Nervous SystemEndocrineSystem2014
advertisement

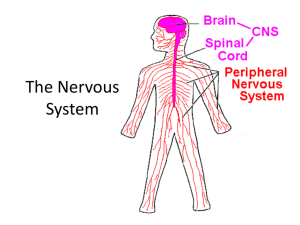
The Nervous System Function: The Nervous System is responsible for controlling all the functions and movements in the body and allows you to respond to changes in your environment using electrical signals. The Nervous System consists of two parts: Peripheral Nervous System Central Nervous System • Central Nervous System, essentially the processing area. • Peripheral Nervous System which detects and sends electrical impulses that are used in the nervous system. Central Nervous System •The Central Nervous System is essentially the processing area. •The Central Nervous System is responsible for receiving and interpreting signals from the peripheral nervous system and also sends out electrical signals to the body. •The Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System • The Nervous System outside the brain and the spinal cord • This includes the 5 Senses: – Touch (Pressure and Temperature) – Sight (Eyes) – Hearing (Ears) – Taste (Taste buds on Tongue) – Smell (Olfactory Bulbs in the Nose) Your spinal cord is made of bundles of neurons that carry impulses from all parts of the body to the brain and from the brain to all parts of your body. The joints between vertebrae are called gliding joints, where one part of a bone slides over another bone. Brain Divisions: There are three main components of the brain, the brainstem, cerebellum and the cerebrum. •The Brainstem – controls the involuntary actions of the body like heart rate and breathing. •The Cerebellum - Consisting of two hemispheres, the cerebellum is primarily concerned with movement, balance and muscle memory. •The Cerebrum – information from the senses are interpreted and memory is stored. All of the different structures in the Nervous System work together to maintain homeostasis. What is the endocrine system? The endocrine system is a complex collection of hormone-producing glands that control basic body functions such as metabolism, mood, growth and sexual development. Some hormones also allow you to respond to stress How does the Endocrine System Regulate the Body? It is made of glands that secrete hormones directly into your bloodstream These hormones cause changes in your body What is a hormone and what do they do? • A hormone is a “chemical messenger” – A chemical that delivers a message • Hormones are made in the glands of your endocrine system and secreted into your blood • They travel through your blood until they reach special target cells Examples of Hormones Hormone Gland Function Melatonin Pineal Causes sleepiness: “circadian rhythm” Adrenalin Adrenal Fight or flight response Growth hormone Pituitary Stimulates growth and cell reproduction Insulin Pancreas Regulates energy and glucose (sugar) in the blood Testosterone Testes Production and regulation of male reproductive system Estrogen Ovaries Production and regulation of female reproduction system How does the Endocrine System Compare to the Nervous System? • Like the nervous system, the endocrine system is a controlling system of the body • The brain controls the endocrine system, but they work together to regulate the body • In the brain is the hypothalamus, also known as the "master switchboard." How does the Endocrine System Compare to the Nervous System? 1. Hormones are transported around (to their target organs) the body by the blood. Therefore hormonal responses are relatively slow compared with nervous responses. 2. Many hormonal responses (ex: growth) occur over relatively long periods of time. 3. The main purpose of the Endocrine System is to maintain Homeostasis within the body (that is, to keep the internal environment constant/within balance) 4. The key function of the Nervous System is to receive and respond to stimuli. Work with your group to compare and contrast these two systems using a Venn Diagram Endocrine Nervous Why do people pee their pants when they are scared? There’s actually a scientific explanation! The Fight or Flight Response. Fight or Flight Response Controlled by an area of the brain called the hypothalamus: the part of the brain that links the nervous and endocrine systems. Fight or Flight Response When we think we are in danger, the hypothalamus begins a series of nerve cell firings and releases hormones like adrenaline, into our bloodstream. These patterns of nerve cell firing and chemical release cause our body to undergo a series of These changes are designed to either help you fight or run away (flight) to safety in times of danger Stimulus : Response Response = Hypothalamus releases hormones into body Bear = external stimulus Hormones become = Internal stimulus Response = Heart rate and breathing rate increase, sweating increases, blood thickens, blood flow to muscles increase all so we can RUN!