage Gate Systems • • • • Exxon- PIP Product Innovation Process HP- Phased Review Process Guiness- NaviGate others: 3M, Polaroid, Kodak,Rohm and Haas,ICI,Mobil,Dow Chemical, Asahi Chemical, P&G, SC JOhnson Typical 2nd Generation StageGate Process Stages • Set of parallel activities • undertaken by a cross-functional team • gathers information for the next gate Gates • • • • A go/kill decision point with a set of required deliverables pre defined evaluation criteria defined outputs: go/kill/recycle Stage 1: Discovery • R&D • lead user analysis • strategic planning exercises – gaps and opportunities in the market – disruptions Gate 1: Idea screen- Gentle screen • handful of must-meet and should-meet criteria – strategic alignment – project feasibility – opportunity size and attractiveness – product advantage – fit to resources and skills and policies • • • • • Exxon’s PIP: Strategic fit Market attractiveness Technical feasibility Killer variables Stage 2: Scoping • Preliminary market assessment • Preliminary technical assessment • <= 1 month • 10-20 person-days of effort Gate 2: Second Screen • Original set of must-meet and should-meet criteria • new criteria: – – – – sales force customer reaction “killer variable” presence simple financial assessment- payback period • Reckitt &Colman now Reckitt-Benckiser: • “Does the initial evidence suggest that the concept can win in the marketplace?” 3rd Generation Stage-Gate Process Stage 2: Building the Business Case or the critical homework stage • • • • Market investigations and research studies Detailed technical analysis Detailed financial analysis Outcome: a business case for the project – Product definition – Project justification – Detailed project plan Gate 3: Go to development Last point before heavy spending • Process audit of Stage 2 • Project evaluation on established criteria • Financial emphasis • Review and approval of – Development plan – Preliminary operations and marketing plan • Designation of full team with authority Stage 3: Development • Lab tests, in-house tests, alpha tests • Deliverables: labtested product prototype • In parallel: marketing and operations • Deliverables: – detailed test plans, launch plans – Production/operations plans including facilities requirements Deliverables: Updated financial analysis; resolution of regulatory, legal and patent issues Gate 4: Go to testing • • • • • Review of development work and process Match to original definition is checked Review financial data Approval of test or validation plans Review of detailed marketing and operations plans for executability Stage 4: Testing and Validation • Validity of – – – – Product Production process Customer acceptance Project economics • In-house product tests • User or field product trials • Trial, limited production or pilot production • Pre-test market, test market or trial sell • Revised business and financial analysis Gate 5: Go to launch • Final kill point • Audit of process in stage 4 • Review operations and marketing plans for implementation at the next stage • Criteria: expected financial return and appropriateness of launch and start-up operations plans Stage 5: Launch • Implementation, fine tuning, success Post-launch review • 6-19 months from launch • Change status from new product to regular product • Disband NP team • Review project and product performance – – – – – – Revenues Costs Expenditures Profits Timing Learning What the Stage Gate Process is not • • • • Functional, phased review Rigid Bureaucratic Project management 3rd Generation Stage-Gate systems Flexibility RCB’s triage: system change, fasttrack, major Fuzzy gates Conditional go-ahead subject to new information Fluidity Overlapping activities Focus Portfolio thinking on focus Facilitation Key master,process manager, gate meister, process keeper Forever green- adaptive International Paper’s web based gates; RCB’s “suck-in” externally developed new ideas The first stages Summary of Stage 1 Actions Gate 3 Deliverables Stage Gates 1,2,3 Must-Meet Criteria Stage Gate 3 Should-Meet Criteria