What are the parts and function of a flower?
advertisement

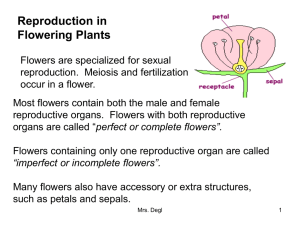
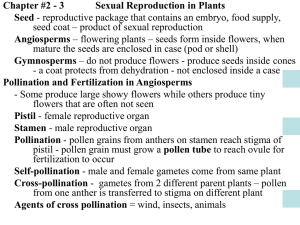
What are the parts and function of a flower? Adrian Ang 5A-3 Group 3 Male Parts •Anther- contains the pollen - also called the pollen head •Filament- supports the anther - also called the stalk Female Parts •Stigma- receives the pollen from the anther •Style- holds the stigma - leads down the ovary •Ovary- contains the ovules Sources • www.google.com.images • MyPals Are Here Science 5A What is pollination and the agents of pollination? Sedrick Keh 5A-18 Group 3 Pollination The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the flower Pollen can come from the same flower or a different flower Agents of pollination Are the things that help in pollinating the flower Some examples are insects like bees and butterflies, birds and wind The agents of pollination are attracted to the flowers because of their color or their scent Sources All pictures are from google images Words from My Pals Are Here Science 5A How does pollination happen? Sedrick Keh 5A-18 Group 3 • Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower • Two types of pollination: 1. Self - pollination 2. Cross – pollination Process of Pollination • The pollen is carried from the anther to the stigma of the same plant (self) or another plant (cross) by the agents of pollination • This process is called pollination •After pollination (when the pollen grain lands on the stigma) , fertilization will take place Sources • Pictures are all from google images • Words from My Pals Are Here Science 5A and Exploring and Protecting Our World 4 BY: Francis Guevara 5A-17 ► There are two kinds of Fertilisation ► External Fertilisation ► Internal Fertilisation ► In external fertilisation, The eggs are fertilised outside the body of the female ► Female lays its eggs and male releases its sperms on the eggs ► Frogs and fish are examples of animals which fertilise eggs externally ► It reduces the survival rate of the developing eggs ► Eggs are Fertilised inside the body of the female ► Increases the chances of successful sexual reproduction ► Leopards and Human beings are Examples of things that undergo internal fertilisation ► After pollen lands on the stigma of a flower fertilisation occurs ► Each pollen grain produces a tube called a pollen tube ► The pollen tube grows down from the stigma, through the style to the ovary ► The inside of the ovary contains ovules inside each ovule is the egg cell ► The pollen tube guides the male reproductive cells from the pollen down to the ovule. ► When the pollen tube reaches the ovule, a male reproductive cell fuses with the egg cell. This process is called fertilisation. ►waterwatchadelaide.net.au ►http://www.istockphoto.com/stock-photo- 368101-fertilized-egg-8-cell-stage.php ►My Pals are here! 5Ap.72,79 ►noorclinic.com ►caribbeanedu.com ►theflowerexpert.com PREPARED BY: ADRIAN CHUA (Group 3) Introduction In reproduction, flowers play an important role. They are the reproductive organs of plants. Flowers develop into fruits. The fruits protect and help to disperse the seeds. Flowers help in reproduction of plants by forming fruits. The male and female parts of a flower contain male and female gametes respectively that fuse to form seed. This process takes place inside the ovary, which matures to form fruit. Pollination Pollen must fertilize an ovule to produce a viable seed. This process is called pollination, and is often aided by animals like bees, birds etc, which fly from flower to flower collecting sweet nectar and in the process, they transfer pollen around, depositing it on some stigmas on a subsequent flower. After a male's pollen grains have landed on the stigma, pollen tubes develop within the style, burrowing down to the ovary, where the sperm fertilizes an egg cell in Fertilization When a pollen grain lands on a stigma it becomes hydrated and soon germinate. It produces a passage called a pollen tube. At the tip of the pollen tube is a male cell. Once the pollen tube reaches the ovary, it pushes its way into the ovule. There, the male cell fuses with the female egg cell. This process is called fertilization. Upon fertilization, the seed is formed. The fruit develops only after the seed is formed. FRUITS AND SEEDS After fertilization, the ovules develop into seeds. The ovary will enlarge and eventually become a fruit. So a fruit is a matured ovary holding the seeds. The fruit develops to protect the seeds and in some cases to become attractive to animals that will be agents of seed dispersal. A fruit is a seed container derived from an ovary and any tissues that surround it. As such, fruits are products of flowers and therefore only occur in flowering plants. The function of fruit is two-fold: to protect the developing seed to aid in the dispersal of the seed Summary While the beauty of flowers may seem relatively simple, the process of their creation is complex. Though a combination of factors, flowers create seeds and fruit that serve as the by product of their reproduction In general, the mature ovary constitute the fruit Fruits are formed after the flower has been pollinated and fertilized A fruit results from maturation of one or more flowers Sources From flower to Fruit – www.botany.hawaii.edu/faculty/web/fFlowerFruit How do Flower make seeds and fruits/eHow.com – www.ehow.com/facts How Seeds are formed – www.healthguidance.org Fruit – wikipedia,the free encyclopedia Flowering Plant – wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Seeds and Fruits – plantphy.info/plant-human/seedfruitlab.shtm http://www.itmonline.org/jintu/oldmen.htm http://www.hilalplaza.com/BlackSeed.html http://www.tutorvista.com/topic/flower-plant-reproduction http://picsdigger.com/keyword/seeds%20fruit/ THANK YOU FOR LISTENING!