Revising - Learning Development@the Library
advertisement

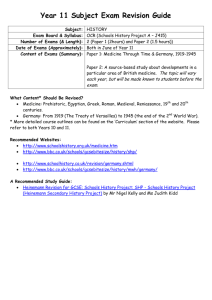
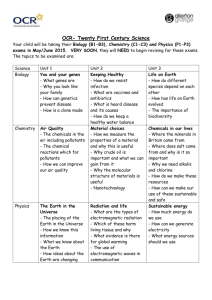
Revision and exam preparation Daren Mansfield and Cheryl Cliffe Academic Subject Librarians Aim & Learning Outcomes Aim: • To consider how to succeed in examinations by effective revision and preparation Learning Outcomes: • identify preferred learning style • identify and employ effective strategies for before, during and after an exam Good and bad experiences Introductions • Discuss good and bad experiences… • What would you have done better? • What exam strategy would you adopt? Revising • Get organised – Select topics for revision – Divide the unit into topics/sub topics – Notes - collate, condense and summarise – Revision schedule – Study in short spells – Past exam papers – Build up your handwriting speed – What can be achieved under exam conditions? • What’s your learning style? - Learning style questionnaire (10 mins) Learning styles and study methods VISUAL LEARNER• Involves memory and • note taking techniques AUDITORY LEARNER• Music • Aural Mnemonics • Technology • Repetition • Friends and groups KINAESTHETIC LEARNER• Also known as tactile learners • Learning by doing Before the exam • Be positive – Understand reasons for exams – They are an advantage to you – You have control over the process – Check your own learning • How many exams will you have? • When, where and what are the exams? • How will you be assessed? Managing stress & relaxation techniques • • • • • • Breathe calmly Healthy diet Sleep 7 hrs a day Regular exercise Celebrate success Take regular breaks During the exam • Positive mindset • Try not to panic/breathe deeply • Take time to read ALL the instructions and ALL the questions……then re-read the questions, make notes/highlight keywords • Divide your time equally among questions carrying the same marks • Use rough paper to organise structure and thoughts • Time – Go over what you have written – At end read answers and make amendments Writing exam essays • • • • Fewer examples than coursework Miss out background detail No reference list Grammatical and spelling errors and rushed handwriting generally less important but must be legible! ‘What if I go blank?’ • Too Tense – use relaxation technique • Brainstorm • Keep writing – jot down words on spare paper to prompt your memory • Who? When? What? Where? Planning response to exam question • Devise potential exam question – – – – Deconstruct question Plan your structure Use mind map – identify relevant headings Consider time spent on each paragraph After the exam • Don't beat yourself up, what is done is done! • Think about what you could improve/focus on for the next exam – How well did you prepare? – What could you have done better? – What will you do differently next time? • Always another opportunity • Put it in perspective! Additional support • Enrol on the Bb community Learning Development @ Lincoln • Further hints and tips in: – Cottrell, S. (2007) The exam skills handbook. Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan – Tracy, E. (2006) The student’s guide to exam success. 2nd ed. Maidenhead: Oxford University Press [ebook] – Cottrell, Stella. (2008). The Study Skills Handbook. Basingstoke : Palgrave Macmillan. Finally… GOOD LUCK!