AP readiness Animal
advertisement

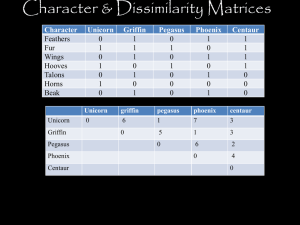
Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia •Eukaryotic •Multicellular •Nucleus with no cell wall •Motile at some point •Consumer Important vocabulary • Symmetry – how organism is divided Radial – same in all directions Bilateral – two sides similar • Coelom – body cavity Acoelomate – no coelom Pseudocoelomate – lined on one side with tissue Eucoelomate – lined on both sides with tissue • Cephalization - Sense organs are in one area • Blastopore – early developmental stage • Tissue layers - # of tissues (and what it becomes) Endoderm -inner Ectoderm- outer Mesoderm -middle • Gut – digestive organs Gastrovascular cavity complete (mouth to anus) • Segmentation – is body in repeated sections • Cleavage Spiral - Protostome Radial - Deuterostome Ceolom Symmetry Tissue Layers Gut Cleavage Blastopore Cephalization Segmentation • • • • • • • • • • Phylum to Know Porifera – sponges Cnidaria – sea anemones, corals, jellyfish Platyhelminthes- flatworms Nematoda – roundworms Annelida – segmented worms (earthworms) Mollusca – snails, shellfish, slugs Arthropoda – insects, crustaceans, spiders Echinodermata – sea urchins, sea cucumbers Chordata - fish, amphibians, birds, us Others mentioned – Ctenophores, Rotifers, Hemichordata Phylum Porifera - Sponges • Multicellular • Asymmetrical – no symmetry • No body tissues • Skeleton of CaCO3 or silica • Filter feeder • Hermaphroditic • Can reproduce asexually by splitting or budding Phylum Cnidaria – Corals, jellyfish • Radial symmetry • 2 tissue layers (endo, ectoderm, mesoglea) • Gastrointestinal sac • Hermaphroditic • Can reproduce asexually by budding or splitting (coral) • Stinging cells (Nematocyst) Phylum Platyhelminthes - flatworms • • • • • • Bilateral symmetry 3 tissue layers Acoelomate Gastrointestinal sac Some cephalization Can reproduce asexually by fission (splitting) Phylum Nematoda - roundworms • • • • Bilateral symmetry 3 tissue layers Psuedocoelomates True gut – mouth to anus • Most separate sexes Phylum Annelida – segmented worms • • • • • • • • Bilateral symmetry 3 tissue layers Euceolomate Complete gut – mouth to anus Cephalization Segmented Spiral cleavage – Protostome Blastopore forms mouth Phylum Mollusca – Clams, snails, squid • • • • • • • • • Bilateral symmetry 3 tissue layers Euceolomate Complete gut – mouth to anus Cephalization Segmented Spiral cleavage – Protostome Blastopore forms mouth Shelled- 1 or 2 (some lost or internal) Phylum Arthropoda – Insects, spiders, crabs • • • • • • • • • Bilateral symmetry 3 tissue layers Euceolomate Complete gut – mouth to anus Cephalization Segmented Spiral cleavage – Protostome Blastopore forms mouth Exoskeleton of chitin Phylum Echinodermata - sea star, sea urchin • • • • • • • • • • Bilateral symmetry 3 tissue layers Euceolomate Complete gut – mouth to anus Cephalization Segmented Radial cleavage – Dueterostome Blastopore forms anus Pentamerous symmetry as adult Asexual and sexual reproduction Phylum Chordata – lancelets, sea squirts, us • • • • • • • • • • • • Bilateral symmetry 3 tissue layers Euceolomate Complete gut – mouth to anus Cephalization Segmented Radial cleavage – Dueterostome Blastopore forms anus Notochord – spine, skull Dorsal hollow nerve chord – spinal cord, brain Pharyngeal gill slits - pharynx Post-anal tail - coccyx Chordate sub phylum • Urochordata • Cephalochordata • Sea squirt or • Lancelet tunicate • Sessile as adult • Vertebrata • Includes 6/7 classes • Agnatha • Chondrichtyes • Osteicthyes • Amphibia • Reptilia • Aves • Mammalia Class Agnatha – jawless fish • Skull • Lack jaws Hagfish Lampreys Class Chondricthyes – cartilaginous fish • Cartilaginous skeleton • Jaw sharks skates rays Class Osteicthyes – bony fish • Skeleton of bone Tuna Salmon All other familiar fish Class Amphibia – Salamanders, toads, frogs, caecilians • Four walking legs • Water as young, land as adult • Needs water for eggs • Moist skin Class Reptilia – Snakes, lizards, turtles, tortoise, crocidilians, tuataras • • • • Scaly skin Lungs Claws AMNIOTIC EGG Amniotic egg Class Aves - birds • Feathers • Endotherm – steady internal body temp. • Wings • Toothless beak Class Mammalia – horses, us • Fur • Mammary glands – milk • 4 chambered heart • Endotherm Monotreme – egg laying Marsupial – pouched Placental – live birth with placenta Which is yours?